- Home
- /
- Article



Configure single sign-on in Control Hub with Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS)
 In this article
In this article Feedback?
Feedback?You can configure a single sign-on (SSO) integration between Control Hub and a deployment that uses Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS 2.x and later) as an identity provider (IdP).
Single sign-on and Control Hub
Single sign-on (SSO) is a session or user authentication process that permits a user to provide credentials to access one or more applications. The process authenticates users for all the applications that they are given rights to. It eliminates further prompts when users switch applications during a particular session.
The Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML 2.0) Federation Protocol is used to provide SSO authentication between the Webex cloud and your identity provider (IdP).
Profiles
Webex App only supports the web browser SSO profile. In the web browser SSO profile, Webex App supports the following bindings:
-
SP initiated POST -> POST binding
-
SP initiated REDIRECT -> POST binding
NameID format
The SAML 2.0 Protocol supports several NameID formats for communicating about a specific user. Webex App supports the following NameID formats.
-
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient -
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified -
urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress
In the metadata that you load from your IdP, the first entry is configured for use in Webex.
SingleLogout
Webex App supports the single logout profile. In Webex App, a user can sign out of the application, which uses the SAML single logout protocol to end the session and confirm that sign out with your IdP. Ensure your IdP is configured for SingleLogout.
Integrate Control Hub with ADFS
The configuration guides show a specific example for SSO integration but do not provide exhaustive configuration for all possibilities. For example, the integration steps for nameid-format urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient are documented. Other formats such as urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified or urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress will work for SSO integration but are outside the scope of our documentation.
Set up this integration for users in your Webex organization (including Webex App, Webex Meetings, and other services administered in Control Hub). If your Webex site is integrated in Control Hub, the Webex site inherits the user management. If you can't access Webex Meetings in this way and it is not managed in Control Hub, you must do a separate integration to enable SSO for Webex Meetings.
Depending on what is configured in the Authentication mechanisms in ADFS, Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) can be enabled by default. If enabled, applications that are launched through Windows (such as Webex App and Cisco Directory Connector) authenticate as the user who's signed in, regardless of what email address is entered during the initial email prompt.
Download the Webex metadata to your local system
| 1 |
Sign in to Control Hub. |
| 2 |
Go to . |
| 3 |
Go to the Identity provider tab and click Activate SSO. |
| 4 |
Select an IdP. |
| 5 |
Choose the certificate type for your organization:
Trust anchors are public keys that act as an authority to verify a digital signature's certificate. For more information, refer to your IdP documentation. |
| 6 |
Download the metadata file. The Webex metadata filename is idb-meta-<org-ID>-SP.xml. |
Install Webex metadata in ADFS
Before you begin
Control Hub supports ADFS 2.x or later.
Windows 2008 R2 only includes ADFS 1.0. You must install a minimum of ADFS 2.x from Microsoft.
For SSO and Webex services, identity providers (IdPs) must conform to the following SAML 2.0 specification:
-
Set the NameID Format attribute to urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient
-
Configure a claim on the IdP to include the uid attribute name with a value that is mapped to the attribute that is chosen in Cisco Directory Connector or the user attribute that matches the one that is chosen in the Webex identity service. (This attribute could be E-mail-Addresses or User-Principal-Name, for example.) See the custom attribute information in https://www.cisco.com/go/hybrid-services-directory for guidance.
| 1 |
Sign in to the ADFS server with administrator permissions. |
| 2 |
Open the ADFS Management console and browse to . |
| 3 |
From the Add Relying Party Trust Wizard window, select Start. |
| 4 |
For Select Data Source select Import data about the relying party from a file, browse to the Control Hub Metadata file that you downloaded, and select Next. |
| 5 |
For Specify Display Name, create a display name for this relying party trust such as Webex and select Next. |
| 6 |
For Choose Issuance Authorization Rules, select Permit all users to access this relying party, and select Next. |
| 7 |
For Ready to Add Trust, select Next and finish adding the relying trust to ADFS. |
Create claim rules for Webex authentication
| 1 |
In the main ADFS pane, select the trust relationship that you created, and then select Edit Claim Rules. On the Issuance Transform Rules tab, select Add Rule. |
| 2 |
In the Choose Rule Type step, select Send LDAP Attributes as Claims, and then select Next. 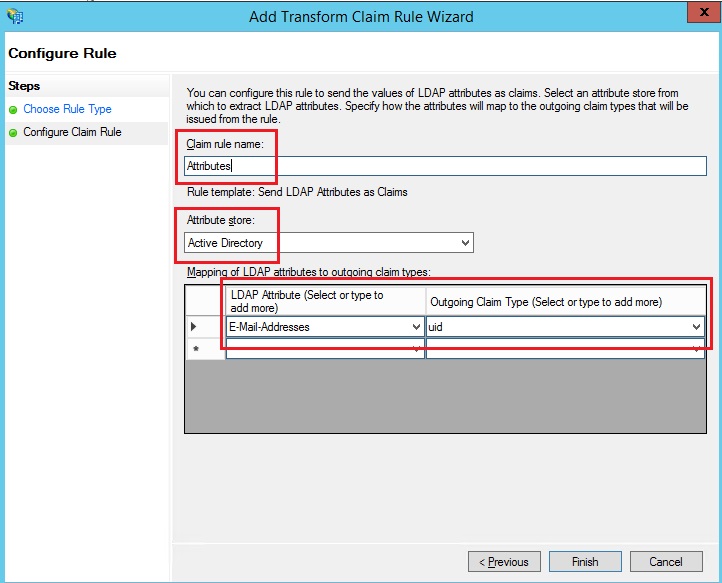 |
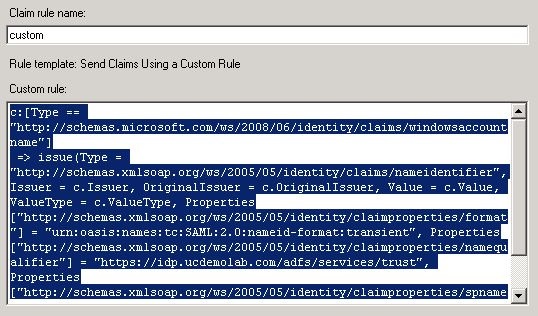
| 3 |
Select Add Rule again, select Send Claims Using a Custom Rule, and then select Next. This rule provides ADFS with the “spname qualifier” attribute that Webex does not otherwise provide. |
| 4 |
Select Relying Party Trust in the main window, and then select Properties in the right pane. |
| 5 |
When the Properties window appears, browse to the Advanced tab, SHA-256 and then select OK to save your changes. |
| 6 |
Browse to the following URL on the internal ADFS server to download the file: https://<AD_FS_Server>/FederationMetadata/2007-06/FederationMetadata.xml You may need to right click on the page and view page source to get the properly formatted XML file. |
| 7 |
Save the file to your local machine. |
What to do next
You're ready to import the ADFS metadata back in to Webex from the management portal.
Import the IdP metadata and enable single sign-on after a test
After you export the Webex metadata, configure your IdP, and download the IdP metadata to your local system, you are ready to import it into your Webex organization from Control Hub.
Before you begin
Do not test SSO integration from the identity provider (IdP) interface. We only support Service Provider-initiated (SP-initiated) flows, so you must use the Control Hub SSO test for this integration.
| 1 |
Choose one:
|
| 2 |
On the Import IdP metadata page, either drag and drop the IdP metadata file onto the page or use the file browser option to locate and upload the metadata file. Click Next.
You should use the More secure option, if you can. This is only possible if your IdP used a public CA to sign its metadata. In all other cases, you must use the Less secure option. This includes if the metadata is not signed, self-signed, or signed by a private CA. Okta does not sign the metadata, so you must choose Less secure for an Okta SSO integration. |
| 3 |
Select Test SSO setup, and when a new browser tab opens, authenticate with the IdP by signing in. If you receive an authentication error there may be a problem with the credentials. Check the username and password and try again. A Webex App error usually means an issue with the SSO setup. In this case, walk through the steps again, especially the steps where you copy and paste the Control Hub metadata into the IdP setup. To see the SSO sign-in experience directly, you can also click Copy URL to clipboard from this screen and paste it in a private browser window. From there, you can walk through signing in with SSO. This step stops false positives because of an access token that might be in an existing session from you being signed in. |
| 4 |
Return to the Control Hub browser tab.
The SSO configuration does not take effect in your organization unless you choose first radio button and activate SSO. |
What to do next
Use the procedures in Synchronize Okta Users into Cisco Webex Control Hub if you want to do user provisioning out of Okta into the Webex cloud.
Use the procedures in Synchronize Microsoft Entra ID users into Cisco Webex Control Hub if you want to do user provisioning out of Entra ID into the Webex cloud.
You can follow the procedure in Suppress Automated Emails to disable emails that are sent to new Webex App users in your organization. The document also contains best practices for sending out communications to users in your organization.
Update Webex relying party trust in ADFS
Before you begin
You need to export the SAML metadata file from Control Hub before you can update the Webex Relying Party Trust in ADFS.
| 1 |
Sign in to the ADFS server with administrator permissions. |
| 2 |
Upload the SAML metadata file from Webex to a temporary local folder on the ADFS server, eg.
|
| 3 |
Open Powershell. |
| 4 |
Run Note the |
| 5 |
Run Make sure to replace the file name and target name with the correct values from your environment. See https://docs.microsoft.com/powershell/module/adfs/update-adfsrelyingpartytrust.If you've downloaded the Webex SP 5 year certificate and have Signing or Encryption Certificate Revocation turned on, you need need to run these two commands: |
| 6 |
Sign in to Control Hub, then test the SSO integration: |
ADFS troubleshooting
ADFS errors in Windows logs
In the Windows logs, you may see an ADFS event log error code 364. The event details identify an invalid certificate. In these cases, the ADFS host is not allowed through the firewall on port 80 to validate the certificate.
Error occurred during an attempt to build the certificate chain for the relying party trust
When updating the SSO certificate, you may be presented with this error when signing in:
Invalid status code in response.
If you see that error, check the Event Viewer logs on the
ADFS server and look for the following error: An error occurred during an attempt to
build the certificate chain for the relying party trust
'https://idbroker.webex.com/<org-ID>' certificate identified by thumbprint
'754B9208F1F75C5CC122740F3675C5D129471D80'. Possible causes are that the
certificate was revoked, the certificate chain could not be verified as specified by the
relying party trust's encryption certificate revocation settings, or the certificate is not
within its validity period.
If this error occurs you must run the commands
Set-ADFSRelyingPartyTrust -TargetIdentifier https://idbroker.webex.com/<orgID>
-EncryptionCertificateRevocationCheck None
Federation ID
The Federation ID is case-sensitive. If this is your organizational email address, enter it exactly as ADFS sends it, or Webex cannot find the matching user.
A custom claim rule cannot be written to normalize the LDAP attribute before it is sent.
Import your metadata from the ADFS server that you set up in your environment.
You can verify the URL if necessary by navigating to in ADFS Management.
Time synchronization
Ensure that your ADFS server's system clock is synchronized to a reliable Internet time source that uses the Network Time Protocol (NTP). Use the following PowerShell command to skew the clock for the Webex Relying Party Trust relationship only.
Set-ADFSRelyingPartyTrust -TargetIdentifier "https://idbroker.webex.com/$ENTITY_ID_HEX_VALUE" -NotBeforeSkew 3
The hexadecimal value is unique for your environment. Please replace the value from the SP EntityDescriptor ID value in the Webex metadata file. For example:
<EntityDescriptor xmlns="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:metadata" entityID=" https://idbroker.webex.com/c0cb726f-a187-4ef6-b89d-46749e1abd7a">

 .
.
