- Home
- /
- Article


Secure Calling and Spam mitigation
 In this article
In this article Feedback?
Feedback?Telephony networks face threats from spam calls and phishing attacks, which affect enterprises, small businesses, and consumers. Spam calls waste business time, while phishing attacks can compromise confidential information and disrupt critical services including banking, healthcare, and government operations.
As part of the secure calling experience, Webex provides robust threat protection against such attacks. The following Webex Calling capabilities help mitigate these threats:
-
STIR Shaken based policy on Control Hub
-
Certified Calling Reputation provider (CCRP) integration
Spam mitigation using STIR/SHAKEN policy
Service providers use STIR/SHAKEN in their networks to protect consumers from spam calls. This framework is already active across the United States and Canada as part of the FCC guidelines. By validating caller ID information, it helps flag suspicious calls and gives users more confidence when picking up calls from unfamiliar numbers.
Understanding the STIR/SHAKEN standard
Secure Telephone Identity Revisited (STIR) and Signature-based Handling of Asserted Information Using toKENs (SHAKEN) is a framework of interconnected standards. This ensures that calls traveling through interconnected phone networks have their caller ID signed as legitimate by originating service provider and validated by the receiving service provider before reaching the consumers.
To convey verification results through the verstat parameter in the
SIP P-Asserted-Identity header, the terminating service providers use these
options:
-
TN-Validation-Passed— validation was successful with result as A, B, C attestation to the calling number. -
TN-Validation-Failed— caller could not be verified. -
No-TN-Validation— this can be result of verification failure for various reasons. For example: The E.164 number malformed.
SHAKEN attestation levels A, B and C let the originating service provider attest their relationship to the calling numbers.
-
A: the service provider can attest that caller has the right to use the phone number as the caller ID.
-
B: the customer is known. However, it is unknown if they have the right to use the caller ID.
-
C: it doesn't meet the requirements of A or B. For example: an international call.
Verstat value and attestation
Webex Calling processes the verstat parameter in the incoming call and
displays the Caller-ID disposition on the Cisco clients.
This table shows the verstat information that is used to drive
caller-ID notification to clients:
|
Vertsat value |
Attestation level |
Value that is displayed on Cisco clients |
|---|---|---|
|
TN-Validation-Passed |
Not Provided |
Verified Caller |
|
A |
Verified Caller | |
|
B |
Possible Spam | |
|
C |
Possible Spam | |
|
TN-Validation-Failed |
Any value |
Potential Fraud |
|
No-TN-Validation |
Any value |
Possible Spam |
|
No verstat Parameter |
Any value |
Possible Spam |
Cisco clients that support Unified Call History show an icon according to the Caller-ID disposition in the call history record.
On Webex App, the attestation text and icon is displayed and on MPP devices only the icon is displayed.
Verification of the on-net calls
In addition to the PSTN calls, Caller-ID disposition for on-net calls is done according to following rules:
-
On-net call between Webex calling users—Verified user (with icon).
-
On-net call from Cisco Unified Communications Manager user to Webex Calling user—Verified user (with icon). Calls from on-premises Cisco Unified Communication Manager user are classified based on the Caller-ID that matches with the configured enterprise dial-plan.
-
On-net call from Webex Calling user to On-Premises Cisco Unified Communications Manager user—No indication on Cisco Unified Communication Manager client.
For mid-call features such as Call Transfer, Call Park, Call Pickup, Call Forwarding, and Caller ID, the Caller-ID disposition is based on the processing of the verstat value of the initial call leg.
When an incoming call to a Webex Calling user is forwarded and the calling number is changed, then Caller-ID disposition
is decided based on verstat value in the incoming call request.
Supported devices
Spam detection is supported on the following Cisco endpoints:
-
Webex App—Desktop and Mobile version 42.5 or higher.
-
MPP phones—Supports 6800, 7800, 8800 and 9800 MPP devices with firmware version 11.3.7 or higher.
Administrator Configuration
Provision user notification using Control Hub
An administrator can configure sending the user indication for unverified callers. An administrator can configure to block calls that have failed STIR/SHAKEN validation. This ensures that potential fraud calls aren’t sent to the user’s endpoint.
To configure the notification settings at the organization-level, follow these steps:
| 1 |
Sign in to Control Hub. |
| 2 |
Go to Services > Calling. |
| 3 |
Go to Service settings and scroll down to Caller ID Validation. |
| 4 |
Use the toggle to activate the following options:
The call indication features and the Called ID settings apply only for Webex Calling locations in the United States of America and Canada. Other locations see calls presented normally, regardless of the Caller ID settings. |
Configure CUBE for spam indication
To pass the verstat information to Webex Calling, organizations in the United States and Canada that use on-premises PSTN connected to Webex Calling using Local Gateway or CUBE must configure these settings on CUBE.
Configure CUBE, if the PSTN service provider sends the
verstat parameter during new call setup:
-
The tags referenced here are based on the Local Gateway Configuration Guide.
-
Doing this configuration even when the service provider isn’t sending the
verstatparameter won’t affect calls.
voice class sip-copylist 200
sip-header From
sip-header P-Asserted-Identity
sip-header P-Attestation-Indicator
dial-peer voice 200
voice-class sip copy-list 200
voice class sip-profiles 100
rule 90 request INVITE peer-header sip P-Asserted-Identity copy "(;verstat=[A-Z|a-z|-]+)" u01
rule 91 request INVITE sip-header P-Asserted-Identity modify "@" "\u01@"
rule 92 request ANY peer-header sip From copy "(;verstat=[A-Z|a-z|-]+)" u02
rule 93 request ANY sip-header From modify "@" "\u02@"
rule 94 request INVITE peer-header sip P-Attestation-Indicator copy "(.*)" u03
rule 95 request INVITE sip-header P-Attestation-Indicator add "P-Attestation-Indicator: Dummy Header"
rule 96 request INVITE sip-header P-Attestation-Indicator modify "Dummy Header" "\u03"
rule 97 request INVITE sip-header P-Attestation-Indicator modify "P-Attestation-Indicator: $" "Remove: Me"
rule 98 request INVITE sip-header Remove removeFor calls from PSTN, where the service provider doesn’t support STIR/SHAKEN:
If the PSTN provider doesn’t send verstat information in the incoming call, don’t change the default value of the Present calls from unverified callers as normal calls setting on the Control Hub. If the setting is disabled, then users see the Possible Spam indication on their clients.
Certified caller reputation providers with Webex Calling
Webex Calling continues to strengthen secure collaboration with the integration of Certified Calling Reputation Providers (CCRPs). This integration proactively protects you from emerging threats, so you can enjoy the seamless communication experience you expect.
The feature uses real-time reputation intelligence to dynamically assess incoming PSTN calls and automatically take action by blocking known threats, challenging suspicious callers through CAPTCHA verification, and allowing trusted calls to connect without disruption. Available for customers with Headquarters in North America through the certified provider Mutare, this cloud-managed solution provides enterprise-grade protection against spam and vishing attacks with minimal configuration. This means your team can focus on what matters most: having meaningful conversations with legitimate callers.
Feature workflow
The following steps explain how this feature works:
| 1 |
Subscribe for reputation service with Mutare, Cisco's CCRP. For more details and to sign up for the CCRP service with Mutare, visit CCRP for Webex Calling. Customers should use Connect with Mutare to sign up. Mutare's on boarding team will guide you through the subscription process and ensure your account is properly provisioned. |
| 2 |
After you complete your subscription, Mutare provisions a unique Company ID and Secret Key for your organization. These secure credentials establish a trusted connection between your Webex Calling environment and the Mutare's reputation platform. You must configure these credentials in the Control Hub. |
| 3 |
Customize your call handling policies by configuring reputation threshold levels that align with your organization’s security posture and business needs. For more information, see the following configuration section. |
| 4 |
Once you save your configuration, Webex Calling automatically establishes a secure connection between your organization's Webex environment and your dedicated tenant in Mutare's CCRP platform. |
| 5 |
Incoming PSTN call arrives at Webex Calling. |
| 6 |
Before the call is routed to the destination, Webex Calling extracts caller’s number from SIP From header (or P-Asserted-Identity if needed). |
| 7 |
Real-time query is sent to Mutare with the caller’s number. |
| 8 |
CCRP returns the reputation score based on verification against a database of global numbers. |
| 9 |
Webex applies the configured policy to handle call appropriately. |
| 10 |
Call connects, is challenged, or is blocked based on score and configured thresholds. |
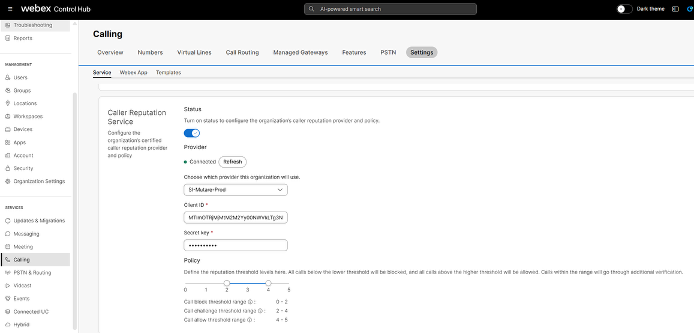
Configure caller reputation provider
To configure the caller reputation provider and policy settings at the organization-level, follow these steps:
| 1 |
Sign into Control Hub. |
| 2 |
Navigate to . |
| 3 |
Go to Settings and scroll down to Caller Reputation Service. |
| 4 |
Enable the toggle to configure the caller reputation provider and policy settings.
If your account has expired, contact your caller reputation provider. After your license is restored, click Try Again option to revert the expired state. |
Precedence hierarchy of call filtering
The integration of CCRP with Webex Calling provides an advanced spam avoidance solution that works within the Webex Calling precedence hierarchy to protect users from unwanted calls. This ensures legitimate calls get through.
The precedence level of call filtering in Webex Calling is as follows: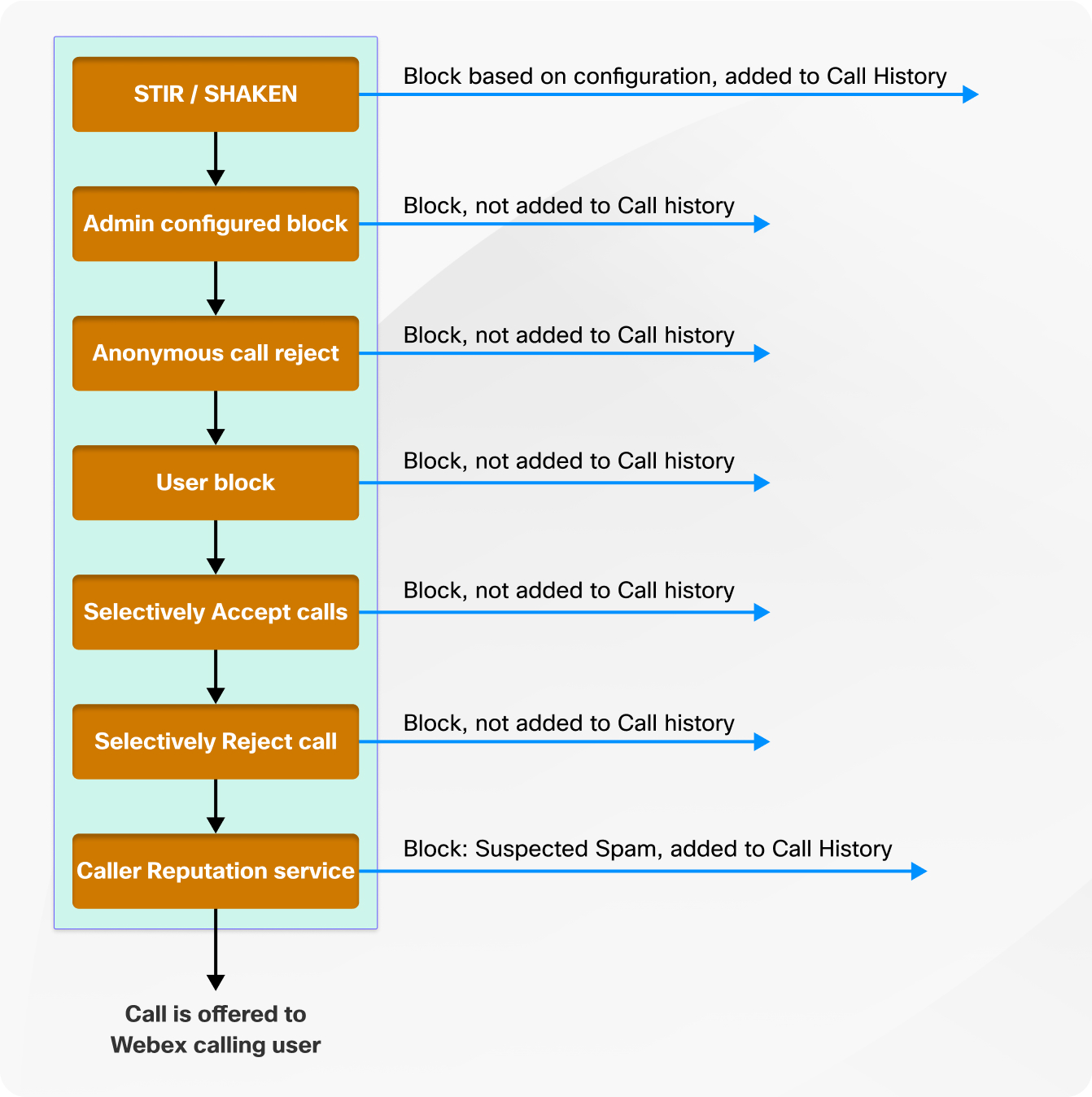
Call disposition and reporting
|
Treatment type |
Action/Outcome |
|---|---|
|
Block |
The call isn’t offered to the called user. The call is released with cause 603. The call is logged in called user’s call history with the disposition "blocked”. |
|
Challenge (CAPTCHA) |
The caller is given three attempts to pass the challenge. There’s a 15-second timeout between entering digits.
|
|
Allow |
The call is presented to the user as a normal call without any indication. |
|
No or slow response from Mutare |
The call is presented to the user with the results of STIR/SHAKEN attestation, if available from the PSTN carrier. |
-
If a call is marked as Potential SPAM after STIR/SHAKEN processing but gets a high reputation score or passes CAPTCHA test from Mutare’s call reputation service, it will be presented as a normal call to the Webex Calling user.
-
If a call is marked as Verified caller after STIR/SHAKEN processing but gets a low reputation score or fails CAPTCHA test from Mutare’s call reputation service, the call will be blocked.
To enhance call data and reporting, the following fields are added to the Call Detail Record (CDR) to capture information from the reputation service:
- Call Score
- Call Reputation Service Result
- Caller Reputation Score Reason
For more details on these fields, see Webex Calling detailed call history report.
Caller reputation scoring process for group features
Caller reputation scoring is performed only once for each incoming call when it first enters the system. This process covers all types of endpoints, including Workspaces and group features such as auto attendants, call queue, and hunt groups. For destinations that receive calls from group features, no additional Caller Reputation check is done, since the initial assessment already occurs at the group or feature entry point. For calls that fail the reputation check for which the called number is assigned to a group feature, no call history entry is created.
Callback calls from Emergency numbers that include a Callback header, don’t go through screening by the reputation provider.
Support and service partnership
Cisco and Mutare have established a support partnership to ensure customers receive prompt, expert assistance for the Caller Reputation Service integration. For issues related to Webex Calling infrastructure, call routing, or Control Hub configuration, customers must contact Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) through their standard support channels. For matters specific to the CCRP service including reputation score calculations, provider portal access, account provisioning, or billing questions, customers should engage directly with Mutare's dedicated support team.
This support structure ensures that each inquiry reaches the appropriate team who can provide the most effective and efficient resolution.
Limitation
Users must regularly review the blocked calls list in their call history to identify any false positives. If any numbers appear in the blocked list by mistake, especially those missed calls that shouldn’t be blocked, users should contact their administrator to have those numbers unblocked.