- Home
- /
- Article


Colocation of Local Gateway and Site Survivability on Cisco IOS Managed Gateways
 In this article
In this article Feedback?
Feedback?As an administrator, use this article to know about the colocation of Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway services on Cisco IOS Managed Gateways.
Overview
Webex Calling supports the colocation of a Survivability Gateway with a Local Gateway on the same Cisco IOS managed gateway. That is, you can use the same Cisco IOS gateway device to configure Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway services. Hence, you don’t need to have two different Cisco IOS managed gateways assigned as the Survivability Gateway and Local Gateway.
This article discusses the considerations for the colocation of Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway services in comparison to the standalone deployment of these services.
-
For information on standalone Local Gateway services, see Configure Local Gateway on Cisco IOS XE for Webex Calling and Enroll Cisco IOS managed gateways to Webex Cloud.
-
For information on standalone Survivability Gateway services, see Site survivability for Webex Calling.
-
The total number of registrations supported by a platform is the sum of phone and trunk registrations. Also, concurrent line and trunk registrations aren’t anticipated. Hence, the colocation of these functions on a single device doesn't impact the scale numbers of Survivability Gateway or Local Gateway.
Due to detected vulnerabilities, Webex Calling will deprecate the RSAES-PKCS1-v1_5 encryption scheme used by the Site Survivability solution on September 1, 2024. Beyond this date, the RSAES-OAEP encryption scheme is mandatory.
To ensure continued operation with this encryption scheme, upgrade your Site Survivability Gateways to Cisco IOS XE Dublin 17.12.3 before September 1, 2024. No configuration changes are required to use the new encryption scheme following this upgrade.
Prerequisites
Cisco IOS XE Dublin 17.12.3 and later.
Limitations and restrictions
The following are the known limitations for colocation of services in Cisco IOS managed gateways:
-
High Availability isn’t supported for Local Gateways.
-
Config validation isn’t supported for Local Gateways.
-
In Control Hub, the gateway must be provisioned as a Survivability Gateway service.
-
If the customer has provisioned the gateway as a Local Gateway, they need to unassign, and then reassign the service as Survivability Gateway.
-
Colocation is specific to Cisco IOS Gateway. Customers using third-party Local Gateway must deploy Survivability Gateway separately.
-
Colocation for partner-deployed Local Gateway shared across multiple customers isn’t applicable.
For limitations and restrictions specific to the standalone gateway services, see Enroll Cisco IOS managed gateways to Webex Cloud and Site survivability for Webex Calling.
Call routing considerations for colocation
Call routing for colocation is based on a routing strategy that involves a combination of dial peer groups (DPG) and regular routing based on destination patterns. This is different from the call routing strategies used for standalone Cisco IOS managed gateway services. A standalone Local Gateway service uses a DPG-based call routing strategy. Standalone Survivability Gateway routes call using destination patterns.
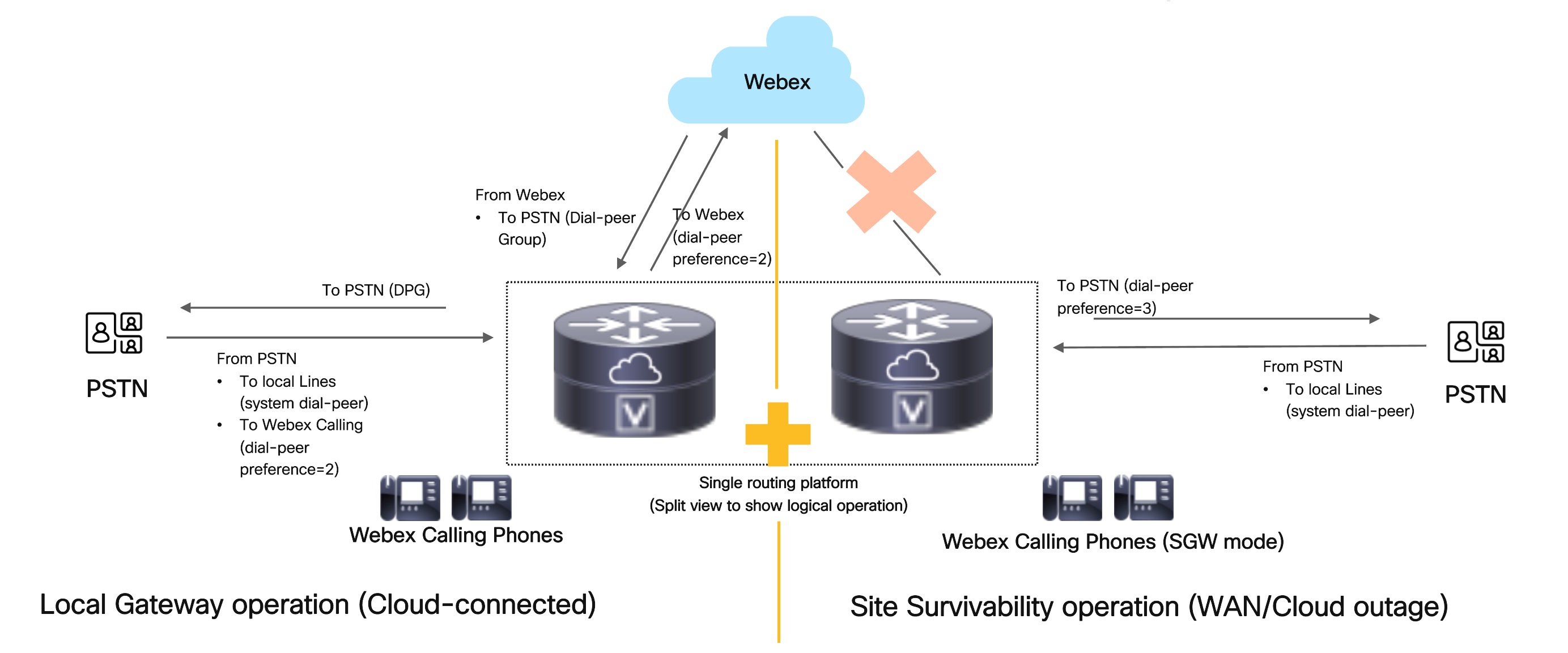
Consider the following when configuring call routing for colocation scenarios:
-
For calls from Webex Calling—The inbound dial-peer from Webex Calling is matched based on the Local Gateway hostname or DTG parameter in the URI. The inbound dial-peer is tied to a DPG having PSTN. The call is then routed to PSTN. In short, there’s no change in call routing from the existing Local Gateway routing strategy.
-
For calls from PSTN—Remove the call routing based on dial-peer groups. Route the calls using regular destination-pattern based routing. That is, an inbound dial-peer isn’t tied to a DPG in this strategy. Inbound dial-peer from PSTN is matched based on PSTN IP address in Via URI. Regular dial-peer look up would be done and a call would be routed based on dial-peer preference. The call is routed to a locally registered endpoint for survivability mode or to Webex Calling for active mode.
-
For calls from locally registered endpoints (applicable for site survivability mode during WAN outages)—Route the calls using regular destination-pattern based routing. In this strategy, an inbound dial-peer is matched to a line side dial-peer. Regular dial-peer look up is performed and a call would be routed based on dial-peer preference. The call is routed to a locally registered endpoint, PSTN, or Webex Calling.
-
A preference can be defined for each outbound dial-peer. This preference is used to decide the order of selection of dial-peers for the setup of an outgoing call. Lower the value, higher is the preference. For call routing in colocation, the dial-peer preference is set as follows:
-
Default preference of 0 to route calls to locally registered endpoints
-
Preference of 2 to route calls to Webex Calling trunk
-
Preference of 3 to route calls to PSTN trunk
-
The following table summarizes the call routing behavior for all inbound and outbound calls in Webex Calling that involves colocation of Cisco IOS managed gateway services:
| Inbound from | Outbound to |
Gateway service |
Call routing |
Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
PSTN |
Webex Calling |
Colocation of Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway |
Destination pattern (.T) based Dial-peer having preference 2 |
|
|
PSTN |
Local endpoints |
Colocation of Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway |
Destination pattern based |
Using the dynamic dial-peers created based on registrations. No configurations to perform on these system dial-peers. It would automatically have the highest precedence. |
|
Local endpoints |
PSTN |
Colocation of Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway |
Destination pattern based Dial-peer having preference 3 |
|
|
Local endpoints |
Webex Calling |
Colocation of Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway |
Destination pattern (.T) based Dial-peer having preference 2 |
This is applicable only if Local Gateway trunk towards Webex Calling is still up even in Survivability Gateway mode. |
|
Webex Calling |
PSTN |
Local Gateway |
Dial-peer group based |
Nailed-up connection to PSTN |
|
Local endpoints |
Local endpoints |
Survivability Gateway |
Destination pattern based |
Using the dynamic dial-peers created based on registrations. No additional dial-peer configuration changes are needed on these system dial-peers. |
For detailed information on call routing considerations for colocation of Cisco IOS managed gateway services, refer to Webex Calling Preferred Architecture.
Configure colocation of services
If you need to assign a new Cisco IOS managed gateway for the colocation of Local Gateway and site survivability services, assign your gateway as a Survivability Gateway on the Control Hub. For information on assigning the Gateway as a Survivability Gateway, see Enroll Cisco IOS Managed Gateways to Webex Cloud to add the gateway to Control Hub.
Depending on the type of trunking that is used, you can configure colocation using one of the following:
Configure colocation for registration-based trunking
| 1 |
Configure certificates. It’s mandatory that you use certificates signed by a trusted Certificate Authority. For more information on how to request and create certificates, see Configure certificates. |
| 2 |
Configure global voice commands. The voice configuration includes common settings related to both Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway services. The following is a sample global voice configuration: |
| 3 |
Configuration specific to Survivability Gateway. Set up voice register global, pool, and codec preferences for endpoints registering to Survivability Gateway. The following is a sample configuration specific to Survivability Gateway: |
| 4 |
Configuration specific to Local Gateway. For more information, see Registration-based Local Gateway. It includes configuration of the tenant used for registering the Local Gateway trunk to Webex Calling, the associated SIP profiles and codec preferences. The following is a sample configuration specific to Local Gateway: |
| 5 |
Configuration specific to PSTN. It includes setting up the tenant for PSTN and associated sip-profiles (if any), and codec preferences. The following is a sample configuration specific to PSTN: |
| 6 |
Configure inbound PSTN dial-peer. It includes dial-peer selection for incoming PSTN calls based on header matching. The following is a sample configuration for inbound PSTN dial-peer: |
| 7 |
Configure outbound Webex Calling dial-peer. It includes dial-peer selection for outbound Webex Calling trunk based on dial-peer group. The following is a sample configuration for outbound Webex Calling dial-peer: |
| 8 |
Configure inbound Webex Calling dial-peer. It includes dial-peer selection for incoming Webex Calling calls based on matching the DPG parameter in the Request-URI header. Dial-peer Group is used for routing the calls directly to the outbound PSTN. The following is a sample configuration for inbound Webex Calling dial-peer: |
| 9 |
Configure outbound PSTN dial-peer. It’s used for routing PSTN calls in Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway modes. Change the destination-pattern from the current BAD to a pattern suitable for PSTN calls. This is required for routing of PSTN calls from locally registered endpoints. You can do this either directly using destination-pattern or through E164 pattern-map. The following is a sample configuration for outbound PSTN dial-peer: |
| 10 |
Configure outbound PSTN dial-peers for emergency calls in survivability mode. It is used for dial-peer selection based on E164 pattern match. These dial-peers are matched only for calls originating from endpoints registered directly to Survivability Gateway in Survivability mode. Provision one or more dial-peers based on the supported dial plan in survivability mode and the associated calling permissions. The following is a sample configuration for outbound PSTN dial-peers for emergency calls in survivability mode: |
| 11 |
Configure dial-peer hunt. It is used to select dial-peers for routing based on the preference set on dial-peers. |
Configure colocation for certificate-based trunking
Before you begin
Configuration of colocation for certificate-based trunking is similar to registration-based trunking, except for those specific to Local Gateway trunk and tenants.
| 1 |
Configure certificates. It’s mandatory that you use certificates signed by a trusted Certificate Authority. For more information on how to request and create certificates, see Configure certificates. |
| 2 |
Configure global voice commands. The voice configuration includes common settings related to both Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway services. The following is a sample global voice configuration: |
| 3 |
Configuration specific to Survivability Gateway. Set up voice register global, pool and codec preferences for endpoints registering to Survivability Gateway. The following is a sample configuration specific to Survivability Gateway: |
| 4 |
Configuration specific to Local Gateway. For more information, see Certificate-based trunking. It includes configuration of the trunk and tenant required to perform certificate exchange in the Local Gateway, the associated SIP profiles and codec preferences. The following is a sample configuration specific to Local Gateway: |
| 5 |
Configuration specific to PSTN. It includes setting up the tenant for PSTN and associated sip-profiles (if any), and codec preferences. The following is a sample configuration specific to PSTN: |
| 6 |
Configure inbound PSTN dial-peer. It includes dial-peer selection for incoming PSTN calls based on header matching. The following is a sample configuration for inbound PSTN dial-peer: |
| 7 |
Configure outbound Webex Calling dial-peer. It includes dial-peer selection for outbound Webex Calling trunk based on dial-peer group. The following is a sample configuration for outbound Webex Calling dial-peer: |
| 8 |
Configure inbound Webex Calling dial-peer. It includes dial-peer selection for incoming Webex Calling calls based on matching the DPG parameter in Request-URI header. Dial-peer Group is used for routing the calls directly to the outbound PSTN. The following is a sample configuration for inbound Webex Calling dial-peer: |
| 9 |
Configure outbound PSTN dial-peer. It is used for routing PSTN calls in Local Gateway and Survivability Gateway modes. Change the destination-pattern from current BAD to a pattern suitable for PSTN calls. This is required for routing of PSTN calls from locally registered endpoints. You can do this either directly using destination-pattern or through E164 pattern-map. The following is a sample configuration for outbound PSTN dial-peer: |
| 10 |
Configure outbound PSTN dial-peers for emergency calls in survivability mode. It is used for dial-peer selection based on E164 pattern match. These dial-peers are matched only for calls originating from endpoints registered directly to Survivability Gateway in Survivability mode. Provision one or more dial-peers based on the supported dial plan in survivability mode and the associated calling permissions. The following is a sample configuration for outbound PSTN dial-peers for emergency calls in survivability mode: |
| 11 |
Configure dial-peer hunt. It is used to select dial-peers for routing based on the preference set on dial-peers. |


