- Home
- /
- Article

Webex Calling media optimization with Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE)
 In this article
In this article Feedback?
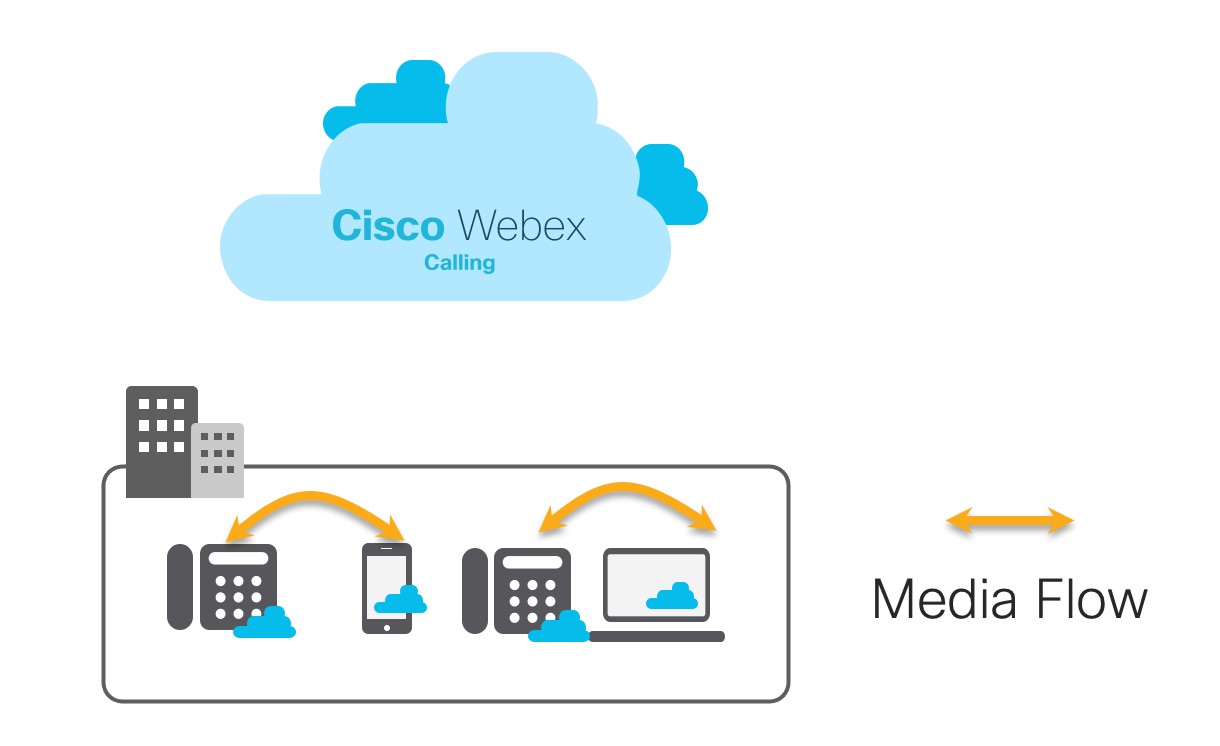
Feedback?Webex Calling media optimization enables devices to send media directly, reducing latency and bandwidth for the best possible call experience.
The media path is optimized between supported devices using Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE).
Prerequisites and limitations
Media optimization is supported across desk phones (excluding DECT & ATA devices), Webex, and the Local Gateway solution. When you make calls within your organization, between supported devices, the media for your call flows directly between the devices whenever possible. This provides lower latency and better quality.
For global enablement dates, refer What's New in Webex Calling.
-
By default, media optimization is enabled on the desk phone devices and Webex and, usually, doesn’t require specified configuration.
-
For Local Gateway, you can enable media optimization with the command STUN usage lite, which is reviewed in Register Local Gateway to Webex Calling
Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) is a standardized set of methods. This includes a network protocol for traversal of network address translator gateways in applications of real-time Voice, Video, Messaging, and other interactive communications.
-
The Local Gateway (CUBE) supports ICE-lite. There are several restrictions to ICE support on the CUBE. For more detail, see ICE-lite support on CUBE.
-
Media optimization support on Local Gateway requires a minimum CUBE software version of 17.3 or 16.12.5.
-
Media optimization with a Local Gateway requires network reachability between the device and the Local Gateway. This can be achieved by either:
-
Assigning a public IP address to the Local Gateway.
-
Ensuring that the Local Gateway host address is accessible to a device within the same network as the Local Gateway.
-
-
To route calls, signaling data is sent to the Webex Calling cloud. An active internet connection is always required to make Webex Calling calls. However, media makes up most traffic for a call.
-
Calls can only be optimized within a single organization. For interorganization calls, media must flow through the PSTN for regulatory reasons.
-
If Call Recording is enabled, media for recorded calls is routed to the cloud and aren’t optimized.
ICE (Media optimization) and Call Recording are both features that independently introduce a small audio delay at the beginning of the call and when used together the audio delay is slightly longer and more noticeable to customers.
Phases of Webex Calling media optimization
Media optimization uses the Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE) to discover optimized media paths.
This happens in the following phases:
-
Candidate discovery
When you make a call, an endpoint must first discover a list of addresses where it can receive media. These addresses or candidates include an endpoint’s local and a server reflexive address that you can use to contact the endpoint through a NAT. You can determine the server reflexive address by querying a STUN server in the Webex Calling cloud.
-
Candidate exchange
In this phase, endpoints exchange the list of candidate addresses that are collected in Candidate discovery using SIP.
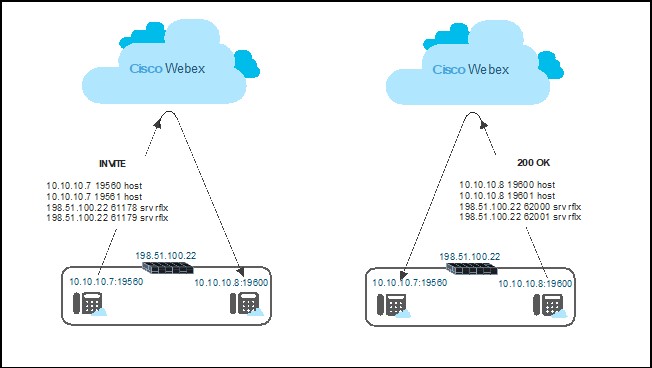
-
Connectivity checks
Endpoints test the candidate addresses exchanged in Candidate exchange to determine the best media path between two devices.
-
Media path optimization
Using a reinvite, the endpoints now begin to send media through the optimized path.
Analytics for media optimization
|
Data for optimized calls is available through the Media Quality analytics page or alternatively through the Troubleshooting tool within the Control Hub. |


