- Home
- /
- Article

































Webex Contact Center Setup and Administration Guide
 In this article
In this article Feedback?
Feedback?Webex Contact Center is a cloud-based solution that enhances customer experience by providing a seamless, intuitive, and flexible platform for managing customer interactions. This guide acts as your navigational compass, offering administrators a clear path through Webex Contact Center setup and management.
Webex Contact Center Overview
Webex Contact Center overview
This guide is no longer updated as many management portal entities have migrated to Control Hub and decommissioned from the management portal. For help on entities now managed through Control Hub, visit the Webex Help Center page for Contact Center administrators.
Contact centers of multisourcing enterprises leverage a combination of sourcing solutions, including captive, outsourced, and offshore. The typical multisource contact-center environment is organizationally complex, consisting of sites located all over the world, and staffed by direct company employees and/or outsourced agents.
In this environment, most locations operate independently and use disparate contact center technologies, including routing, administrative solutions, and reporting tools. This combination of tools and technologies makes both management and quality monitoring across different locations extremely challenging.
Cisco’s Webex Contact Center offers a unique solution that combines contact center and IP technologies in a global call management service. The Webex Contact Center solution is built on the Cisco Midpoint Call Management ® technology, a centralized control point for managing and monitoring calls and contacts across a heterogeneous contact center environment.
Offered as a cloud service, Webex Contact Center provides enterprises with full control over their global contact center queues and creates the appearance of a single, unified contact center environment. Calls, chats, and emails are distributed to the contact center sites where agents are available. When agents are occupied, contacts are queued centrally so they can be serviced by the next available agent irrespective of the physical location of the agent.
In the voice context, by queuing calls centrally, enterprises can offload the queuing function from their premises-based equipment, thus achieving substantial cost savings in telecom hardware, toll charges, and bandwidth use. More importantly, a call can be directed to the next available agent at any site because the endpoint of the call can be anywhere around the globe, Webex Contact Center seamlessly integrates remote agents and at-home agents into the enterprise’s multisource contact center environment.
About Sites, Teams, Entry Points, and Queues
A Webex Contact Center tenant is an enterprise that has contact centers at one or more sites. The enterprise also has entry points for incoming contacts that are associated with queues. Incoming contacts can be toll-free numbers for voice calls, designated email addresses for emails, or chats with agents. For example, an enterprise that is named Acme might have an entry point that is named Welcome. Welcome classifies contacts into AcmeBilling and distributes to teams of agents in Chicago, Manila, and Bangalore.
Each Webex Contact Center tenant profile consists of sites, teams, entry points, and queues.
-
A site is a physical contact center location under the control of the enterprise or an outsourcer. For example, Acme might have sites in Chicago, Manila, and Bangalore.
-
A team is a group of agents at a specific site who handle a particular type of contact. For example, Acme might have teams at their Chicago site that are named Chi_Billing, Chi_Sales, and Chi_GoldCustomerService, and teams at their Bangalore site named Bgl_Billing, Bgl_GoldCustomerService, and Bgl_Experts. Agents can be assigned to more than one team, but an agent can service only one team at a time.
-
An entry point is the initial landing place for the customer contacts on the Webex Contact Center system. For the voice contacts, typically one or more toll-free or dial numbers are associated with an entry point. IVR call treatment is performed while a call is in the entry point.
-
A queue is where active contacts are kept while they await handling by an agent. Contacts are moved from the entry point into a queue and are distributed to agents.
Tenants that use the outdial feature are also configured with at least one outdial entry point and one outdial queue.
Telecom managers, contact center managers, and other representatives of the enterprise who are authorized to access the Webex Contact Center service have a view of contact center activity at their enterprise through the Webex Contact Center Management Portal.
In addition to sites, teams, entry points, and queues, the Provisioning module of the Webex Contact Center Management Portal provides an interface to add agents and assign them to teams. Each agent is configured with a desktop profile , a value that determines the agent’s permission levels and Agent Desktop behaviors, including which wrap-up and idle codes are available to the agent. Thus, you should add wrap-up and idle codes before you define desktop profiles and define desktop profiles before you define agents. If your enterprise is provisioned with the optional skills-based routing feature, you should also add skills and skill profiles before you define teams and agents.
Webex Contact Center supports mapping only PSTN numbers in the globalized +E.164 format to entry points. Extension numbers are not supported for this purpose.
Webex Contact Center Management Portal
You can access the Webex Contact Center Management Portal through a web browser. The Portal provides access to Webex Contact Center modules that enable authorized users to perform various tasks such as:
-
View real-time and historical contact center data
-
Silently monitor interactions directed to destination sites
-
Create agent accounts and other contact center resources
-
Create and edit scheduled contact routing strategies and team capacity strategies to control contact treatment and distribution
In addition, the Webex Contact Center Management Portal landing page displays graphs of real-time and historical call activity and current agent status.
Your assigned user profile determines your access to Webex Contact Center modules and functionality.
For information about how to access and work with the Webex Contact Center Management Portal, see Supported browsers for Webex Contact Center.
Webex Contact Center Modules
After you sign in to the Management Portal, click the module on the navigation bar that you want to access. If the navigation bar is collapsed, click the navigation button on the top-left corner of the Management Portal landing page to expand it. If you can't see a module in your interface, then either you don’t have the appropriate permissions to access the module, or it’s an optional module that your enterprise doesn’t have license to.
The following table describes the modules that authorized users can access through the Webex Contact Center Management Portal.
|
Module |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Provisioning |
Allows authorized users to create, view, and edit the settings that are provisioned for the enterprise. The module provides access to the Audit Trail, Agent Skills Report, Provisioned Items Report, and Provisioned Skills Report. |
|
Reporting and Analytics |
Allows authorized users to segment, profile, and visualize the data in contact center systems. The module also helps to identify the key variables that impact productivity and desired business outcomes. For more information, see Webex Contact Center Analyzer User Guide. |
|
Business Rules |
Allows authorized users of the Analyzer module to incorporate customer data into the Webex Contact Center environment for custom routing. |
|
Agent Desktop |
Allows authorized users to access the Desktop interface for handling customer contacts and supervisor capabilities. For more information, see all the articles related to Agent Desktop and Supervisor Desktop. |
|
Routing Strategy |
Provides a web-based user interface to manage and configure contact handling strategies. Authorized users can create and schedule global routing and team capacity strategies, and alter them in real time in response to changes in business dynamics. For more information, see Contact Routing. |
|
Call Monitoring |
Allows authorized users to silently monitor the quality of service being delivered across their multisource contact centers. The power of the Webex Contact Center service lies in the unique ability to monitor any call across any site. Through a simplified web interface, users can select the queue, team, site, or agent that they want to silently monitor. Authorized users can provide instructions to the monitored agent without being heard by the caller, and can join a call being monitored and participate in the conversation. For more information, see Monitor Calls. |
|
Call Recording |
Optional module that allows authorized users to record calls. |
|
Recording Management |
Optional module that allows authorized users to search for and play calls recorded through the Webex Contact Center Call Recording feature. For more information, see About Recording Management. |
|
Audit Trail |
Allows authorized users to view details about provisioning changes made for their enterprise and export the data to a data analysis tool, such as Microsoft Excel. For more information, see Access Audit Trail Reports. |
About Time Zones
All dates and times displayed on the Webex Contact Center Management Portal and in the Webex Contact Center modules reflect the time zone that is provisioned for the enterprise with the following exceptions:
-
Dates and times displayed on the main pages of the Real-Time Reports and Call Monitoring modules reflect the browser time.
-
Time values in routing strategies are based on the time zone that is provisioned for the entry point or queue. If no time zone is specified, the time zone is provisioned for the enterprise.
Dates are converted to UTC time when they are saved to the database, so the system behavior, such as time-of-day routing, is applied universally across the multi-site contact center network, regardless of which time zones the sites are located in. The system filters the historical reports based on the enterprise time zone.
To specify a different time zone for displaying the time values in routing strategies, see View routing strategies by time zone.
When you edit a tenant time zone, you must relogin to see the changes.
PCI compliance
Webex Contact Center is fully Payment Card Industry (PCI) compliant to protect customer organizations from data loss while using voice and digital channels. We protect and secure PCI data and related information in strict adherence to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). This compliance enables you to:
-
Prevent logging and storing of any sensitive information that is related to PCI data.
-
Mask and encrypt customer sensitive information such as debit or credit card details.
-
Drop attachments if PCI data is detected.
-
Restrict attachments in the email and chat services if it contains cardholder information.
-
Allow administrators to configure either to reject or drop the email or chat content if it has PCI data in the email subject line or email or chat body.
For more information, see Webex Contact Center Privacy Data Sheet from Cisco Trust Portal.
In Webex Contact Center, PCI is enabled by default. To know more about the file types that are supported across all digital channels for regular attachments, see Supported attachment types for digital channels in Webex Contact Center.
Embedded images aren’t supported in attachments.
Get Started with Webex Contact Center
This chapter describes the tasks that you need to do the first time you login to the Webex Contact Center .
System requirements
This section of the article details the system requirements for Webex Contact Center.
Supported browsers for Webex Contact Center
The following table lists the supported operating systems and browsers for various client devices to access the Webex Contact Center:
|
Browser |
Microsoft Windows 10 |
Microsoft Windows 11 |
Mac OS X |
Chromebook |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Google Chrome |
76.0.3809 |
103.0.5060.114 |
76.0.3809 or higher |
76.0.3809 or higher |
|
Mozilla Firefox |
ESR 68 or higher ESRs |
ESR V102.0 or higher ESRs |
ESR 68 and higher ESRs |
NA |
|
Microsoft Edge |
42.17134 or higher |
103.0.1264.44 or higher |
NA |
NA |
|
Chromium |
NA |
NA |
NA |
79 or higher |
Domain access required for Desktop
To ensure that the Desktop responds as expected on your network, add the following domains to the Firewall/VPN (Virtual Private Network) allowed list:
An * shown at the beginning of a URL (for example, *.webex.com) indicates that services in the top level domain and all subdomains must be accessible.
| Domain / URL | Description |
|---|---|
| Webex Contact Center services URLs | |
|
cdn.jsdelivr.net cdnjs.cloudflare.com *.broadcloudpbx.net:443 *.s3.amazonaws.com *.amazonaws.com |
Content Delivery Network (CDN) services to efficiently deliver static files |
|
*.cisco.com:443 *.ciscoccservice.com:443 |
Contact Center micro-services |
|
*.ciscospark.com:443 *.wbx2.com:443 *.webex.com:443 |
Webex micro-services. |
| Additional services related to Webex Contact Center—Third Party domains | |
|
*.imiengage.io:443 *.webexengage.com |
Digital channels |
|
*.split.io:443 *.lr-ingest.com:443 *.pendo.io:443 |
Performance tracking, error and crash capture, and session metrics |
| *.googleapis.com *.gstatic.com | Analyzer |
Public IPs and Domain details
To enhance security and minimize unauthorized access, you can view the list of static IP addresses we support on Webex Engage and Webex Connect that you can allowlist to access the necessary information.
| Data center | Webex Engage | Webex Connect |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Ireland |
52.214.81.91 |
52.17.23.194 34.250.50.84 52.211.238.186 |
| AWS Oregon (US) |
52.40.46.90 |
35.161.238.252 35.166.68.236 |
| AWS Canada |
52.60.155.95 |
35.183.154.158 52.60.35.202 |
| AWS London |
3.9.151.19 |
3.9.155.97 18.169.201.157 |
| AWS Sydney |
3.105.22.233 |
13.210.45.137 54.206.189.15 52.62.185.51 |
| AWS India/Mumbai |
15.206.109.168 13.234.73.181 |
13.233.242.129 65.1.39.117 |
| AWS Singapore |
175.41.183.21 18.136.231.158 18.138.98.217 |
13.215.247.149 18.142.200.115 54.254.195.37 |
| Azure US | 20.55.248.119 |
20.55.240.2 20.57.8.223 20.57.8.222 20.185.49.217 |
| AWS TC |
34.251.147.218 34.251.254.148 34.255.20.69 | N/A |
This article lists the system configuration limits for all entities in Webex Contact Center.
|
Configuration entities |
Entity attribute |
Maximum allowed limit for tenants |
|---|---|---|
|
Sites | Active |
300 |
|
Teams |
Agent based |
3000 |
|
Teams |
Agent based - Users |
100 |
|
Teams |
Capacity based | 100 |
|
Teams | Capacity based - Active |
50 |
|
Teams |
Capacity based - Inactive |
100 |
|
Auxiliary code |
Idle |
1000 |
|
Auxiliary codes |
Wrapup |
1000 |
|
Entry points | Active |
6000 |
|
Oudial entry points | Active |
1000 |
|
Users | Active | 20000 |
|
Users |
Supervisors |
3000 |
|
Users |
Teams |
50 |
|
Multimedia profiles | Active |
150 |
|
Desktop layouts | Active |
200 |
|
Skills | Active | 1000 |
|
Skills |
Text | 200 |
|
Skills |
Text length |
50 |
|
Skills |
Enum limits |
200 |
|
Skills |
Enum length |
50 |
|
Skill profiles |
9000 | |
|
Skill profiles | Skills |
50 |
| Queues | Skill requirements | 50 |
| Queues | Skill-based routing type | 500 |
| Queues | Team-based routing type | 10500 |
|
Global variables | Active |
5000 |
|
Threshold rule |
Active |
1000 |
|
Desktop profiles |
Active |
1500 |
|
Desktop profiles |
Maximum auto-wrapup timeout |
600000 milliseconds |
|
Desktop profiles |
Auxiliary codes—wrapup codes |
50 |
|
Desktop profiles |
Auxiliary codes—idle codes |
50 |
|
Desktop profiles |
Transfer targets |
150 |
|
Desktop profiles |
Buddy teams |
150 |
|
Desktop profiles |
Dial plans |
10 |
|
Desktop profiles |
Agent Dial number validation criteria |
10 |
|
Desktop profiles |
Viewable statistics queues |
100 |
|
Desktop profiles |
Viewable statistics teams |
100 |
|
User profiles |
Active |
1500 |
|
User profiles |
Access rights - sites |
20 |
|
User profiles |
Access rights - teams |
100 |
|
User profiles |
Access rights - entry points |
50 |
|
User profiles |
Access rights - queues |
250 |
|
Routing Strategy |
Global |
200 |
|
Routing Strategy |
Global entry points |
500 |
|
Routing Strategy |
Per entry point |
20 |
|
Dialed numbers |
Entry Point |
15000 |
|
Dialed numbers |
Per entry point |
500 |
|
Contact service queue |
Inbound |
11000 |
|
Contact service queue |
Outbound |
5000 |
|
Contact service queue |
Distribution groups |
20 |
|
Contact service queue |
Distribution groups - teams |
50 |
|
Contact service queue |
Distribution groups - total teams |
250 |
|
Contact service queue |
Service level threshold - telephony |
86400 seconds |
|
Contact service queue |
Service level threshold - chat |
86400 seconds |
|
Contact service queue |
Service level threshold - digital |
604800 seconds |
|
Contact service queue |
Service level threshold - email |
1209600 seconds |
|
Contact service queue |
Maximum time in queue - telephony |
86400 seconds |
|
Contact service queue |
Maximum time in queue - chats |
86400 seconds |
|
Contact service queue |
Maximum time in queue - digital |
604800 seconds |
|
Contact service queue |
Maximum time in queue - email |
1209600 seconds |
| Call recording schedule |
Per queue |
20 |
|
Call monitoring Schedule |
2000 | |
|
Call monitoring Schedule |
Queues |
250 |
|
Call monitoring Schedule |
Sites |
20 |
|
Call monitoring Schedule |
Teams |
100 |
|
Call monitoring Schedule |
Agents |
500 |
|
Call recording Schedule |
Sites |
20 |
|
Call recording Schedule |
Teams |
100 |
|
Call recording Schedule |
Agents |
500 |
|
Address Book |
3000 | |
|
Address Book |
Entries |
6000 |
|
Address Book |
Total entries |
100000 |
|
Outdial ANI |
400 | |
|
Outdial ANI |
Entry |
200 |
|
Outdial ANI |
Total entries |
2000 |
|
Audio file |
17250 | |
|
Audio file | Size in bytes |
5242880 |
|
Audio file |
Total size in bytes |
2097152000 |
|
Call monitoring |
Dashboard - queues |
250 |
|
Call monitoring |
Dashboard - sites |
20 |
|
Call monitoring |
Dashboard - teams |
100 |
|
Call monitoring |
Dashboard - agents |
500 |
|
Recording management |
Queues |
250 |
|
Recording management |
Sites |
20 |
|
Recording management |
Teams |
100 |
|
Recording management |
Agents |
500 |
|
Recording management |
Wrapup codes |
50 |
|
Recording management |
Tags |
50 |
|
Call monitoring |
Maximum concurrent sessions |
1000 |
|
Maximum concurrent supervisor sessions |
Maximum concurrent supervisor sessions |
1000 |
|
Business Hours |
5000 | |
|
Overrides |
Overrides |
5000 |
|
Holiday list |
5000 | |
|
Business Hours |
Working hours |
50 |
|
Overrides |
Overrides |
100 |
|
Holiday list |
150 | |
|
Number of Connectors |
Per connector Type |
There is no maximum limit on the total number of connectors; however, each connector type has it's own maximum limit.
|
|
CCAI Config |
100 |
The table lists the system limits for visualization of filters on the UI of the Management Portal for recording management, call recording and call monitoring schedules features:
|
Application/Feature |
Entity with Filters |
Description |
Maximum allowed limit |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Recording Management |
Queues |
The maximum number of filters for queues. |
250 |
|
Sites |
The maximum number of filters for sites. |
20 | |
|
Teams |
The maximum number of filters for teams. |
100 | |
|
Agents |
The maximum number of filters for agents. |
500 | |
|
Wrap-Up Codes |
The maximum number of filters for wrap-up codes. |
50 | |
|
Tags |
The maximum number of filters for tags. |
50 | |
|
Call Recording Schedules |
Sites |
The maximum number of filters for sites. |
20 |
|
Teams |
The maximum number of filters for teams. |
100 | |
|
Agents |
The maximum number of filters for agents. |
500 | |
|
Call Monitoring Dashboard |
Queues |
The maximum number of filters for queues. |
250 |
|
Sites |
The maximum number of filters for sites. |
20 | |
|
Teams |
The maximum number of filters for teams. |
100 | |
|
Agents |
The maximum number of filters for agents. |
500 | |
|
Call Monitoring Schedules |
Queues |
The maximum number of filters for queues. |
250 |
|
Sites |
The maximum number of filters for sites. |
20 | |
|
Teams |
The maximum number of filters for teams. |
100 | |
|
Agents |
The maximum number of filters for agents. |
500 |
The listed entities have a maximum limit on the number of characters that can be used for the Name field.
|
|
|
The table lists the supported configuration limits for routing and queuing. Active limits are the operable limits for configurations to work optimally. Maximum limits are the threshold limits for configurations to work at maximum capacity. We recommend that you use configuration values that are within the parameters mentioned in the Maximum Limits column of this table.
|
Configurations |
Active Limits |
|---|---|
|
Maximum number of agents for a team |
50 |
| Maximum number of concurrent agents for a team | 10000 |
|
Maximum number of teams for a Call Distribution Group |
50 |
|
Maximum Call Distribution Groups in a queue |
20 |
|
Maximum number of teams in a queue, across all Call Distribution Groups |
250 |
|
Maximum number of agents for a queue (maximum agents in a team x maximum teams for a Call Distribution Group x maximum Call Distribution Groups in the queue) |
500 |
|
Maximum time in a queue (voice) |
1 day |
|
Maximum skills for a skill profile |
50 |
|
Maximum number for a Capacity-Based Team |
100 |
|
Maximum Capacity-Based Teams for an organization |
50 |
|
Maximum number of concurrent calls for Capacity-Based Teams (maximum number for a Capacity-Based Team x maximum number of Capacity-Based Teams for an organization) |
5000 |
|
Maximum skill requirements for a contact |
10 |
|
Maximum number of concurrent calls for call monitoring |
1000 |
|
All outbound (Preview and Progressive) campaigns for an organization |
100 |
|
Maximum number of agents in a campaign |
500 |
Sign in to Management Portal
Sign in to the Webex Contact Center Management Portal through a web browser with your sign in credentials. You can access the modules and functionalities that your administrator grants access to.
To sign in to the Management Portal:
| 1 |
Sign in to https://admin.webex.com. |
| 2 |
Click Services from the left pane. |
| 3 |
On the Contact Center card, click Settings. |
| 4 |
Under the Advance Configuration section, click the Management Portal link. You can bookmark this link and access the portal directly with this link. The Management Portal landing page appears. For more information, see About Management Portal Components. After you sign out, close all Webex Contact Center windows before you sign in again. |
About Management Portal Components
The Webex Contact Center Management Portal landing page has multiple components that you can access based on your authorization.
The following table describes the components of the Management Portal landing page:
|
Component |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Navigation bar |
Displays the modules that you are authorized to access. For more information, see Webex Contact Center Modules You can see either the name of the module or, if the navigation bar is collapsed, an icon that represents the module. Hover the mouse pointer over an icon to display the module name. To expand or collapse the navigation bar, click the button on the upper-left side of the landing page. |
|
Dashboard |
Displays the number of calls that are currently in IVR, in queue, connected, and the number of currently available agents. The rest of this panel displays four charts. Three of them provide real-time statistics for the current call activity, interval call activity, and site-level agent activity. The fourth chart provides historical statistics. You can click the icon at the top of a chart to display the corresponding report in the Reporting and Analytics module window. To change the size of a chart, point to a corner or edge and when the mouse pointer changes to a two-headed arrow, drag the corner or edge to shrink or enlarge the chart. To restore the original size of resized charts, click Reset Widgets. |
|
Settings button |
Expands and collapses a panel where you can do the following:
|
|
Your name button |
Displays the following options in a drop-down list:
|
About Dashboards
The Webex Contact Center Management Portal landing page provides the following dashboards:
-
Entry Point - Site level Dashboard (default)
-
Contact Center Overview - Realtime
-
Contact Center Overview - Historical
-
Agent State Data - Realtime
For detailed information about the visualizations available in each dashboard, see the Visualizations section in the Cisco Webex Contact Center Analyzer User Guide.
You can access the dashboards from the drop-down list at the top-left corner of the Dashboard tab.
-
Access to the above listed dashboards is based on access privileges configured in the User Profile settings in the management portal. For more information, see User Profiles.
-
The dashboard summary view is available to all the users who access the Management Portal.
Entry Point - Site Level Dashboard
Displays information about the number of contacts that are in IVR and Queues.
-
Snapshot Entry Point IVR Realtime - Chart: Indicates the number of calls that are in the IVR.
-
Entry Point Interval Realtime - Chart: Indicates the number of contacts (voice, email, and chat) per entry point in real time for a specific interval. By default, the interval is 30 minutes and the duration is from the start of the day.
-
Site Interval Realtime - Chart: Indicates the number of connected contacts (voice, email, and chat) per site in real time since the start of the day.
-
Entry Point Contact Volume - Chart: Indicates the number of connected contacts per entry point on a daily interval, for the last seven days.
Contact Center Overview - Historical
Displays information about contacts handled, contacts abandoned, and contacts in queues for a specified duration and time interval. You can use the Interval and Duration drop-down lists in the dashboard to filter the data based on the selected time interval and duration. To refresh the data, use the Refresh icon.
The following information is available:
-
Average Service Level: Indicates the percentage of contacts that are handled within the configured service level for the queue.
-
Total Contacts Handled: Indicates the total number of contacts (voice, email, social, and chat) handled.
-
Total Contacts Abandoned: Indicates the total number of contacts (voice, email, social, and chat) abandoned.
-
Average Handled Time: Indicates the average time that is taken to handle a contact (voice, email, social, and chat).
-
Longest Contact in Queue: Indicates the time in queue for the contact (voice, email, social, or chat) with the longest waiting time.
-
Contact Details in Queue: Shows the details of contacts (voice, email, social, and chat) that are currently in queue.
In addition, the Team Details - Historical dashboard displays the following information in a specified duration and time interval:
-
Teams
-
Agents in Teams
-
Agent Login
-
Contacts handled by the agents
You can filter the data using the following filters available in the dashboard:
-
Agent Name
-
Team Name
-
Interval
-
Duration
Agent State Data - Realtime
As an administrator or supervisor, you can monitor the agent state data using the Agent State Data - Realtime dashboard. The dashboard displays the following information:
-
The name of the agent.
-
The site and team to which the agent is assigned.
-
The login time of the agent.
-
The most recent known state of the agent.
-
The duration for which the agent has been in the most recent state.
-
The idle code, if the agent is in the Idle state.
The filters at the top of the dashboard enable you to display the agent state data for selected sites, teams, or agents. The list of sites, teams, or agents available in the filters depends on the teams or sites to which the administrator or supervisor has access rights. For more information, see Access Rights.
Agent State Data - Realtime dashboard provides you the ability to sign out agents based on the agent state. The most recent agent states and descriptions are available in the following table.
|
Most Recent State |
Indicates that |
|---|---|
|
Connected |
The agent is connected to at least one channel. This state includes Ringing and Wrap-Up also. An icon indicates the most recently connected channel in the State Duration field. |
|
Available |
The agent is available on the desktop, but hasn’t received an active contact. |
|
Idle |
The agent has set an Idle state. Check the Idle Code field for more information. |
An option to forcefully sign out an agent is available, if a regular sign out is not possible. The administrator or supervisor should exercise caution while forcefully signing out the agent, as the agent's current contacts are cleared.
For Chat and Email channels, when the supervisor tries to forcefully sign out an agent from the Management Portal, the agent gets signed out; but the chat session remains open. The contact clean up functionality is not available for these channels.
To sign out an agent, click Sign Out in the Action field. You receive a notification that the agent is successfully signed out.
You can access the Agent State Data - Realtime dashboard only if you have View or Edit permissions to the Logout Agents module. To sign out agents, you must have Edit permissions to the module. For more information, see Module Settings.
-
The Social channel type appears in the reports if your enterprise has purchased the Social Channel add-on.
-
The Deployment Name filter appears only for Cloud Connect users.
For more information about reports, see the Types of Records Available in Each Repository section in the Webex Contact Center Analyzer User Guide.
Change User Interface Colors
You can set colors or skins in the selection panel and in the banner on the pages:
| 1 |
Click the Gears icon at the top-right corner of the Management Portal. |
| 2 |
Click the tab displaying the Wrench icon, and select a skin. The colors change immediately.
|
| 3 |
(Optional) Click the Reset icon to restore the default color. |
Create a Custom Theme
You can customize the banner color and images for the Management Portal user interface by creating a custom theme. You must have proper authorization to customize the user interface.
To create a custom theme:
| 1 |
Click the Gears icon at the top-right corner of the Management Portal. |
| 2 |
Click the tab displaying the Custom Theme icon. |
| 3 |
In Banner Color, enter the HTML (hexadecimal) code for a color or click the small box on the right and select a color. |
| 4 |
(Optional) Click the folder button for each listed image type, navigate to the image file in your system that you want to use, and click Open. The supported file types are PNG, JPG, JPEG, and GIF. |
| 5 |
Click Save. The user interface updates with the new theme.
|
| 6 |
(Optional) Click Reset to revert your changes. |
View and Regenerate Your API Key
To view or regenerate your API key:
| 1 |
Click the Gears icon at the top-right corner of the Management Portal. |
| 2 |
Click the tab displaying the API Key icon. |
| 3 |
(Optional) Click the link to view the API key. |
| 4 |
Click Regenerate Key to regenerate your API key. |
Access Audit Trail Reports
The Audit Trail page provides an interface where you can view details about the provisioning module changes to your account in last three years. However, you can fetch data for a seven-day period only. You can also download the details in a Microsoft Excel or an Adobe PDF file. Ensure that you have permission to view the reports.
To display an audit trail report:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose Audit Trail. | ||||||||
| 2 |
Select the filters:
| ||||||||
| 3 |
Click Apply Filters. | ||||||||
| 4 |
(optional) Click Download PDF or Download EXCEL to download the report. |
Provisioning Webex Contact Center Resources
Provisioning your Webex Contact Center is an important step that includes various tasks for setting up the Webex Contact Center. Refer to the following sections for details.
Tenant Settings
You can now access tenant settings directly from the Control Hub of newly enhanced Webex Contact Center. For more information, visit Tenant Settings help on Webex Help Center.
If you are still accessing tenant settings through Webex Contact Center Management Portal, you can continue with the following instructions.
You can use the Webex Contact Center Management Portal to configure the tenants that your administrator provisions for your enterprise. To view the tenant settings for your enterprise, click your enterprise name under the Provisioning module in the navigation bar.
Click the following tabs to configure the tenant settings:
General Settings
The General Settings tab displays the following settings.
In the following table, the check mark (✓) at the Tenant column indicates the settings that the authorized users of your enterprise specify. Similarly the ✓ mark in the Partner column identifies the settings that the partner administrator specifies. The ✓ in the Webex Contact Center column identifies the settings that the Webex Contact Center administrator specifies.
To modify the settings, click Edit at the bottom of the page.
|
Setting |
Description |
Tenant |
Partner |
Webex Contact Center |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tenant Details |
||||
|
Name |
The name of your enterprise. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Description |
(Optional) The description for your enterprise. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Time Zone |
The time zone that you provision for your enterprise. For more information, see About Time Zones. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Status |
The status of the tenant. You cannot change the status of the tenant. |
Desktop settings
The Desktop section displays the following settings.
-
Agent experience: Set the inactivity timeout and auto wrap-up interval.
-
Voice features: Enable or disable force default DN, end call, and end consult.
-
RONA timeouts: Configure RONA (Redirection on No Answer) timeouts for unanswered calls.
-
System settings: Set lost connection recovery timeouts.
Manage RONA timeouts
The contact center administrators can manage the Redirection on No Answer (RONA) timeout settings for agents and customers.
To configure the RONA timeout settings for both inbound and outbound call scenarios:
| 1 |
Log in to the customer organization on Control Hub. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
Navigate to . | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 |
In the RONA timeouts section, enter the timeout values in seconds, for the channels. The table shows the default value and the allowed range for the RONA timeout settings.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 |
Click Save. |
Provisioning
The Provisioning tab displays the following settings. The partner administrator and the Webex Contact Center administrator specify these settings.
To modify the settings, click Edit at the bottom of the page.
|
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
|
System Profile |
|
|
Workforce Options |
Allows the supervisors to manage the human resources. Supervisors can proactively analyze and adjust for daily realities and make smarter decisions to manage resources to optimize service levels. Workforce Options enable one or more of the following Workforce Optimization options for your enterprise:
The availability of these features depends on your license. Contact your organization administrator for more information. |
|
Campaign Management |
Enables the third-party software List and the Campaign Manager (LCM) module for a tenant. LCM manages the upload, selection, and rescheduling of contacts. It also provides campaign manager reports. The availability of this feature depends on your license. Contact your organization administrator for more information. |
|
Speech Enabled IVR |
If this setting is Yes, your enterprise allows customers to post questions or concerns in plain language to the system. The availability of this feature depends on your license. Contact your organization administrator for more information. |
Settings
The Settings tab displays the following settings. An asterisk (*) indicates that the settings are not available to tenants with standard licenses.
In the table below, the ✓ mark in the Tenant column indicates the settings that authorized users of your enterprise specify. Similarly, the ✓ mark in the Partner column identifies the settings that the partner administrator specifies. The ✓ in the Webex Contact Center column identifies the settings that the Webex Contact Center administrator specifies.
To modify the settings, click Edit at the bottom of the page.
|
Setting |
Description |
Tenant |
Partner |
Webex Contact Center |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Call Settings |
||||
|
Short Call Threshold |
The time interval, in seconds, to determine whether the call is short or abandoned. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Sudden Disconnect Threshold |
The time interval in seconds to determine whether the agent handles the call or the call ends. The time determines if there is an issue with the connectivity or with the behavior of the agent. You can consider a call as disconnected, if the call terminates within this time interval after it reaches a destination site. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Default Outdial ANI |
The default dial number for the tenant to make outdial calls. The default dial number is displayed in the customer's caller ID, if an agent does not select a specific outdial ANI (Automatic Number Identification) for an outdial call.
To select a default outdial ANI for the tenant, click Edit at the bottom of the page. The Default Outdial ANI drop-down list contains all of the existing dial numbers that are mapped to entry points. To set a dial number as the default outdial ANI, select the dial number from the drop-down list. |
✓ |
||
|
Timeout Settings |
||||
|
Desktop Inactivity Timeout |
Desktop Inactivity Timeout enables you to automatically sign out an agent from the desktop after being inactive for the specified time. An agent is considered inactive for not performing any activity on the Agent Desktop while in the Idle state. Agent activity includes handling contacts, working on custom widgets, or performing any task on the Agent Desktop. The default setting is set to No. If the setting remains at No, then the agents who are signed in will be charged for agent license usage until their session is explicitly signed out. If the setting is Yes, system automatically signs out an agent after being idle for the provided timeout duration. You can provide an idle timeout value from 3 to 10,000 minutes. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Concurrent Voice Contact Settings |
||||
|
Concurrent Voice Contact Entitlements |
The number of concurrent voice contact sessions that the tenant is entitled to. This entitlement is based on the following formula: ((Number of committed Standard Agent licenses + Number of committed Premium Agent licenses) x 3) + Number of Add-on IVR port licenses One session (interaction) in surge protection includes all the inbound and outbound calls related to that session.
|
|||
|
Voice Contact Surge Percentage |
The percentage of voice contact sessions that the tenant can have, over and above the Concurrent Voice Contact Entitlements. The default surge percentage is 30%. |
|||
|
Maximum Concurrent Voice Contact Threshold |
The maximum number of concurrent voice contact sessions that are allowed for the tenant. The contact center drops any inbound or outbound voice contacts after reaching this threshold. This value is derived from the Concurrent Voice Contact Entitlements and the Voice Contact Surge Percentage fields. For example, if the concurrent voice contact entitlements is 300 and the surge percentage is 30% (default value), the Maximum Concurrent Voice Contact Threshold is calculated as: 300 x 1.3 = 390
|
|||
|
Concurrent Digital Contact Settings |
||||
|
Concurrent Digital Contact Entitlements |
The number of concurrent digital contact sessions that the tenant is entitled to. This entitlement is based on the following formula: (Number of committed Standard Agent licenses + Number of committed Premium Agent licenses) x 2 x 15
|
|||
|
Digital Contact Surge Percentage |
The percentage of digital contact sessions that the tenant can have, over and above the concurrent digital contact entitlements. The default surge percentage is 30%. |
|||
|
Maximum Concurrent Digital Contact Threshold |
The maximum number of concurrent digital contact sessions that are allowed for the tenant. The contact center drops any new digital contacts after reaching this threshold. The value of Maximum Concurrent Digital Contact Threshold is set to 30% higher than the concurrent digital contact entitlements. Maximum Concurrent Digital Threshold = Concurrent Digital Contact Entitlements * 1.3. This value is derived from the Concurrent Digital Contact Entitlements and the Digital Contact Surge Percentage fields: Maximum Concurrent Digital Threshold = (Number of committed Standard Agent licenses + Number of committed Premium Agent licenses) x 2 x 15 x 1.3 For example, if the concurrent digital contact entitlements is 300 and the surge percentage is 30% (default value), the maximum concurrent digital contact threshold is calculated as: 300*1.3 = 390
|
|||
|
Other Settings |
||||
|
Maximum Callback Attempts |
The number of times the system attempts a requested callback if the initial callback attempt fails. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Retry Callback Interval |
The number of seconds between the callback attempts in case the initial callback attempt fails. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Pause/Resume Enabled |
If this setting is Yes, agents can pause and resume recording a call. For example, the agent can pause a call recording while obtaining sensitive information from the customer, such as credit card information. If this setting is No, you can enable this feature for individual queues at another time. You can use this feature only if your administrator enables the Privacy Shield feature for your enterprise. For more information, contact your administrator. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Recording Pause Duration |
This setting specifies the amount of time for which the system pauses the call recording. After the time has elapsed, the system automatically starts recording the call. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Check Agent Availability |
If this setting is Yes, the system does not route any contacts to the teams with no logged-in agents. If this setting is No, you can enable this setting for individual queues. For more information, see Adding an Entry Point or Queue. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Record All Calls |
If this setting is Yes, the system records all inbound and outdial calls. If this setting is No, the system records calls based on the settings for each queue. |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
Entry Points and Queues
You can configure and map Entry points and Queues through the Control Hub now, following their decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Set up a Channel for creating an Entry Point and Manage Queues articles.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Sites
You can configure Sites through Control Hub now, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Manage sites article.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Teams
Teams are now accessible through the Control Hub, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Manage teams article.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Users
User configuration is accessible through the Control Hub now, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Add Users article.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
User Profiles
User configuration is accessible through the Control Hub now, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Manage User Profiles article.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Work Types
When you create an idle or wrap-up code, you associate it with a work type. Work types group idle and wrap-up codes in auxiliary reports.
Create a Work Type
To create a work type:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . | ||||||||
| 2 |
Click + New Work Type. | ||||||||
| 3 |
Enter the following details and click Save:
|
Edit a Work Type
To edit a work type:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . | ||||||||||
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the work type that you want to edit and click Edit. Except the Type, you can edit the following settings:
|
Deactivate a Work Type
You cannot deactivate a work type if there are any auxiliary codes that are associated with the work type. When you try to deactivate such a work type, a message informs you that you cannot deactivate the work type. You can click the information icon in the message to view the list of entities that you have associated with this work type.
After you deactivate a work type, you can still see it in the Work Types page as Not Active work types. Historical reports also display details of the deactivated work types.
To deactivate a work type:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the work type that you want to deactivate and click Mark Inactive. |
| 3 |
Click Yes to confirm. The status of the work type changes to Not Active.
Once the object is marked inactive, it can be permanently deleted. For more information, see Delete inactive objects permanently. |
Activate a Work Type
To activate a work type:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the work type that you want to activate and click Restore. |
| 3 |
Click Yes to confirm. The status of the work type changes to Active.
|
Auxiliary Codes
Idle or wrap up codes are two types of Auxiliary codes. Agents select Idle or Wrap-Up codes in Webex Contact Center Agent Desktop to indicate their unavailability or status of the customer contacts. Idle codes typically indicate why an agent is not available to take customer contacts, such as during a lunch break or meeting. Wrap-up codes indicate the result of the customer contacts, for example, the agent escalated the contact, or sold a service.
You associate each idle or wrap-up code with a work type. Work types are values that the system uses to group idle and wrap-up codes in auxiliary reports. For more information, see Create a Work Type.
Agents can use an idle or wrap-up code if you assign the code to their profile.You must add at least one idle code and one wrap-up code in a desktop profile. For more information, see Desktop Profiles.
If your enterprise uses the outdial feature, it is recommended that you create a wrap-up code such as Outdial Failed. Agents can use this code when they are in the wrap-up state after initiating an outdial call that fails to connect.
Create Idle or Wrap-Up Codes
To create an idle or wrap-up code:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . The Aux Codes Idle Codes page appears. To view the list of wrap-up codes, click Wrap Up Codes at the top of the page.
| ||||||||||||||
| 2 |
Click + New Idle Code or + New Wrap Up Code. | ||||||||||||||
| 3 |
Enter the following details and click Save.
|
Edit Idle or Wrap-Up Codes
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . | ||||||||||||
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the idle or wrap-up code that you want to edit and click Edit. | ||||||||||||
| 3 |
Enter the following details and click Save.
|
Delete Idle or Wrap-up Codes
You cannot delete the idle or wrap-up code that is set as default. A message informs you that you cannot suspend or delete the default aux-code if you try to delete it. You must set another idle or wrap-up code to default before deleting the chosen wrap-up or idle code. See Edit Idle or Wrap-Up Codes to change the default setting.
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the idle or wrap-up code and click Mark Inactive. |
| 3 |
Click Yes to confirm. The status of the idle or wrap-up code changes to Not Active.
Once the object is marked inactive, it can be permanently deleted. For more information, see Delete inactive objects permanently. |
Desktop Profiles
You can configure Desktop Profiles through Control Hub now, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Manage Desktop Profiles article.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Address Books
Address books contain entries with phone numbers. Instead of entering a number manually when starting a call, agents can use the address book to select an entry to dial. Agents can access an address book after you add it to their Desktop Profile. For more information, see Dial Plan in Desktop Profiles.
You can create address books that are available to all sites or only to a specific site. The value of Maximum Address Books in the tenant settings of your enterprise determines the number of address books that you can create. For more information, see Tenant Settings.
Currently, Address Books support only English language and when an address book is updated, the administrator must inform the agents to reload the bowser or sign out and sign in again to view the updates.
Create an Address Book
To create a new address book:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . | ||||||||||
| 2 |
Click + New Address Book. | ||||||||||
| 3 |
Enter the following details and click Save.
| ||||||||||
| 4 |
(Optional) In the Entry List, click the + icon to add new entries in the address book. | ||||||||||
| 5 |
In the Add Address Book dialog box, enter the following details:
The maximum number of entries in an address book is 6000. For more information on bulk operations on an address book, see Bulk operations in Webex Contact Center. |
Edit an Address Book
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . | ||||||||
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis button beside the address book that you want to edit and click Edit. You can edit the following fields in the General Settings tab:
| ||||||||
| 3 |
In the Entry List section, under the Action column, click the edit button to edit an entry. | ||||||||
| 4 |
You can edit the following in the Edit Address Book dialog box:
| ||||||||
| 5 |
(Optional) In the Entry List section, under the Action column, click Delete to delete an entry. | ||||||||
| 6 |
(Optional) Click the + icon to add a new entry to the entry list. | ||||||||
| 7 |
Click Save. |
Delete an Address Book
You cannot delete an address book if you associate it with any other entities such as, desktop profile. When you try to delete these address books, you get an error message. Click the information icon at the end of the message to view the list of all the associated entities.
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the address book that you want to delete and click Delete. |
| 3 |
Click Yes to confirm. |
Outdial Automatic Number Identification (ANI)
The Outdial Automatic Number Identification (ANI) feature allows an agent to select a phone number as the caller ID for an outdial call.
To make an outdial ANI list available to an agent, add the outdial ANI list to a Desktop Profile, and assign the profile to the agent. For more information, see Desktop Profiles.
Create an Outdial ANI
To create an outdial ANI:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . | ||||||
| 2 |
Click + New Outdial ANI. | ||||||
| 3 |
Enter the following details in the General Settings section:
The Name and Description fields allow alphanumeric characters, space, hyphen (-), and underscore ( _ ). | ||||||
| 4 |
Click the + icon in the Outdial ANI Entry List section to add a new outdial ANI entry. | ||||||
| 5 |
Enter the following details in the Add Outdial ANI dialog:
| ||||||
| 6 |
Repeat Step 5 and Step 6 to add another outdial ANI entry to the list. | ||||||
| 7 |
Click Save. Newly added entries are in the Outdial ANI Entry List section. |
Edit an Outdial ANI
To edit an outdial ANI:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the outdial ANI that you want to edit and click Edit. |
| 3 |
You can edit the following:
|
| 4 |
Click Save. |
Delete an Outdial ANI
You cannot delete an outdial ANI if you have associated it with any entity, for example, a desktop profile.
To delete an outdial ANI:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the outdial ANI that you want to delete and click Delete. |
| 3 |
Click Yes to confirm. |
Dial Plans
The Dial Plan page allows you to define validation criteria for the:
-
Dial Number (DN) that an agent uses to sign in to the Agent Desktop.
-
DN that an agent uses for outdialing.
If you satisfy the validation prerequisites, the system validates DNs that agents enter in the Desktop environment against the syntax rules that are defined in one or more dial plans. The following table describes the validation prerequisites.
|
DN usage |
Validation prerequisites |
|---|---|
|
Agent Desktop sign-in |
Configure Desktop Profiles > Agent DN Validation as follows:
|
|
Outdial calls |
Configure Desktop Profiles > Dial Plan as follows:
Note: Agents use the Desktop dial pad to make outbound calls. To display the dial pad, you must have the correct setup. Contact your administrator for the setup. |
If you allow agents to enter DNs without requiring validation and their entries don't comply with valid syntax, the Desktop rejects sign-ins and outbound calls fail.
You can choose from two default dial plans and create new dial plans. The default dial plans are:
-
US
-
Any Format
The default US dial plan accepts entries such as:
-
1-800-555-1234
-
1 (800) 555-1234
-
18005551234
-
18005551234,,,222
In this example, commas indicate pauses before entry of an extension number.
The default Any Format dial plan accepts entries such as:
-
123
-
5551234
-
555-1234
-
8005551234
-
1800FLOWERS
-
bruce.matthews
You can use the Any Format dial plan to validate a DN, the first part of an email address, or a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) uniform resource identifier (URI).
All dial plans require a regular expression for the system to recognize what defines a valid entry. The regular expression comprises the syntax rules that the system uses to interpret what is valid.
You can create separate dial plans with appropriate regular expressions to specify the required syntax for the:
-
DN that an agent uses to sign in to the Desktop Station Credentials pop-up window.
-
DN an agent enters in the Enter number to call field of the Desktop dial pad.
Optionally, you can specify a prefix and characters that the system must strip from the entry in the dial pad.
The regular expressions of the default dial plans are described in the following sections. You can refer to the syntax rules that are described in these sections to guide you in formulating regular expressions for the dial plans you create.
For an outdial call, the system performs the following steps to determine the validity of an entry an agent makes in the Enter number to call field of the Desktop dial pad:
-
Strip the characters specified in the dial plan’s Stripped Characters field from the entry in the Enter number to call field.
In the default US and Any Format dial plans, the specified Stripped Characters are left parenthesis, right parenthesis, space, and hyphen.
-
Validate the resulting entry according to the criteria defined in the regular expression of the chosen dial plan. If the entry meets the criteria, it's deemed valid.
-
If the entry is invalid, prepend the entry that is specified in the Prefix field.
In the US dial plan, the specified prefix is number 1.
-
Validate the resulting entry according to the defined regular expression again.
Regular expression for the default US dial plan
The regular expression that is specified for the US dial plan is:
1[0-9]{3}[2-9][0-9]{6}([,]{1,10}[0-9]+){0,1}
Following is a description of what this regular expression specifies.
-
The first digit must be 1.
-
Three digits in the range of 0–9 must follow.
{3} means 3 digits in the preceding range [0-9]
-
One digit in the range of 2-9 must follow.
-
Six digits in the range of 0-9 must follow.
{6} means six digits in the preceding range [0-9]
-
Zero or one occurrence of the following sequence can follow: between one and ten commas [,] followed by one or more digits [0-9].
{1,10} means one to ten pauses as specified by one comma [,] per pause
+ means one or more digits in the preceding range [0-9]
{0,1} means zero or one occurrence of the sequence of pauses [,] followed by one or more digits in the preceding range [0-9]
Regular expression for the default Any Format dial plan
The regular expression that is specified for the Any Format dial plan is:
([0-9a-zA-Z]+[-._])*[0-9a-zA-Z]+
Following is a description of what this regular expression specifies.
-
The dial pad entry can start with zero or more sets of the following sequence:
one or more alphanumeric characters [0-9a-zA-Z] followed by one hyphen, period, or underscore [-._].
-
+ means one or more alphanumeric characters in the preceding range [0-9a-zA-Z]
-
* means zero or more of the preceding sequence of alphanumeric characters [0-9a-zA-Z] followed by one hyphen, period, or underscore [-._].
-
-
One or more alphanumeric characters [0-9a-zA-Z] must follow.
Create a Dial Plan
Before you begin
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . The Dial Plan page appears. This page displays a list of existing dial plans. | ||||||||||
| 2 |
Click + New Dial Plan. | ||||||||||
| 3 |
Configure the following settings.
| ||||||||||
| 4 |
Click Save. |
Edit a Dial Plan
Before you begin
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . The Dial Plan page appears. This page displays a list of existing dial plans. | ||||||||||
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the dial plan you want to edit and choose Edit. The Edit Dial Plan page appears.
| ||||||||||
| 3 |
You can edit the settings described in the following table. When you are done editing, click Save.
|
Delete a Dial Plan
Before you begin
-
You require Administrator privileges to complete this procedure.
-
Before deleting a dial plan, ensure that it isn't provisioned for a desktop profile or used to validate an agent's sign-in Dial Number (DN). If you can't delete a dial plan, contact your Full Administrator.
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose The Dial Plan page appears. This page displays a list of all existing dial plans. |
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the dial plan you want to delete and choose Delete. The Heads Up! dialog box appears.
|
| 3 |
Click Yes to confirm. |
Global Variables
You can configure Global Variables through Control Hub now, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Manage Global Variables article.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Multimedia Profiles
You can configure Multimedia Profiles through Control Hub now, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Manage Multimedia Profiles article.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Desktop Layout
You can configure Desktop Layout through Control Hub now, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Manage Desktop Layouts and Create custom desktop layout articles.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Skill Definitions
You can create Skill Definitions through the Control Hub now, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Manage Skill Definitions article.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Skill Profiles
You can configure Skill Profiles through Control Hub now, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Manage Skill Profiles article.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Threshold Rules
If your enterprise uses the Threshold Alerts feature, authorized users can create threshold rules to monitor agent and call data.
Call Metrics
You can configure threshold rules for call metrics. For each rule, specify a value that triggers the alert. Configure call metrics as described in this table.
|
Metric |
Entity Type |
Trigger Value Type |
|---|---|---|
|
Abandoned Calls |
Queue |
Count |
|
Average Queue Time |
Queue |
Duration |
|
Average Speed of Answer |
Queue |
Duration |
|
Blind Transferred Calls |
Queue |
Count |
|
IVR Calls |
Entry Point |
Count |
|
Longest Time in Queue |
Queue |
Duration |
|
Number of Calls in Queue |
Queue |
Count |
|
Overflow Calls |
Queue |
Count |
|
Service Level Threshold |
Queue |
Percentage |
|
Short Calls |
Entry Point |
Count |
|
Transferred Calls |
Queue |
Count |
Agent Metrics
You can configure rules for agent metrics. For each rule, specify a value that triggers the alert. Configure agent metrics as described in this table.
From the list of metrics given the table below, Webex Contact Center supports only following three: Available Agents, Idle Agents, and Number of Logged in Agents.
|
Metric |
Entity Type |
Trigger Value Type |
|---|---|---|
|
Available Agents |
Site or Team |
Count |
|
Connected Agents |
Site or Team |
Count |
|
IB Average Handle Time |
Site or Team |
Duration |
|
Idle Agents |
Site or Team |
Count |
|
Not Responding Agents |
Site or Team |
Count |
|
Number of Agents in Outdial |
Site or Team |
Count |
|
Number of Logged in Agents |
Site or Team |
Count |
|
OB Average Handle Time |
Site or Team |
Duration |
|
Occupancy |
Site or Team |
Percentage |
By default, the maximum number of rules that are allowed for a tenant is 50. To increase this to a higher limit, contact Cisco Support.
Create a Threshold Rule
A threshold alert is displayed in the Agent Peformance Statistics report on the Agent Desktop if you set Agent Viewable to Yes for the threshold rule and select the threshold alert in the desktop profile. For more information, see Desktop Profiles.
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
On the Threshold Rules page:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 |
Specify or change the settings for the rule. You can specify or change the following settings in the General Settings area:
You can specify or change the following settings in the Entity Information area:
You can specify or change the following settings in the Threshold Information area:
You can specify or change the following settings in the Email Information area:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 |
Click Save. |
Copy a Threshold Rule
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . | ||||||||||
| 2 |
On the Threshold Rules page, click the ellipsis button beside a listed rule and click Copy. | ||||||||||
| 3 |
Specify or change the settings for the rule. You can specify or change the following settings in the General Settings area:
| ||||||||||
| 4 |
You can specify or change the following settings in the Entity Information area:
| ||||||||||
| 5 |
You can specify or change the following settings in the Threshold Information area:
| ||||||||||
| 6 |
You can specify or change the following settings in the Email Information area:
| ||||||||||
| 7 |
Click Save. |
Edit a Threshold Rule
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . | ||||||||||
| 2 |
On the Threshold Rules page:
| ||||||||||
| 3 |
Specify or change the settings for the rule. You can specify or change the following settings in the General Settings area:
| ||||||||||
| 4 |
You can specify or change the following settings in the Threshold Information area:
| ||||||||||
| 5 |
You can specify or change the following settings in the Email Information area:
| ||||||||||
| 6 |
Click Save. |
Deactivate a Threshold Rule
Before you begin
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside the threshold rule that you want to deactivate and click Mark Inactive. |
| 3 |
Click Yes to confirm. The status of the threshold rule changes to Not Active.
Once the object is marked inactive, it can be permanently deleted. For more information, see Delete inactive objects permanently. |
Activate a Threshold Rule
| 1 |
On the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis icon beside a threshold rule with the status Not Active and click Restore. |
| 3 |
Click Yes to confirm. The status of the threshold rule changes to Active.
|
Entry Point Mappings
You can Map Entry Points with Dialed Number Skill Definitions through the Control Hub now, following its decommissioning from the Tenant Management Portal. For updated help, refer to Set up a Channel article.
See Administrator's help for Webex Contact Center to find updated content on all migrated entities.
Reports for the Provisioned Items
Use the Management Portal to generate reports about the active resources that the Webex Contact Center administrator provisions for your enterprise.You can view the following reports:
|
Report |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Site Report |
The details of the sites for your enterprise. For more information, see About Sites, Teams, Entry Points, and Queues |
|
Team Report |
The details of the teams for your enterprise. For more information, see About Sites, Teams, Entry Points, and Queues |
|
Agent Report |
The details of the agents for your enterprise. For more information, see Desktop Profiles. |
|
Inbound EP Report |
The details of the entry points for your enterprise. For more information, see Entry Points and Queues. |
|
Inbound Queues Report |
The details of the queues for your enterprise. For more information, see Entry Points and Queues. |
|
Outdial EP Report |
The details of the outdial entry points for your enterprise. For more information, see Entry Points and Queues. |
|
Outdial Queues Report |
The details of the outdial queues for your enterprise. For more information, see Entry Points and Queues. |
|
Desktop Profile Report |
The details of the desktop profiles for your enterprise. For more information, see Desktop Profiles. |
|
Skill Report |
The details of the skills that are available for your enterprise. This report is available if your enterprise uses the Skill-Based Routing. For more information on how to define the skills for your enterprise, see Skill Definitions. Currently we do not support Skill-Based Routing. |
|
Skill Profile Report |
The details of the mapping of the skills and the corresponding profiles. This report is available if your enterprise uses the Skill-Based Routing. For more information on how to define the profiles for the skills, see Skill Profiles. |
|
Routing Report |
The details about the mapping of the routing strategies with the entry points, queues, and teams. For more information on how to define routing strategies, see . |
|
Agent Skills Report |
The details about the agents and their corresponding skills. This report is available if your enterprise uses the Skill-Based Routing. For more information on how to define the skills for your enterprise and Desktop Profiles, see Skill Definitions and Desktop Profiles. Note: Currently we do not support Skill-Based Routing. |
Manage Reports for the Provisioned Items
To email the report or download the report for any provisioned item:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
Select the required type of report. For more information on the types of the reports, see Reports for the Provisioned Items. |
| 3 |
Download the report as either an Excel sheet or PDF. For the Routing Report, you have to select the type of the routing strategy for which you want to generate the report. The options are:
|
Delete inactive objects permanently
Webex Contact Center allows administrators to permanently delete configuration objects that have been marked inactive. This helps customers remove unwanted configurations, keep a lightweight configuration footprint, and improve application performance. Before deleting a configuration object permanently, you will need to mark it inactive. You can also periodically delete inactive objects using an automatic purge tenant level setting.
You can permanently delete the following configuration object types:
-
Users
-
User Profiles
-
Desktop Profiles
-
Work Types
-
Auxiliary Codes
-
Threshold Rules
-
Skill Profile
-
Teams
-
Sites
-
Entry Points
-
Outdial Entry Points
-
Queues
-
Outdial Queues
-
Desktop Layouts
-
Global Variables
-
Multimedia Profiles
-
Skill Definitions
The maximum number of inactive users is 5000. The maximum inactive objects for all other object types is 100. If this limit is reached, you must delete inactive objects to be able to deactivate more objects. If the configuration object has associated objects, you must inactivate all the referenced objects.
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose Provisioning. |
| 2 |
Select an entity. |
| 3 |
To permanently delete a configuration object manually, on the entity page, click the ellipsis icon beside the object. Select Delete. |
| 4 |
On the dialog box that informs you that the object will be permanently deleted and can't be recovered, click Yes. A message appears that the object is permanently deleted. To configure an automatic purge of inactive objects for permanent deletion, see the article Configure auto-purge of inactive entities. |
Business Rules
About Business Rules Engine
Business Rules Engine (BRE) provides a means for tenants to incorporate their data into the Webex Contact Center environment for custom routing and for general implementation. Administrators can use the BRE solution with Webex Contact Center to use business data for their organization in flows.
For more information about BRE, visit the Webex Contact Center Business Rules Engine User Guide.
Contact Routing
A new and improved method for routing and queueing is now available. For more information, see Understand Routing and Queueing in Webex Contact Center.
Working with Flow Designer
Flow Designer
For more information about the Flow Designer module and the configuration details, visit the Flow Designer Guide in the Webex Help Center.
Call Monitoring
Monitor Calls
The Call Monitoring module enables authorized users to silently monitor any active call that is managed by the Webex Contact Center service at any time, across any site, and to verify that customers are being served in a professional manner. Authorized users can also create monitoring schedules, coach an agent who is connected to a call by providing comments that only the agent can hear, and barge in on calls as needed.
Monitoring Overview
The Webex Contact Center Call Monitoring module enables contact center managers to monitor the quality of service being delivered across their multisource contact centers. Through a simplified Web interface, authorized users can select a combination of one or more queues, sites, and teams, as well as a specific agent that they want to monitor. After these criteria are entered, the system places a request to monitor the next call that matches the combination of all the criteria when the call is distributed to the destination site. Monitoring can be done on a continuous, one time only (ad hoc), or scheduled basis, and authorized users can monitor a call that is already in progress.
The audio for the call is delivered through an inbound phone call using a phone number associated with the user engaged in monitoring. Authorized supervisors can coach an agent during a connected call by providing comments that only the agent can hear and can barge in on a call and become part of the conversation between the agent and the customer.
Note the following:
-
You cannot make a continuous monitoring request and an ad-hoc request for the same target at the same time.
-
If a scheduled request and a continuous request are made for the same target, the continuous request takes precedence. When the continuous request is paused or canceled, the scheduled request is enabled.
-
If a scheduled request and an ad-hoc request are made for the same target, the ad-hoc request takes precedence. When the ad-hoc request is either canceled or completed, the scheduled request is enabled.
-
If you sign out of the Management Portal while a monitoring request is still active, a message asks if you want to cancel the monitor request or continue monitoring.
If you select Yes, any active ad-hoc, or continuous monitoring requests are canceled after you log out. Any scheduled requests are suspended.
Monitor Calls
The Call Monitoring page provides an interface for monitoring a call on a continuous or one-time only basis.
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose Call Monitoring. | ||||||
| 2 |
In the Monitoring Filter panel, specify one or more queues, sites, teams, and agents that you want to monitor. If you set a queue, site, team, or agent list to All, it includes only entities to which you have access in the request. | ||||||
| 3 |
In the Callback Number field, enter the phone number and click Register. If you must update a number, enter the new callback number and click Update. Enter the callback number in one of the following formats:
| ||||||
| 4 |
To prevent this monitoring session from being displayed on the Management Portal for other users, check the Use Invisible Mode check box. | ||||||
| 5 |
Click one of the options in the following table to submit your call monitoring request. The system disables these options if you don't have a callback number registered.
Your request appears in the Monitor Requests list along with any pending requests from other agents. The monitored call appears in the Calls Being Monitored list. For more information about the Call Monitoring page, see Viewing Call Monitoring Information. | ||||||
| 6 |
If your user profile has authorization, you can click the Coach or Barge In button in the Action column to coach the agent or barge in on the monitored call. For details, see Barge in on a Call. | ||||||
| 7 |
When the call ends, click Monitor Next Call to monitor the next call in the queue. Alternatively, if you choose the Continuous Monitor option, the system sends the next call in the queue to you. | ||||||
| 8 |
Click Cancel to cancel the monitoring activity for that request. If you choose Continuous Monitor, click the Pause button to temporarily halt incoming calls. You can click the Resume button to resume call monitoring. If an agent goes into the Not Responding state, the call goes back to the queue and the caller hears music on hold. The Desktop disconnects the supervisor who is monitoring the call during this time. If the supervisor is scheduled to monitor a call but has not picked up the call, the call widget disappears from the Monitor Requests list, and the phone stops ringing. |
Coach an Agent
If the Whisper Coach feature is enabled in your user profile, you can speak to an agent who is being monitored without being heard by the customer.
-
The coaching session continues, even if the call is transferred to another agent, until the call either ends or is transferred to another number (agent-to-DN transfer).
-
If the coached agent consults with another agent, you hear music on hold and are not able to continue coaching the agent until the caller is taken off hold.
Whisper Coach is not available through Extensible Supervisor Desktop (ESD).
While coaching an agent, you can barge in on the call if the Barge In feature is enabled in your user profile.
To silently coach an agent:
| 1 |
While you monitor a call (as described in Monitor Calls) and the call is connected to an agent, click Coach. Do not click Coach if the call is waiting in a queue after being transferred by the agent to another queue. Doing so causes your coach request to fail. The Coach button is not available when the agent transfers the call to another number (DN transfer). |
| 2 |
Provide verbal instructions to the agent. |
| 3 |
To remove yourself from the call, hang up. The call is removed from the Calls Being Monitored list. |
Barge in on a Call
| 1 |
While you are monitoring or coaching a call, and the call is connected to an agent (and not waiting in a queue), click Barge In. You are immediately connected to the call. The Barge In button disappears from the page. |
| 2 |
To remove yourself from the call, hang up. The call is removed from the Calls Being Monitored list. |
Viewing Call Monitoring Information
To view call monitoring information, from the Management Portal navigation bar, click Call Monitoring
The Call Monitoring page displays the following:
-
Controls for requesting a monitoring session. For more information, see Monitor Calls.
-
A chart of active and queued calls for the queue that is currently selected in the Monitoring Filter panel on the left side of the page.
-
The Monitoring Requests/Calls Being Monitored table, which displays the two lists described in the following sections.
If you resize the Call Monitoring window to a very narrow size, the Monitoring Requests/Calls Being Monitored table displays at the bottom of the window. It might appear that the table is missing, but you can see it if your scroll to the bottom of the window.
Calls Being Monitored List
The Calls Being Monitored list displays information about all calls currently being monitored in your enterprise.
When a monitored call is transferred to a specific phone number (agent-to-DN transfer), it is removed from the Calls Being Monitored list and thus, the Coach and Barge In buttons are no longer available.
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Queue |
The queue that received the call. |
|
Site |
The contact center location to which the call was distributed. |
|
Team |
The team to which the call was distributed. |
|
Agent |
The name of the agent being monitored or a numeric ID code if the call was answered by a capacity-based team resource instead of by a Webex Contact Center agent. |
|
Monitoring Status |
The status of the monitoring session:
|
|
Supervisor Name |
The name of the person monitoring the call. |
|
Supervisor Number |
The phone number of the person monitoring the call. |
|
Duration (mm:ss) |
The number of minutes and seconds since the call arrived. |
|
Action |
Buttons that you can click to coach or barge in on a call that is being monitored, if authorized by your user profile. |
Monitoring Requests List
The Monitor Requests list displays information about all monitoring requests in your enterprise.
If a monitoring request includes multiple queues, sites, teams, or agents, you can display a list of them in a tool tip by placing your mouse on a value in the Queue, Site, Team, or Agent column.
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Request Type |
The request types are:
|
|
Queue |
The queues included in the request. If multiple queues are included, you can display a list of them by pointing to the value displayed in the column. |
|
Site |
The sites included in the request. If multiple sites are included, you can display a list of them by pointing to the value displayed in the column. |
|
Team |
The teams included in the request. If multiple teams are included, you can display a list of them by pointing to the value displayed in the column. |
|
Agent |
The agents included in the request. If multiple agents are included, you can display a list of them by pointing to the value displayed in the column. |
|
Monitoring Status |
The status of the monitoring session:
|
|
Supervisor Name |
The name of the person who submitted the request. |
|
Supervisor Number |
The phone number of the person who submitted the request. |
|
Action |
Buttons that you can click to pause, resume, or cancel a monitoring request. |
Working with Monitoring Schedules
The Monitoring Schedules page in the Call Monitoring module enables authorized users to schedule call monitoring requests at specific times of the day or week. Note the following:
- Monitoring schedules will be re-assigned to the user who edits a schedule, even if the creator of the schedule is a different user. Please ensure that users editing monitoring schedules are able to monitor agents.
-
The start and end times specified in the Call Monitoring Schedule use the enterprise time. However, calls are monitored in local time. Be sure to adjust for this when you specify the start and end times in your monitoring schedules.
Create or Edit a Monitoring Schedule
To create a new monitoring schedule or edit an existing schedule:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . | ||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
To create a new schedule:
| ||||||||||||||||
| 3 |
To copy or edit an existing schedule from the list view, click the ellipsis button beside a listed schedule and choose Copy or Edit. | ||||||||||||||||
| 4 |
On the page that appears, specify the appropriate settings as described in the following table:
| ||||||||||||||||
| 5 |
Click Save. |
Activate or Deactivate Monitoring Schedules
You can activate or deactivate a monitoring schedule by editing the Status field in the settings for the schedule, or you can click a button in the list view Monitoring Schedules page as follows:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
Click the ellipsis button beside a listed schedule and click Activate or Deactivate. |
Export the Monitoring Schedule List
To export the monitoring schedule list to a data analysis tool such as Microsoft Excel:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
In the list view, click Action on the upper-right side of the page header and choose Excel or CSV. |
| 3 |
In the dialog box that opens, either click Open to open the file, or click Save, navigate to the directory where you want to save the file, and then click Save. |
Delete a Monitoring Schedule
To delete a monitoring schedule:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
In the list view, click the ellipsis button beside a listed schedule and click Delete. |
| 3 |
Click Yes to confirm the deletion. |
Call Recording
Create or Edit a Recording Schedule
To create or edit a call recording schedule:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose the Call Recording module. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
On the Recording Schedules page, select a queue from the Queue drop-down list. All call recording schedules for that queue are displayed. From here, you can:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 |
To create a new schedule:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 |
To copy or edit an existing schedule, from the list view, click the ellipsis button beside a listed schedule and click Copy or Edit. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 |
On the page that appears, specify the appropriate settings as described in the following table, and then click Save.
|
Deleting a Recording Schedule
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose the Call Recording module. |
| 2 |
On the Recording Schedules page, select a queue from the Queue drop-down list. |
| 3 |
Click the ellipsis button beside a listed schedule and click Delete. |
Recording Management
About Recording Management
The optional Webex Contact Center Recording Management module enables authorized users to search for and play audio files that are recorded through the Webex Contact Center Call Recording feature. In addition, authorized users can create tags that can be assigned to audio files for use as search criteria, specify which global (previously known as CAD) variables to store with recordings, and view recent Recording Management activity.
For configuration objects that have been deleted, an option to filter data using the deleted object names will not be available. It is recommended to query and fetch the data by a date range. The result set will contain details of calls handled for those configuration objects which are permanently deleted.
Stereo Recording
The Stereo Recording feature replaces the combined mono output file with a stereo output file. The stereo file provides the audio streams of the agent and the other participant (the caller or the called party) as two separate audio channels within a single recording. This enables better voice analytics than in a mono file, where the audio is mixed into a single stream.
To play a stereo recorded file, the Webex Contact Center Recording Management module enables authorized users to search for and play stereo recorded audio files. For more information, see Search for and Play Recordings.
Search for and Play Recordings
To search for and play a recording:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose Recording Management. By default, the search page lists the recordings for the previous 13 months from the current date. To search based on specific criteria, use the following search fields on the left pane to filter the recordings:
| ||||||||
| 2 |
To filter the list based on more criteria, click the Advanced Search button. In the dialog box that appears, you can filter the search results based on Recording Duration and Call Attributes:
| ||||||||
| 3 |
Click the Search button to search. If the search criteria match, then the Search Results page lists the recordings. | ||||||||
| 4 |
Click the ellipsis button beside an entry. The following options appear:
|
Assign and Remove Tags
You can assign the same tag to multiple recordings and you can assign multiple tags to an individual recording.
To assign a tag to a recording or remove a tag from a recording:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose Recording Management. |
| 2 |
On the Search page, perform a search for the recordings you want to either assign tags to or remove tags from, as described. |
| 3 |
Click the ellipsis button beside a listed recording on the Search Results page and click Tags. On the upper part of the dialog box that opens, the list of tags assigned to the recording is displayed on the right and a list of tags that are available is displayed on the left. |
| 4 |
To assign a tag to the recording, select a tag in list on the left and click Assign Tag to move it to the list on the right. |
| 5 |
To remove a tag from the recording, select a tag in the list on the right and click Remove Tag to move it to the list on the right. |
| 6 |
When you are finished, click Save. |
Search Attributes
The Recording Management > Search Attributes page provides access to controls where you can perform the tasks described in the following topics:
Create and Export Tags
The Tags section of the page enables authorized users to create and export a list of tags that can be assigned to recordings (see Assign and Remove Tags).
To create a tag or export a list of tags:
| 1 |
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose . |
| 2 |
In the Tags section of the page that appears, do one of the following:
|
Digital Channels
Webex Contact Center supports various digital channels like Facebook Messenger, LiveChat, Email, SMS, Apple Messages for Business, and WhatsApp. With changing habits and lifestyle preferences, these digital channels offer consumers an opportunity to connect with businesses through their preferred channels.
Supported Digital Channels
For information about the supported digital channels and their configuration details, visit Set up digital channels in Webex Contact Center.
Opt Out When in Queue
Queue is where the contact waits before the system assigns to an agent or a dial number. The queue is created in the Provisioning module of the Management Portal.
The customer is presented with the opt-out of the queue menu with information about the estimated wait time and the position in the queue. The customer can choose to opt out and exit the queue.
Task Flow to Set Up the Opt-Out Functionality
To set up the opt-out functionality:
| 1 |
Create new opt-out-of-queue flow from the Cisco Webex Contact Center Management Portal (). |
| 2 |
Configure the Play Music activity in the Flow Designer. Specify the audio file, music duration, and the start offset. |
| 3 |
Configure the Queue Contact activity to place the contact in a queue or the Queue to Agent activity to route the contact directly to a preferred agent. |
| 4 |
Configure the Get Queue Info activity to know the current position in the queue and the estimated wait time. |
| 5 |
Configure the Menu activity for the wait-in-queue prompt or the opt-out-of-queue prompt with the Text-to-Speech functionality enabled. |
| 6 |
Configure the Callback flow if the contact selects to opt out of the queue and registers for a callback in the opt-out-of-queue prompt selection. |
| 7 |
Click Publish Flow. For more information, see Publish a Flow. |
View Opt-out-of-Queue Report
The Opt-out-of-Queue report captures the average wait time in a queue after the customer chooses to opt out of the queue. For more information about how to view the Opt-out-of-Queue report, see the Webex Contact Center Analyzer User Guide.
Blended Multimedia Profiles
Overview
If you are using Multimedia Profiles from Webex Contact Center Control Hub, see Manage multimedia profiles article for the latest updates. However, if you are accessing multimedia profiles through Management portal, you can proceed with this section of Setup and Admin Guide.
Blended Multimedia Profiles offer Webex Contact Center administrators the ability to configure the media channel types (voice, chat, email, and social) and the number of contacts of each media channel that an agent can handle simultaneously.
Administrators can configure multimedia profiles of the following types:
-
Blended
-
Blended Real-time
-
Exclusive
The administrator can then associate the multimedia profile to agents at the site, team, or agent level.
Advantages of Blended Multimedia Profiles
Blended Multimedia Profiles enable organizations to provide dedicated attention to customers, promoting better quality of service, improved customer experience, and better conversion rates. Also, organizations can balance the load across media channels when experiencing uneven load in some channels, enabling efficient utilization of agents.
Setting Up Blended Multimedia Profiles
To set up Blended Multimedia Profiles:
-
The administrator configures the Blended Multimedia Profile using the Multimedia settings in the Provisioning module of the Management Portal.
-
The administrator associates the Blended Multimedia Profile to an agent, team, or site.
In the Agent Desktop, agents are assigned contacts based on the multimedia profile associated with them at any point in time.
Administrators and supervisors can view multimedia profile settings of agents and the number of contacts of each media channel type that the agents handled, via the Agent Details report. This report is available in the Webex Contact Center Analyzer.
Configure a Multimedia Profile
As an administrator, do the following to configure a multimedia profile:
-
From the Management Portal navigation bar, choose Provisioning > Multimedia Profiles.
-
On the Multimedia Profiles page, click + to create a new multimedia profile or click the ellipsis button to edit an existing multimedia profile.
-
In the Media Details section, select the blended multimedia profile as required. The available multimedia profile types are:
-
Blended: Allows you to specify the media channels and the number of contacts per media channel that an agent can handle simultaneously (for example, 1 voice, 3 chats and 5 emails).
-
Blended Real-time: Contacts of only one real-time media channel (either voice or chat) will be assigned to an agent at a point in time, along with contacts of other media channel types (email and social).
For Blended and Blended Real-time multimedia profiles, the maximum number of contacts that can be assigned to an agent is 1 for voice, and 5 for chat, email and social.
-
Exclusive: Select this profile type to assign only one contact to the agent across all media channels, at a point in time.
-
For more information, see Create a Multimedia Profile.
Associate a Multimedia Profile to an Agent, Team, or Site
After you configure the multimedia profile, associate the profile to a site, team, or agent via the Provisioning module in the Management Portal. For more information, see Sites, Teams, and Users.
A multimedia profile associated with an agent takes precedence over the multimedia profile of the agent's team. A multimedia profile of the team takes precedence over the multimedia profile associated with the site.
Assign Contacts to Agents
In the Agent Desktop, contacts are assigned to an agent based on the multimedia profile associated with the agent.
View Agent Details
As an administrator or supervisor, you can view the multimedia profile settings of agents and the number of contacts of each channel type handled by the agents, via the Agent Details report in the Webex Contact Center Analyzer.
For more information, see Agent Details Report in the Visualization chapter in the Cisco Webex Contact Center Analyzer User Guide.
Courtesy Callback
About Courtesy Callback
A customer calling the contact center can be offered an option to receive a callback rather than waiting in the queue to connect to an agent. The customer can be offered the callback option during peak hours when the wait time is longer, or during non-working hours of the contact center.
Advantages of Courtesy Callback
Courtesy callback enables the contact center to offer better quality of service, and increase customer retention. The customer experience is enhanced, because the contact receives a proactive call from an agent rather than having to wait to connect to the agent.
Setting Up Courtesy Callback
To set up courtesy callback, the flow developer needs to configure the callback flow using the Flow Designer.
-
Prior to configuring the courtesy callback flow, the contact center administrator must configure the inbound entry point and queue for courtesy callback.
-
Courtesy callback isn't supported with capacity-based teams (CBT). CBTs have no individual agents assigned to them, and courtesy callback requires an Agent ID to function. Therefore, if the courtesy callback flows to an entry point or a queue served by a CBT, the call fails.
-
Courtesy callback should be configured after a queuing activity. This should not be used as a first-class queuing activity in a flow.
When a customer dials in to the contact center and waits in queue for an agent, the customer can be provided with the option to opt out of the queue and receive a callback instead. The customer's position in the queue is retained for receiving the callback. The contact will remain in a queue based on the duration set in MAX_TIME_IN_QUEUE configuration. When an agent is available, the agent is offered the callback request in the Agent Desktop, based on the customer’s position in the queue. After the agent accepts the callback request, the call is dialed out to the customer. When the interaction ends, the agent chooses a wrap-up code to wrap up the call.
A Courtesy Callback report is available in Webex Contact Center Analyzer, for the supervisor and administrator to view callback statistics. In addition, agents can gain insights on their callback statistics via the Team Stats- Historic
Agent Performance Statistics (APS) report.
Configure the Callback Flow
Ensure that the administrator has set up the inbound entry point and queue for courtesy callback. For more information about how to set up entry points and queues, see Entry Points and Queues.
As a flow developer, set up the courtesy callback flow using the Flow Designer. The following figure illustrates a sample courtesy callback flow:
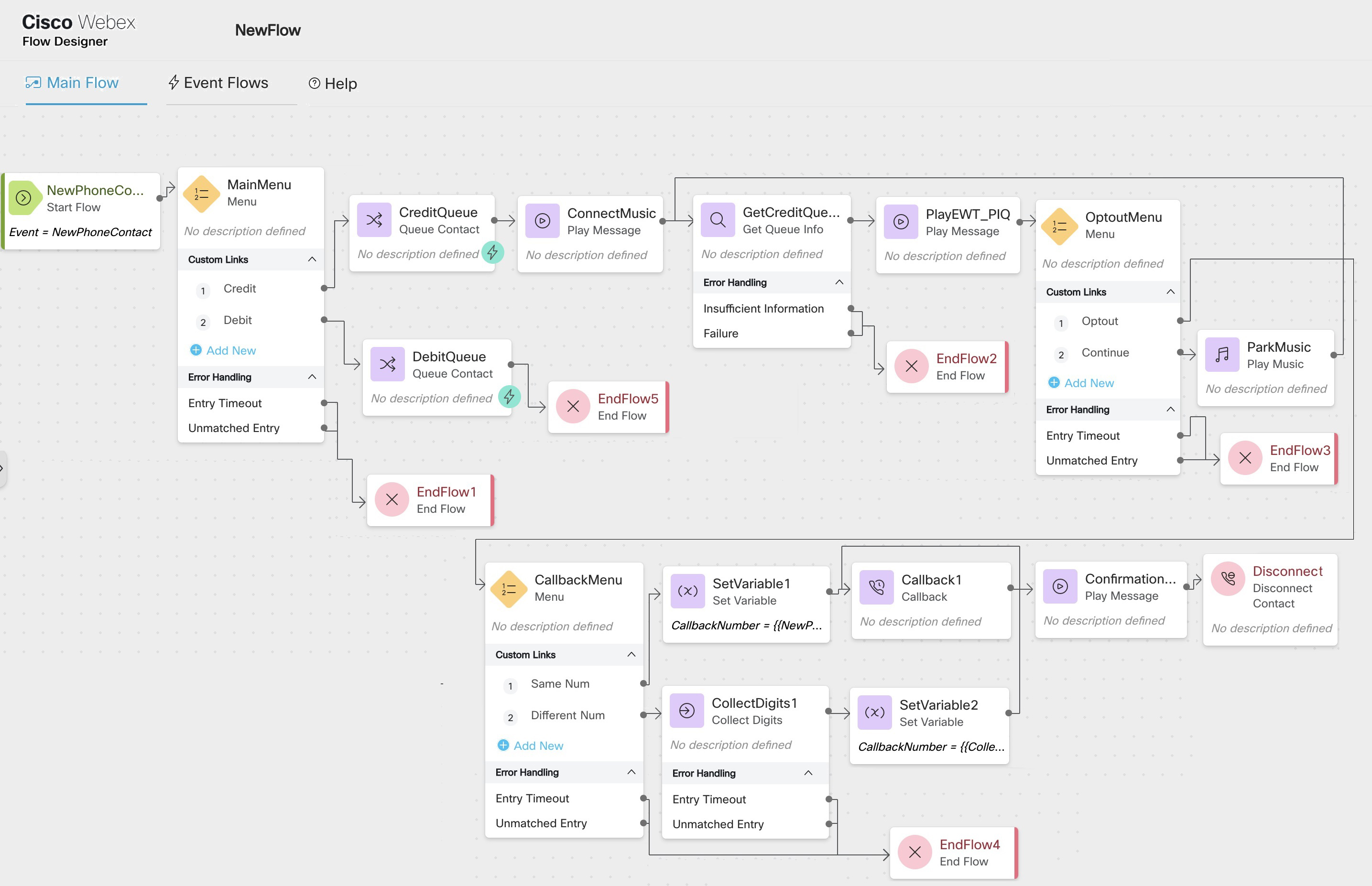
For more information on how to configure a flow using the Flow Designer, see Flow Designer Overview.
The following steps summarize the sample courtesy callback flow:
-
The customer dials into the IVR.
-
The customer contact is routed to an appropriate queue in accordance with the Menu and Queue Contact configuration. The sample flow and the sequence of steps depicted here are based on this scenario.
Alternatively, you can enable the customer to opt out of the call and receive a callback before the call is routed to a queue; for example, during non-working hours of the contact center. The contact can then be routed to an appropriate queue by configuring the Callback activity.
When the customer waits in a queue (call is parked) for an agent, you can engage the customer with the following activities:
-
Play Music: Plays a static .wav file as the customer waits in queue.
-
Play Message: Informs the customer of the position in queue (PIQ) and the estimated wait time (EWT) using this activity. Use the Get Queue Info activity to fetch the EWT/PIQ.
You can configure the Play Music activity and the Play Message activity to play the audio files intermittently, until an agent is available or until the customer opts out of the queue.
-
-
The customer can be offered an Opt Out of Queue menu option, based on the EWT/PIQ. You can configure any of the following options when the customer opts out of the queue:
-
Leave a voice mail: Configure a Blind Transfer activity to enable the customer to leave a voice mail when the customer opts out of the queue.
-
Receive a courtesy callback: The customer's position in queue is retained to receive a courtesy callback.
The following activities enable you to configure the callback:
-
Menu: Configure a callback menu to enable the customer to choose a callback number.
The customer can provide the callback number, or the customer's ANI (Automatic Number Identification) number is used as the default callback number.
You can use the Collect Digits and Set Variable activities to set the callback number, as illustrated in the callback flow.
-
Callback: Configure the Callback activity to make the courtesy callback. You can configure the Callback activity to use the same queue as the inbound call, or a different queue to make the callback.
Do not configure callback to use a queue served by a capacity-based team (CBT) as it results in call failure. Callback processing requires an Agent ID, and CBTs have no individual agents assigned to them.
If you select the same queue to make the callback, the customer is called back when the agent is available in the queue, based on the customer's position in queue.
If you select a different queue to make the callback, the callback request is placed at the end of the new queue.
You can select a static queue or a variable queue when you configure the Callback activity. For more information on setting the Callback activity parameters, see Callback.
-
You can configure a confirmation message that the callback is registered and then disconnect the contact, by using the Play Message and the Disconnect Contact activities.
-
-
When you design a flow, a Consult interaction can't include a Courtesy Callback activity.
-
You can use a Play Message activity after a Callback activity in a flow. If an agent is found during Callback registration or a Play Message period, the customer is immediately connected to the agent.
Make a Courtesy Callback
After the customer opts out of the queue, a callback request to the customer is initiated when an agent is available in the queue, based on the contact's position in the queue. The agent is offered the callback request in the Agent Desktop.
-
If the agent does not accept the request, the request is routed to another available agent, or continues to wait in the queue until an agent is available.
-
Only a single attempt is made for the courtesy callback. If the call is not successfully connected to the customer, or is rejected by the customer, it isn't retried.
After the agent accepts the call, the call is dialed out to the customer. The customer receives the call from an ANI associated with the contact center. For more information on ANI, see Outdial Automatic Number Identification (ANI).
If the customer does not respond to the call or rejects the call, the callback request is canceled. If the customer answers the call, the callback request is marked as processed.
When the interaction ends, the agent chooses a wrap-up code to wrap up the call.
For more information on how to process a callback request via the Agent Desktop, see Callback section in the Manage your calls in Agent Desktop article.
View Courtesy Callback Reports
The following reports are available for courtesy callback:
-
Courtesy Callback Report: Enables administrators and supervisors to view callback statistics. For more information, see Courtesy Callback Report in the Visualization chapter in the Cisco Webex Contact Center Analyzer User Guide.
-
Team Stats - Historic Report: Enables agents to gain insights on their performance with respect to callback contacts. The APS report is available in the Agent Desktop. For more information, see the Team statistics - historical reports section of the Agent Performance Statistics Reports in the View and manage agent performance reports article.
Self Service
The Webex Contact Center offers Self Service functionality to handle the customer requests without involving human agents. Self Service uses the Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system in the call flow. This IVR includes basic activities such as Play Message, Collect Digits, and Menu. All of these activities can also play the audio dynamically through Text-to-Speech functionality.
The maximum file size supported for audio files is 8 MB. The supported file format is .wav. For more information, see Working with Resource Files.
You can extend interactions in Self Service to have Virtual Agents in the flow. The Virtual Agent can understand caller utterances to deliver a conversational Self Service experience.
You can use the Flow Designer to script any possible use cases in the Self Service space. For more information, see Activities in Flow Designer.
Configure Entry Point and Select the Flow in Routing Strategy
You configure the Entry Point and select the flow in Routing Strategy in the Management Portal.
For more information on how to configure the Entry Point, see Entry Point and Queues. For more information on how to select the flow in Routing Strategy, see Configure Routing Resources.
Enable a Virtual Agent
A virtual agent handles conversations with your customers. The virtual agent understands the intent of the conversation and assists the customer as part of the IVR experience. The virtual agent is powered by Google's Dialogflow capabilities. The administrator has access to the Conversational IVR transcript.
The virtual agent supports the following audio codecs:
- G711A for A-law
- G711U for µ-law
| 1 |
Create a Dialogflow agent to integrate the conversational experience into the IVR system. For more information, see Build a Dialogflow Agent. Include |
| 2 |
Configure a virtual agent in the Control Hub. For more information, see Configure Virtual Agent. |
| 3 |
Add a Virtual Agent activity to the call flow to handle customer queries in conversational format. For more information, see Add Virtual Agent Activity in Flow Designer. |
Build a Dialogflow Agent
Configure Google Dialogflow:
|
Build a Dialogflow agent that provides automated responses. |
Configure Virtual Agent
After you download the Authentication Key, upload the Authentication Key by choosing the JSON file to create the Virtual Agent in the Control Hub.
The administrator must Configure a Virtual Agent in the Control Hub.
After configuring a Virtual Agent on the Control Hub, the administrator can configure the Virtual Agent activity in the Flow Designer.
Add Virtual Agent activity in Flow Designer
After configuring the Virtual Agent on Control Hub, add the Virtual Agent activity in the Flow Designer.
You can add a Virtual Agent to a call flow to handle customer queries in a conversational format. The Virtual Agent understands the intent of the conversation and assists the customer as part of the IVR experience. For more information, see Virtual Agent.
Blind Transfer
The Blind Transfer activity refers to a process wherein a contact is transferred to an external Dial Number (DN) and entry point through the IVR, without agent intervention.
The Blind Transfer activity is applicable when a call should be transferred to an external Dial Number and entry point. The transfer can also be initiated to an external bridge. For more information, see Blind Transfer.
Disconnect Contact
This activity is used to disconnect the contact from the call. This refers to the end of a contact in IVR.
For more information, see Disconnect Contact.
IVR Transcript and global Variables in Agent Desktop
The administrator can provide access to an agent to view the Conversational IVR transcript and to view or edit the global (previously known as CAD) variables based on the configurations set in the call flow.
An agent can view the Conversational IVR transcript and the global variables extracted from the Conversational IVR transcript based on the permissions set in the call flow by the administrator. For more information on the Conversational IVR transcript in Agent Desktop, see IVR Transcript Widget.
For more information on the global variables in Agent Desktop, see Enter call-associated data variables.
IVR and CVA Dialog Flow Report in Analyzer
The IVR and CVA Dialog Flow report enables the administrators and supervisors to view the Self-service operational metrics.
For more information on the IVR and CVA Dialog Flow report in Analyzer, see the section IVR and CVA Dialog Flow Report in the Cisco Webex Contact Center Analyzer User Guide.
Text-to-Speech
The Text-to-Speech capability is powered by Google's Text-to-Speech APIs. To enable this functionality, you must set up a Google Cloud account and configure the Text-to-Speech service.
With Text-to-Speech, you can convert arbitrary strings, words, sentences, and variables into an actual human speech that is played dynamically to the caller. This is in place of playing a prerecorded audio.
To enable Text-to-Speech, follow this task flow:
| 1 |
Create a Service Account to download the private key. For more information, see Create a Service Account for Google Connector. |
| 2 |
Configure the Google Connector in Control Hub to enable the Text-to-Speech capability in Flow Designer. For more information, see Configure a Google Connector. |
| 3 |
To use Text-to-Speech in your prompt, enable the Text-to-Speech toggle. For more information, see Text-to-Speech Toggle. |
Create a Service Account for Google Connector
Complete the following procedure to configure the Google Connector:
|
Create a service account and download the JSON file that contains the Authentication Key. |
Configure a Google Connector
After you download the Authentication Key, upload the Authentication Key by choosing the JSON file to configure the Google Connector in the Control Hub.
-
The administrator must Configure a Connector (see the Google tab) in the Control Hub.
-
Add the ability to read dynamic messages. These messages can contain variables and can be used in a sequence with audio files.
-
If you are using variables, use this syntax: {{ variable }}. You can also use SSML to construct the message. If you are using SSML, insert it inside the <speak></speak> tags.
-
To learn more about Google tags, see: https://developers.google.com/assistant/conversational/df-asdk/ssml%22
After creating the connector, the administrator can enable the Text-To-Speech functionality.
Text-to-Speech Toggle
The Text-to-Speech toggle allows you to create natural-sounding, synthetic human speech as part of activities in your flow that can play messages to the caller, including Menu, Play Message, and Collect Digits. With Text-to-Speech, you can convert arbitrary strings, words, sentences, and variables into an actual human speech. This is in place of playing a pre‐recorded audio.
Text-to-Speech takes two types of input: raw text (plain text) or Speech Synthesis Markup Language-formatted (SSML-formatted) data.
After creating the Google connector, enable the Text-To-Speech toggle in IVR activities in the Flow Designer. For more information, see Menu, Play Message, Collect Digits.
Experience Management for Post Call Surveys in Webex Contact Center
We have enhanced the Experience Management feature to empower Webex Cloud Contact Center customers to listen to and act on the Voice of their Customers. For more information, see the Experience Management - Configure surveys for IVR and Digital Channels for Webex Contact Center article.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Management Portal Problems
Management Portal Problems
If you experience a problem with the Management Portal, the following table may help you solve the problem.
|
Problem |
Description/Workaround |
|---|---|
|
You cannot log in to the Management Portal. |
Check to make sure that you enetered the correct user name and password. |
|
You cannot access a module from the Management Portal, or you cannot see some entry points or queues. |
You do not have the correct privileges to access these modules, entry points, or queues. Contact your Webex Contact Center administrator. |
|
The Management Portal does not display data for agents or calls, or shows that no agents are logged in. |
Make sure that the privacy setting for Internet Explorer is set to Medium. |
|
Occasionally the message |
Log out of the current Webex Contact Center session. Close any remaining Webex Contact Center windows and log in again. |
|
When you resize the Agent view of a real-time agent report, tooltips for idle and wrap-up codes are sometimes displayed in the graph area instead of near the cursor. |
Maximize the window to display the tooltip near the cursor. |
|
Too many abandoned calls are being reported. |
Escalate to Customer Support. |
|
While you view a chart in a report or on a monitoring page, you see the following message |
The system has been unable to refresh the data in the chart since the time indicated in the message, typically because of an intermittent network interruption or server issue. If the problem persists for several minutes, notify your system administrator. |
|
The real-time reports are not refreshing on the Management Portal. |
Escalate to Customer Support. |
|
The real-time report statistics are not displayed. |
Escalate to Customer Support. |
|
In a real-time agent report, the wrap-up count and number of entered wrap-up codes do not match. |
This discrepancy occurs when an agent logs out while still in the Wrap-up state without selecting a wrap-up code. Instruct agents to always go into the Idle state and then click the Log Out button to log out rather than closing the browser while logged in. |
|
Changes to the names of existing idle and wrap-up codes do not appear immediately in agent reports. Instead, agent reports display the previous code names before they were edited or N/A for a new code. |
Log out and then log in again to see the changes. |
|
When exported to CSV format, data in the Agent View of a current snapshot agent report displays incorrectly. |
The Time Value displays in two cells instead of one when exported to CSV format. This is because a comma separates the day from the date and time in the Login Time field. |
|
When you export historical report data to Microsoft Excel that includes date and time in the hh:mm:ss format, Excel displays only the hours and minutes, and not the seconds. |
By default, Excel displays the data in hh:mm format. However, you can double-click in the cell to see the data in hh:mm:ss format. |
|
For a new team, data in the agent interval report displays in half-hour intervals from the time an agent on the team logs in after system restart. |
This is transient for teams that log in for the first time. Normally, data displays in half-hour intervals from midnight. |
|
In the Historical Reports module, occasionally the parameters for a customized default report are not saved after you log out and log in again. |
After you save a custom report, wait 10-15 seconds before logging out. |
|
You cannot make a monitoring request. |
Ensure that you use the correct DN and prefix. |
|
Monitoring session left open for an hour or longer displays a blank page or unexpected behavior |
Close the module and re-open it. |
|
Supervisor phone rings even when the monitoring request is for a different queue. |
If a monitoring request is made for a team and if multiple queues use the same team for routing, any of the queue's calls for that team can be monitored. |
|
A call ends, but the monitoring screen indicates that the call is still in progress. |
Escalate to Customer Support |
|
Signed in agents cannot see changes made to Skill profile. |
The agent needs to sign in again to view the changes. |
Reporting Management Portal Issues to Customer Support
When you escalate a Management Portal issue to Cisco Webex Contact Center Customer Support, make sure to provide the following information:
-
The login and user name of the person experiencing the problem.
-
The time that the issue was first observed.
-
If the problem occurred in the Monitoring module, the number that the supervisor was attempting to call and a call session ID, if available.
Troubleshooting Desktop Problems
Network Interruptions
If a network interruption occurs that lasts for less than two minutes, the Desktop display a Reconnecting message and then successfully reconnect.
If a network interruption lasts longer than two minutes, instruct agents to close the current Desktop window, and then sign in using the primary URL. If the sign in fails with the primary URL, instruct agents to use the backup application center sign in.
Escalate all network interruptions; report the time that the problem occurred and the number of agents affected.
If the network to the primary application center is down, Management Portal users cannot view any statistics.
Desktop Application Problems
If you experience a problem with the Desktop application, the following table may help you solve the problem.
|
Problem |
Description/Workaround |
|---|---|
|
You are not able to sign in to the Desktop. |
|
|
During sign in, the error message |
Check the format of the DN that you entered and make sure that the number is valid. |
|
You accidentally closed the browser window while on a call. |
If you close the browser window while on a call, you cannot sign in again until you complete the call. If you close the browser window while the call is on hold, the system automatically takes the call off hold. |
|
When you refresh the Desktop window, you are signed out and the sign-in screen displays. |
Sign in again. Avoid refreshing the window while signed in. |
|
The status bar on the Desktop displays |
|
|
After reconnecting to the system following a network interruption, you are suddenly signed out. |
Sign in to the Desktop again. If you are unable to sign in, escalate to Customer Support. |
|
Re-launching the Desktop while you are signed in may create problems |
Do not open more than one Desktop application at a time on the desktop. |
|
The Desktop becomes very slow. |
This can happen when you leave the Desktop open for long periods of time. Close both the Desktop and the browser after you sign out of the system. If this does not help, end the process from the Windows Task Manager. |
|
The Desktop occasionally signs out agents following a network interruption. |
Sign in to the Desktop again. |
|
The Desktop is not displayed. |
Minimize the Desktop, and then restore it from the taskbar. |
|
Launch pages and graphs do not display properly. |
Make sure that in Internet Explorer, the Show Pictures option is selected in the Advanced tab of the Internet Options dialog box. |
|
You are available but no calls are sent to you. |
Make sure you are in the Available state and are signed in to the correct team. |
|
You are talking to a customer, but the Desktop status bar displays |
Report the incident to Customer Support. |
|
Your agent softphone is not ringing, but the Desktop status bar displays |
Make sure that you entered the correct DN. |
|
The Desktop status bar displays |
Check to see if the computer network cable has been disconnected or loosened. If you do not see a message indicating that there has been a network problem, escalate to Customer Support. |
|
You answer a call, but the call disconnects after 30 seconds. |
If |
|
The Internet Explorer browser freezes. |
Open Windows Task Manager and end all browser processes. |
|
Pop-up blockers appear. |
From the Internet Explorer Tools menu, disable pop-up blockers. |
|
The Desktop status bar displays a connected state while the phone is ringing. |
Report the incident to Customer Support. |
|
An outbound call fails. |
Make sure you entered the correct DN and prefix. |
|
During a blind transfer, call details do not display on the Desktop of the receiving agent while that agent is in the Reserved state. |
The Reserved state is transient. Call details display when the second agent answers the call. |
Audio Problems
If you experience audio problems with the Desktop, the following table helps to resolve the problems.
|
Problem |
Description/Workaround |
|---|---|
|
Echo or low volume |
Check the phone settings. If using a softphone, check the Microsoft Windows and softphone settings. |
|
Jitter/Stutter audio -OR- High latency |
Bad connectivity, probably due to a network problem. Check to make sure that your PC is not also running other software that uses audio. Escalate to Customer Support. |
|
Cross talk |
Escalate to Customer Support. |
|
One-way audio |
Make sure you are not on mute. If not, escalate to Customer Support. |
| Background noise |
The background noise removal feature is enabled by default for your organization. In situations where the agent wants to hear background noise from the customer, contact Customer Support to disable the feature flag. This feature is available only for Flex 3 premium agents on Webex Contact Centers with regional media support on the Next Generation media platform. |
Reporting Agent Desktop Issues to Customer Support
When you escalate an Agent Desktop issue to Webex Contact Center Customer Support, make sure to provide the following information:
-
Ask the agent to provide a screen capture of the Agent Desktop screen.
-
Include the time that the issue was first observed.
Report Parameters
Call Report Parameters
The following table describes the parameters available in Webex Contact Center real-time and historical call reports. In the table, CSR is an abbreviation for Customer Session Record.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Report |
|---|---|---|
|
% Abandoned |
The percentage of calls that were abandoned during the report interval. (Abandoned/Total) * 100 |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
% Answered |
The number of answered calls divided by the number of calls that entered the queue minus short calls multiplied by 100. (Answered/(Answered + Abandoned)) * 100 |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Abandoned |
The number of calls that were abandoned during the report interval. An abandoned call is a call that was terminated without being distributed to a destination site, but that was in the system for longer than the time specified by the Short Call threshold provisioned for the enterprise. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Abandoned Time |
The cumulative amount of time that calls were in the system for longer than the time specified by the Short Call threshold, but terminated before being distributed to an agent or other resource. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Abandoned within SL |
The number of calls that were terminated while in queue within the Service Level threshold provisioned for the queue or skill (in a skills interval by queue report). Although this metric is visible for outdial calls, it is not meaningful for outdial calls. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Adjusted Service Level % |
The number of calls that were either answered or abandoned within the Service Level threshold provisioned for the queue or skill (in a skills interval by queue report), divided by total calls (including abandoned calls) multiplied by 100. ((In Service Level + Abandoned within SL)/(Answered + Abandoned)) * 100 Although this metric is visible for outdial calls, it is not meaningful for such calls. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Agent |
The name of the agent who handled the call or a numeric ID code if the call was handled by a capacity-based team resource instead of by a Webex Contact Center agent. |
CSR |
|
Agent Start Time |
The time the agent picked up the phone and began talking with the caller. |
CSR |
|
ANI |
The ANI digits delivered with the call. ANI, or Automatic Number Identification, is a service provided by the phone company that delivers the caller's phone number along with the call. |
CSR |
|
Answered |
The number of calls that were routed from the queue to an agent or available resource and were answered by the agent or resource. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Answered Time |
The cumulative amount of time between when calls entered the queue and when they were answered (connected to an agent or other resource) during the report interval. Because answered time is calculated after the call is answered, answered time for calls that are waiting to be answered is not reflected in the report. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Available Agents |
The number of logged-in agents who are currently in the Available state. |
Call Snapshot report |
|
Avg Abandoned Time |
The total amount of time that calls were in the system before they were abandoned divided by the total number of calls that were abandoned: Abandoned Time/Abandoned |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Avg Connected Time |
The total connected time divided by the total number of calls that were answered during the report interval: Connected Time/(Answered + Secondary Answered) |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Avg Handle Time |
The average length of time spent handling a call (connected time plus wrap-up time), divided by number of answered calls: Connected Time+Wrap Up Time/(Answered + Secondary Answered) |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Avg IVR Time |
The total amount of time that calls were in the IVR system divided by the total number of calls that were in the IVR system. |
Real-time Call Interval & Historical Call reports for Entry Points |
|
Avg Queued Time |
The total amount of time that calls were in queue divided by the total number of calls that were queued: Queued Time/Queued |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues. |
|
Avg Speed of Answer |
The total answered time divided by the total number of answered calls: Answered Time/Answered |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Avg Wrap Up Time |
The total amount of time agents spent in the Wrap-up state divided by the total number of answered calls: Wrap Up Time/(Answered + Secondary Answered) |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Blind Transfer Count |
The number of times the call was transferred out of the queue by the agent without the first agent consulting or conferencing with the party to whom the call was transferred |
CSR |
|
Blind Transfers |
The subset of transferred out calls that were transferred by the agent to another agent or an external DN without the first agent consulting or conferencing with the party to whom the call was transferred. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Call Duration |
The amount of time between when the call arrived at the entry point or queue and when it was terminated. |
CSR |
|
Call End Time |
The time the call was terminated. |
CSR |
|
Call Start Time |
The time the call arrived at the entry point or queue. |
CSR |
|
Completed |
The number of calls that ended during the report interval. Answered, abandoned, and disconnected calls are included in this count. Transferred and short calls are not counted. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Conference Count |
The number of times the agent established a conference call with the caller and another agent. |
CSR |
|
Conference Count |
The number of times agents initiated a conference call to an agent or external number. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Conference Time |
The amount of time an agent spent in conference with the caller and another agent. |
CSR |
|
Connected |
The number of calls currently connected to an agent. |
Call Snapshot report |
|
Connected Time |
The time interval between when calls were answered by an agent or other resource and when the calls were terminated. Because connected time is not calculated until the call is terminated, the connected time for a call that is still in progress is not reflected in the report. |
Real-time call interval reports for Sites, Teams, Queues, & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Connected Time |
The total amount of time the call was connected to an agent (talk time plus hold time). |
CSR |
|
Consult Count |
The number of times agents initiated a consult with another agent or someone at an external number during a call. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Consult Count |
The number of times the agent consulted another agent during the call. |
CSR |
|
Consult Errors |
The number of times agents did not respond to a consult invitation. |
CSR |
|
Consult Time |
The amount of time an agent spent consulting with another agent during this call. |
CSR |
|
CTQ Answer Count |
The number of times consult-to-queue requests were answered. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
CTQ Answer Time |
The cumulative amount of time between when consult-to-queue requests were answered and when the consultations ended. |
Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
CTQ Request Count |
The number of times consult-to-queue requests were initiated. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams; CSR |
|
CTQ Request Time |
The cumulative amount of time between when consult-to-queue requests were initiated and when the consultations ended. |
Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams; CSR |
|
Current Service Level % |
The percentage of calls in queue that have not yet reached the Service Level threshold provisioned for the queue (in a queue report) or skill (in the skill rows of a skills-by-queue report). Although this metric is visible for outdial calls, it is not meaningful for outdial calls. |
Call Snapshot report |
|
Disconnected |
The number of calls that were answered (that is, connected to an agent or distributed to and accepted by a destination site), but that were then immediately disconnected within the Sudden Disconnect threshold provisioned for the enterprise. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
DN |
The number the caller dialed (DNIS). |
All DN Canned report |
|
DNIS |
The DNIS digits delivered with the call. DNIS, or Dialed Number Identification Service, is a service provided by the phone company that delivers a digit string indicating the number the caller dialed along with the call. |
CSR |
|
Entry Point |
The name of the entry point associated with the call. |
CSR |
|
From Entry Point |
The number of calls that entered this queue after having been classified into the queue from an entry point by the IVR call control script. The number of calls that entered this queue after having been classified into the queue from an entry point by the IVR flow. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
From Entry Point |
The number of calls that came in to this entry point from another entry point. |
Real-time Call Interval & Historical Call reports for Entry Points |
|
Full Monitored Calls |
The number of calls that were monitored from beginning to end. |
Monitored Calls report |
|
Handle Time |
The amount of time spent handling the call (Connected Time + Wrap Up Time). |
CSR |
|
Handle Time |
The cumulative amount of time spent handling calls: Connected Time + Wrap Up Time |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Handle Type |
How the call was handled. Possible values:
Termination type is about the last step before the call ended, whereas handle type is about the overall handling by contact center. For example, the termination type of a call can be abandoned, while the handle type can be normal in the following case: An incoming call to the contact center was handled by an agent, but was later transferred to another queue and the call ended while the caller was waiting in this queue. |
CSR |
|
Hold Count |
The number of times the call was put on hold. |
|
|
Hold Time |
The amount of time the call was on hold in this queue (for a queue CSR) or in all underlying queues (for an entry point CSR). |
CSR |
|
In IVR |
The number of calls that are currently in the IVR system. |
Call Snapshot report |
|
In Queue |
The number of calls currently in the queues that are covered in the report. In the case of entry-point reports, this is the number of calls that are currently in queues fed by the entry point. In entry point and queue reports, you can click a number in this column to display the Age of Calls in Queue pie chart in a pop-up window. The chart displays the number of calls that have been in the queue for the length of time represented by three time segments. The time segments are derived by dividing the Longest Time in Queue value by three, rounding the resulting value down to the nearest 10 seconds, and then multiplying that value by 1, 2, and 3. For example, if the Longest Time in Queue value is 85 seconds, then 85/3=28.3, which is rounded down to 20, and the chart displays time segments of 20, 40, and 60 seconds. |
Call Snapshot report |
|
In Service Level |
The number of calls that were answered within the Service Level threshold provisioned for this queue or skill (in a skills interval by queue report). Although this metric is visible for outdial calls, it is not meaningful for outdial calls. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Invisible Monitored Calls |
The number of calls that were monitored using the Invisible mode, which prevents the monitoring session from being displayed on Management Portals other than that of the initiating supervisor. |
Monitored Calls report |
|
IVR Ended |
The number of calls that ended in the IVR but were not short calls. |
Real-time Call Interval & Historical Call reports for Entry Points |
|
IVR Time |
The amount of time the call was in the IVR system. |
CSR |
|
IVR Time |
The cumulative amount of time calls were in the IVR system. |
Real-time Call Interval & Historical Call reports for Entry Points |
|
Logged-in Agents |
The number of agents who are currently logged in to this team or to all teams at this site. At the queue level, this is the number of agents logged in to all teams at the sites serving this queue. |
Call Snapshot report |
|
Longest Call In Queue Time |
The longest amount of time a call has been in each queue covered in the report. |
Call Snapshot report |
|
Maximum Wait Time |
The longest amount of time a call was in the queue waiting to be answered. |
Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Midcall Monitored Calls |
The number of calls for which monitoring began after the call was already in progress. |
Monitored Calls report |
|
Monitor Flag |
Whether or not the call was monitored, coached, or barged in on. Possible values:
For information about monitoring, see Monitor Calls. |
CSR |
|
New |
The number of external calls that came in to the entry point. |
Real-time Call Interval & Historical Call reports for Entry Points |
|
New |
The number of calls that came into the system by way of a specific dialed number. |
All DN Canned report |
|
No. of Transfers |
The number of times the call was transferred by an agent. |
CSR |
|
Overflow |
The number of calls that were sent to the overflow number provisioned for the queue and were answered. Typically, a call is sent to an overflow number if it is queued for longer than the maximum time specified in the routing strategy or because an error occurred when the call was sent to an agent. If the call is not answered, it is included in the Abandoned or Disconnected count when the call ends. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Queue |
The name of the queue associated with the call. |
CSR |
|
Queue |
The name of the queue that was monitored. |
Calls Monitored report |
|
Queue Time |
The amount of time the call was in a queue waiting to be sent to a destination site. |
CSR |
|
Queued |
The number of calls that entered the queue during this interval. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Queued Time |
The cumulative amount of time calls were in queue, waiting to be sent to an agent or other resource. Because queued time is calculated after the call leaves the queue, the queued time for a call that is still in the queue is not reflected in the report. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Record Flag |
Whether or not the call was recorded by Webex Contact Center through the optional call recording feature. |
CSR |
|
Requeued |
The number of calls that left this queue after having been transferred by the agent to another queue. For calls to be requeued, the first agent clicks the Queue button, selects a queue from the drop-down list, and clicks Transfer. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
S No. |
A sequence number identifying each leg of a call as it moves through the Webex Contact Center system. Click an entry in this column to open a window that displays the history of the call throughout its life cycle. |
CSR |
|
Secondary Answered |
The number of calls that were answered by an agent after being transferred to the agent by another agent. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Service Level % |
The number of calls that were answered within the Service Level threshold provisioned for the queue or skill (in a skills interval by queue report), divided by total calls (including abandoned calls) multiplied by 100: ((In Service Level)/(Answered + Abandoned)) * 100 Although this metric is visible for outdial calls, it is not meaningful for outdial calls. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams. |
|
Session ID |
A value assigned by the system that uniquely identifies a call during its life cycle. |
CSR |
|
Short |
The number of calls that were terminated within the Short Call threshold provisioned for the enterprise without being distributed to a destination site or connected to an agent. |
Real-time Call Interval & Historical Call reports for Entry Points |
|
Short |
The number of calls that were terminated within the Short Call threshold provisioned for the enterprise without being connected to an agent. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Site |
The contact center location to which the call was distributed. |
CSR |
|
Site |
The name of the site that was monitored. |
Monitored Calls report |
|
Team |
The name of the team to which the call was distributed. |
CSR |
|
Team |
The name of the team that was monitored. |
Monitored Calls report |
|
Terminating Party |
Who terminated the call: Agent or Caller |
CSR |
|
Termination Type |
How the call was terminated. Possible values:
|
CSR |
|
To Entry Point |
The number of calls that were transferred to another entry point. |
Real-time Call Interval & Historical Call reports for Entry Points |
|
To Queue |
The number of calls that were sent to a queue. |
Real-time Call Interval & Historical Call reports for Entry Points |
|
Total Monitored Calls |
The total number of calls monitored during the report time interval. |
Monitored Calls report |
|
Transfer Errors |
The number of times an error occurred during the transfer process. |
CSR |
|
Transferred |
The sum of all calls transferred from this queue to an agent, external DN, or another Webex Contact Center queue: Transferred Out + Requeued |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Transferred In |
The number of calls that were transferred to this entry point by an agent. |
Real-time Call Interval & Historical Call reports for Entry Points |
|
Transferred In |
The number of calls that entered this queue after being transferred into the queue by an agent who clicked the Queue button, selected a queue from the drop-down list, and clicked Transfer. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues & Skills by Queue; Historical Call reports for Queues |
|
Transferred Number |
The phone number to which the agent transferred the call in an agent-to-DN transfer. This parameter appears in the Webex Contact Center window that opens when you click an entry in the S No. (sequence number) column of either an entry point or queue call detail record (CSR). |
CSR |
|
Transferred Out |
The number of calls that left this queue after being transferred by an agent to an external DN or to another agent. Transferred-out calls result when an agent clicks the Agent button, selects an agent from the drop-down list, and clicks Transfer, or when the agent clicks the DN button, enters a phone number, and clicks Transfer. Transferred-out calls may begin as a consultation or conference, but are counted as transferred-out only when the first agent completes the transfer to the second party. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
|
Wrap Up |
The wrap-up code that the agent gave for the call. Note that if the agent wraps up the call after the CSR is generated, the corresponding CSR is updated after the agent selects the wrap-up code for that call. |
CSR |
|
Wrap Up Time |
The amount of time an agent spent in the Wrap-up state during the call. |
CSR |
|
Wrap Up Time |
The cumulative amount of time agents spent in the Wrap-up state during the call. |
Real-time Call Interval reports for Queues, Skills by Queue, Sites, & Teams; Historical Call reports for Queues, Sites, & Teams |
Agent Report Parameters
The following table describes the parameters available in Webex Contact Center real-time and historical agent reports. In the table, ADR is an abbreviation for Agent Detail Report.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Report |
|---|---|---|
|
Action |
Icons you can click to perform an action:
|
Snapshot/Team & Skill views |
|
Agent |
The name of an agent in the report. If your enterprise uses the Multimedia feature and the report includes more than one media channel, you can click the a collapse arrow or expand arrow to the left of an agent name to collapse or expand the data grouped by channel type. |
Snapshot/Agent view; Real-time Agent Interval/Agent-level |
|
Agent Requeue |
The number of times an agent requeued an inbound call. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Snapshot/Agent view; Agent Trace report |
|
Agent Transfer |
The number of times an agent transferred an inbound call to another agent. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Available |
Count: The number of times an agent went into the Available state. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent in the Available state. Average Time: (Not in ADR or Snapshot/Agent view or Agent Trace report) The average length of time agents were in the Available state (Total Available Time divided by Available Count). % Time: (Only in ADR) The percentage of time the agent was in the Available state. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR & Snapshot/Agent view; Agent Trace report |
|
Available |
The number of agents currently in the Available state or, in the Skill view, the number of agents in the Available state who possess the skill. |
Snapshot/Site, Skill, & Skills by Team views |
|
Available Time |
The amount of time agents were in the Available state during the time interval. |
Real-time Agent Interval reports |
|
Average Connected Time |
The connected time divided by the number of calls that were connected during the time interval. |
Real-time Skills Interval by Team |
|
Average Handle Time |
The average length of time spent handling a call (connected time plus wrap-up time, divided by number of calls). |
Real-time Skills Interval by Team |
|
Blind Transfer |
The number of times an agent transferred an inbound call without consulting first. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Snapshot/Agent view; Agent Trace report |
|
Calls Handled |
The number of calls the agent handled (or, for the Skill view, the number of calls the agent handled for that skill) since logging in. Rest the cursor over a number in this column to display a pop-up showing the wrap-up codes the agent entered and how many times each code was entered. |
Snapshot/Team view & Skill view |
|
Calls Handled |
The total number of inbound and outdial calls handled. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports |
|
Channel |
The media channel associated with the activity. (Appears only if your enterprise uses the Multimedia feature.) |
ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Conference |
The number of times the agent initiated a conference call. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Snapshot/Agent view; Agent Trace report |
|
Connected |
The number of agents currently connected to an inbound call, or in the Skill view, the number of agents connected to a call who possess the skill. |
Snapshot/Site, Skill, & Skills by Team views |
|
Connected Time |
The amount of time inbound calls were connected to an agent during the time interval (talk time plus hold time). |
Real-time Skills Interval by Team |
|
Consult |
Count: The number of times an agent answered a consult request plus the number of times an agent consulted other agents. Total Time: Total Consult Answer Time plus Total Consult Request Time. Average Time: (Not in ADR or Agent Trace report) The average length of consulting time (Total Consult Time divided by Consult Count). |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Consult Answer |
Count: The number of times an agent answered a consult request from another agent. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent answering consult requests from agents. Average Time: (Not in ADR or Agent Trace report) The average length of time agents spent answering consult requests (Total Consult Answer Time divided by Consult Answer Count). % Time: (Only in ADR and Agent Trace report) The percentage of time the agent spent answering consult requests. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Consult Request |
Count: The number of times an agent sent a consult request to another agent. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent consulting other agents. Average Time: (Not in ADR or Agent Trace report) The average length of time agents spent consulting other agents (Total Consult Request Time divided by Consult Request Count). % Time: (Only in ADR and Agent Trace report) The percentage of time the agent spent consulting other agents while on an inbound call. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Consulting |
The number of agents currently consulting with another agent. |
Snapshot/Site & Skills by Team views |
|
CTQ |
The number of agents currently consulting with another agent after initiating or answering a consult-to-queue request. |
Snapshot/Site view |
|
Current State |
The agent's current state. In Team and Skill views, if the current state is Idle, the idle code the agent selected is shown in parentheses. No code shows if the agent has just signed in and has not selected an idle code. |
Snapshot/Team, Skill, & Agent views |
|
Disconnected Count |
The number of calls that were connected to an agent, but that were then immediately disconnected within the Sudden Disconnect threshold provisioned for the enterprise. |
Historical Agent Summary & Agent Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Disconnected Hold Count |
The number of times an inbound call was disconnected while the caller was on hold. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
DN |
The dial number the agent used to log in to the Agent Desktop. |
Snapshot/Team, Agent, & Skill views; ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Duration |
The amount of time the agent was in the state. |
Agent Trace Report |
|
Final Logout Time |
The date and time the agent logged out. This column appears only in agent-level summary reports. |
Historical Agent Summary/Agent level |
|
Hold |
The number of agents in the Connected state who have placed the caller on hold. |
Snapshot/Site view & Skills by Team view |
|
Hold Time |
The amount of time callers were on hold during the time interval. |
Real-time Skills Interval by Team |
|
Idle |
The number of times the agent went into the Idle state from a different state. Rest the cursor over a number in this column to display a pop-up showing the idle codes the agent entered and how many times each code was entered. Because an agent can change the idle code while in the Idle state, the number of idle codes displayed in the pop-up can exceed the number of times the agent went into the Idle state. For example, an agent might move from Idle-Break to Idle-Email. |
Snapshot/Team & Skill views |
|
Idle |
The number of agents currently in the Idle state. |
Snapshot/Site & Skills by Team views |
|
Idle |
Count: The number of times an agent went into the Idle state. Total Time: The total amount of time agents spent in the Idle state. Average Time:(Not available in ADR or Agent Trace report) The average length of time agents were in the Idle state (Total Idle Time divided by Idle Count). % Time.:(Not available in Agent Summary and Interval reports) The percentage of time the agent was in the Idle state. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Idle |
Count: The number of times the agent went into the Idle state from a different state. Rest the cursor over the number in this field to see the idle codes the agent entered and how many times each code was used. Because an agent can change the idle code while in the Idle state, the number of idle codes can exceed the number of times the agent went into the Idle state. For example, an agent might move from Idle-Break to Idle-Email. Total Time: The total amount of time the agent spent in the Idle state. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Idle Time |
The amount of time agents were in the Idle state during the time interval. |
Real-time Agent Interval reports |
|
In Outdial |
The number of agents who are connected to or are wrapping up an outdial call. |
Snapshot/Site view & Skills by Team view |
|
In Outdial |
The number of times the agent was connected to or was wrapping up an outdial call. |
Snapshot/Team view |
|
In Time |
The time the agent entered the state. |
Agent Trace report |
|
Inbound |
Reserved Time: The amount of time agents were in the Reserved state, during which incoming calls were ringing but had not yet been answered. Answered Count: The number of inbound calls that were answered by an agent during the time interval. Talk Time: The amount of time agents were talking on inbound calls during the time interval. Hold Time: The amount of time inbound calls were on hold during the time interval. Connected Time: The amount of time inbound calls were connected to an agent during the time interval (inbound talk time plus inbound hold time). Wrap Up Time: The amount of time agents spent in the Wrap-up state after an inbound call during the time interval. Average Connected Time: Inbound connected time divided by the number of inbound calls that were connected during the time interval. Average Handle Time: The average length of time spent handling an inbound call (inbound connected time plus inbound wrap-up time, divided by number of inbound calls). |
Real-time Agent Interval reports |
|
Inbound Average Handle Time |
The average length of time spent handling a call (total connected time plus total hold time and total wrap-up time, divided by connected count). |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Inbound Avg Handle Time |
The average length of time spent handling an inbound call (Total Inbound Connected Time plus Total Wrap Up Time, divided by Inbound Connected Count). |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Inbound Connected |
Hold Count: The number of times an agent put an inbound caller on hold. Connected Count: The number of inbound calls that were connected to an agent. Total Talk Time: The total amount of time an agent was talking with a caller. Total Hold Time: The total amount of time inbound calls were on hold. Total Time: The total amount of time agents were connected to inbound calls. Average Hold Time: (Not in ADR or Snapshot/Agent view or Agent Trace report) The average hold time for inbound calls (Total Hold Time divided by Hold Count). Average Time: (Not in ADR or Snapshot/Agent view) The average inbound connected time (Total Time divided by Connected Count). % Talk Time: (Only in ADR and Agent Trace report) The percentage of inbound connected time the agent was talking with the caller. % Hold Time: (Only in ADR) The percentage of inbound connected time the caller was on hold. % Time: (Only in ADR) The percentage of time the agent was connected to an inbound call. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Snapshot/Agent view; Agent Trace report |
|
Inbound Consult |
Count: The number of times an agent answered a consult request plus the number of times an agent consulted other agents. Total Time: Total Consult Answer Time plus Total Consult Request Time. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Inbound Consult Answer |
Count: The number of times an agent answered a consult request from another agent handling an inbound call. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent answering consult requests from agents handling inbound calls. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Inbound Consult Request |
Count: The number of times an agent sent a consult request to another agent during an inbound call. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent consulting other agents during inbound calls. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Inbound CTQ |
Count: Inbound CTQ Answer Count plus Inbound CTQ Request Count. Total Time: Total Inbound CTQ Answer Time plus Total Inbound CTQ Request Time. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Inbound CTQ Answer |
Count: The number of times an agent answered a consult-to-queue request from an agent who was handling an inbound call. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent answering consult-to-queue requests from agents handling inbound calls. |
Snapshot/Agent view; Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR |
|
Inbound CTQ Request |
Count: The number of times an agent initiated a consult to queue while handling an inbound call. Total Time: The total amount of time between when an agent initiated consult-to-queue requests while handling inbound calls and when the consultations ended. |
Snapshot/Agent view; Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR |
|
Inbound Reserved |
Count: (Not in ADR or Agent Trace report) The number of times an agent went into the Inbound Reserved state, during which a call is coming in to an agent’s station but has not yet been answered. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent in the Reserved state. Average Time: The average length of time agents were in the Inbound Reserved state (Total Available Time divided by Available Count). % Time: (Only in ADR and Agent Trace report) The percentage of time the agent was in the Inbound Reserved state. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Inbound Transfers |
The number of inbound calls the agent transferred to another agent, queue, or number. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Inbound Wrap Up |
Count: The number of times an agent went into the Wrap-up state after an inbound call. In the Snapshot/Agent view, you can rest the cursor over a number in this column to see the wrap-up codes the agent entered and how many times each code was used. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent in the Wrap-up state after an inbound call. Average Time: (Not in ADR, Agent Trace report, or Snapshot/Agent view) The average length of time agents were in the Wrap-up state after an inbound call (Total Wrap Up Time divided by Wrap Up Count). % Time: (Only in ADR and Agent Trace report) The percentage of time the agent was in the Wrap-up state after an inbound call. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report; Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Initial Login Time |
The date and time the agent signed in. |
Historical Agent Summary/Agent level |
|
Login Count |
Total number of times an agent sined in on that day. Appears only if Agents is selected in the Display Results By drop-down list. |
Historical Agent Summary/Agent level |
|
Login Time |
The date and time the agent logged in to the Agent Desktop. |
Snapshot/Team, Agent, & Skill views; ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Logout Time |
The date and time the agent signed out of the Agent Desktop. |
ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Not Responding |
The number of agents currently in the Not Responding state. |
Snapshot/Site & Skills by Team views |
|
Not Responding |
Count: The number of times an agent was in the Not Responding state. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent in the Not Responding state. Average Time: (Not in ADR or Snapshot/Agent view or Agent Trace report) The average length of time agents were in the Not Responding state (Total Not Responding Time divided by Not Responding Count). % Time: (Only in ADR and Agent Trace report) The percentage of time the agent was in the Not Responding state. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report; Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Not Responding Time |
The amount of time agents spent in the Not Responding state during the time interval. |
Real-time Agent Interval reports |
|
Number of Calls |
The number of inbound calls that were connected to the site or team during the time interval. |
Real-time Skills Interval by Team |
|
Occupancy |
The measure of time the agent spent on calls compared to available and idle time, calculated by dividing total connected time (inbound connected time plus outdial connected time) plus total wrap up time (inbound wrap-up time plus outdial wrap up time) by staff hours. |
Snapshot/Agent view; Real-time Agent Interval reports; Historical Agent Summary, Agent Interval, ADR, & Agent Trace report |
|
Occupancy |
The measure of time the agent spent on calls compared to available and idle time, calculated by dividing inbound connected time plus inbound wrap up time by staff hours. |
Real-time Skills Interval by Team |
|
Out Time |
The time the agent left the state. |
Agent Trace report |
|
Outdial |
Attempted: The number of calls that agents initiated during the time interval. Connected: The number of outdial calls that were connected to an agent during the time interval. Reserved Time: The amount of time agents were in the Outdial Reserved state, a state indicating that the agent has initiated an outdial call, but the call is not connected yet. Talk Time: The amount of time agents were talking on outdial calls during the time interval. Hold Tim: The amount of time outdial calls were on hold during the time interval. Connected Time: The amount of time outdial calls were connected to an agent during the time interval (outdial talk time plus outdial hold time). Average Connected Time: Outdial connected time divided by the number of outdial calls that were connected during the time interval. Wrap Up Time: The amount of time agents spent in the Wrap-up state after an outdial call during the time interval. Average Handle Time: The average length of time spent handling an outdial call (outdial connected time plus outdial wrap up time, divided by number of outdial calls). |
Real-time Agent Interval reports |
|
Outdial Avg Handle Time |
The average length of time spent handling an outdial call (Total Outdial Connected Time plus Total Outdial Wrap Up Time, divided by Outdial Connected Count). |
Historical Agent Summary, Agent Interval, ADR, & Agent Trace report |
|
Outdial Conference |
The number of outdial calls the agent conferenced with another party. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Outdial Connected |
Attempted Count: The number of times an agent attempted to make an outdial call. Connected Count: The number of outdial calls that were connected to an agent. Hold Count: The number of times an agent put an outdial call on hold. Total Talk Time: The total amount of time an agent was talking with a party on an outdial call. Total Hold Time: The total amount of time outdial calls were on hold. Total Time: The total amount of time agents were connected to outdial calls. Average Hold Time: (Not in ADR, Agent Trace report, or Snapshot/Agent view) The average hold time for outdial calls (Total Hold Time divided by Hold Count). Average Time. (Not in ADR, Agent Trace report, or Snapshot/Agent view) The average outdial connected time (Total Time divided by Connected Count). |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report; Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Outdial Consult |
Count: Outdial Consult Answer count plus Outdial Consult Request count. Total Time: Total Outdial Consult Answer Time plus Total Outdial Consult Request Time. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Outdial Consult Answer |
Count: The number of times the agent answered a consult request from another agent who was on an outdial call. Total Time: The amount of time the agent was consulted by another agent who was on an outdial call. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Outdial Consult Request |
Count: The number of times the agent consulted another agent while on an outdial call. Total Time: The amount of time the agent consulted another agent during an outdial call. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Outdial CTQ |
Count: Outdial CTQ Answer Count plus Outdial CTQ Request Count. Total Time: Total Outdial CTQ Answer Time plus Total Outdial CTQ Request Time |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Outdial CTQ Answer |
Count: The number of times an agent answered a consult-to-queue request from an agent who was handling an outdial call. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent answering consult-to-queue requests from agents handling outdial calls. |
Snapshot/Agent view; Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR |
|
Outdial CTQ Request |
Count: The number of times an agent initiated a consult to queue while handling an inbound call. Total Time: The total amount of time between when an agent initiated consult-to-queue requests while handling inbound calls and when the consultations ended. |
Snapshot/Agent view; Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR |
|
Outdial Reserved |
Count: The number of times an agent was in the Outdial Reserved state, a state indicating that the agent has initiated an outdial call, but the call is not connected yet. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent was in the Outdial Reserved state. Average Time: (Not in ADR, Agent Trace report, or Snapshot/Agent view) The average amount of time agents were in the Outdial Reserved state (Total Time divided by Count). |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report; Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Outdial Transfers |
The number of outdial calls the agent transferred to another agent, queue, or number. |
Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Outdial Wrap Up |
Count: The number of times an agent went into the Wrap-up state after an outdial call. Total Time: The total amount of time an agent spent in the Wrap-up state after an outdial call. Average Time: (Not in ADR, Agent Trace report, or Snapshot/Agent view) The average length of time agents were in the Wrap-up state after an outdial call (Total Outdial Wrap Up Time divided by Outdial Wrap Up Count). |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports; ADR; Agent Trace report; Snapshot/Agent view |
|
Queue |
If the agent is currently handling a call, the name of the queue that the call came in on. |
Snapshot/Team, Agent, & Skill views |
|
Reason |
The reason the agent logged out. For example:
Other reasons can occasionally occur. |
ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Reserved |
The number of agents currently in the Reserved state, during which a call is coming in but has not yet been answered. |
Snapshot/Site view & Skills by Team view |
|
Reserved |
The number of agents in the Reserved state who possess the skill. |
Snapshot/Skill view |
|
Site |
The name of a site. If your enterprise uses the Multimedia feature and the report includes more than one media channel, you can click the a collapse arrow or expand arrow to the left of a team name to collapse or expand the data grouped by channel type. In the Site view of a current snapshot agent report, you can do the following:
|
Snapshot/Site view; Real-time Agent Interval reports (except Agent-level) |
|
Site |
The site where the team the agent was handling calls for is located. |
ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Skill |
The name of the skill. In the Skill view of the current snapshot agent report you can do the following:
|
Snapshot/Skill view; Real-time Skills Interval by Team |
|
Staff Hours |
The amount of time the agent has been logged in. |
Snapshot/Team, Agent, & Skill views |
|
Staff Hours |
The amount of time the agent was logged in during the time interval. |
Real-time Agent Interval reports & Skills Interval by Team |
|
Staff Hours |
The total amount of time agents were logged in. |
Historical Agent Summary & Interval reports |
|
Staff Hours |
The amount of time the agent was logged in during each login session. |
ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
State |
The time the agent logged in and logged out and each state the agent was in during the login session:
|
Agent Trace report |
|
Talk |
The number of agents in the Connected state who are currently talking with a caller. |
Snapshot/Site & Skills by Team views |
|
Talk Time |
The amount of time agents were talking with callers during the time interval. |
Real-time Skills Interval by Team |
|
Team |
The name of a team in the report. In the Team view and Skills by Team view of a current snapshot agent report you can do the following:
In the Team view, you can click the name of an agent to drill-down to the Agent view for that agent. |
Snapshot/Team view & Skills by Team view; Real-time Agent Interval report/Team & Skills by Team level |
|
Team |
The team the agent was handling calls for. |
ADR; Agent Trace report |
|
Time in Current State |
The amount of time the agent has been in the current state. |
Snapshot/Team, Agent, & Skill views |
|
Total Calls |
Inbound Answered calls plus Outdial Attempted calls. |
Real-time Agent Interval reports |
|
Total Logged In |
The number of agents currently logged in or, in the Skill view, the number of agents currently logged in who possess the skill. |
Snapshot/Site, Team, Skill, & Skills by Team views |
|
Channels Logged In |
The number of media channels to which agents are currently logged in. Appears only if your enterprise uses the Multimedia feature. |
Snapshot/Site, Team, Skill, & Skills by Team views |
|
Wrap Up |
The number of agents currently in the Wrap-up state. |
Snapshot/Site & Skills by Team view |
|
Wrap Up Time |
The amount of time agents spent in the Wrap-up state after an inbound call during the time interval. |
Real-time Skills Interval by Team |
Historical Skill Report Parameters
The following table describes the parameters available in Webex Contact Center historical Skills by Queues reports. Asterisks (*) mark parameters that are available only in a skill summary report, which you can display by drilling down on a skill name in a Skills by Queue report.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Report |
|---|---|---|
|
% Calls Matched |
The percentage of calls for which the initial value of the skill required by the call was equal to the final value when the call was distributed to an agent. (Matched Calls * 100)/ (Connected + Abandoned + Reclassified) |
Skills by Queue |
|
Abandoned |
The number of calls with this skill requirement that were abandoned during the report interval. |
Skills by Queue |
|
Abandoned within SL |
The number of calls that were terminated while in queue within the Service Level threshold provisioned for this skill. |
Skills by Queue |
|
Avg Handle Time |
The average length of time spent handling a call with this skill requirement (total connected time plus total wrap-up time, divided by calls handled). |
Skills by Queue & Skills by Agents |
|
Connected |
The number of calls with this skill requirement that were connected during the report interval. |
Skills by Queue & Skills by Agents |
|
Connected within SL |
The number of calls with this skill requirement that were connected within the Service Level threshold provisioned for this skill. |
Skills by Queue & Skills by Agents |
|
Final Operand* |
The skill operand type that was assigned to the call when it was distributed to an agent with a matching skill. |
Skills by Queue |
|
Final Value* |
The value of the skill requirement assigned to the call when the call was distributed to an agent. |
Skills by Queue |
|
Initial Operand* |
The skill operand type that was assigned to the call when it was distributed to the queue. Possible values:
|
Skills by Queue |
|
Initial Value* |
The value of the skill requirement assigned to the call when it arrived in the queue. |
Skills by Queue |
|
Operand |
The skill operand type that was assigned to the call when it was distributed to the agent. Possible values:
|
Skills by Agents |
|
Reclassified |
The number of calls with this skill requirement that were transferred from the queue by the system. |
Skills by Queue |
|
Reclassified within SL |
The number of calls with this skill requirement that were transferred from the queue by the system within the Service Level threshold provisioned for the skill. |
Skills by Queue |
|
Skill |
The name of a skill. In a Skills by Queue report, you can click an entry in this column to drill down to view daily activity for the month (from a monthly summary) or to view half-hourly data for a day (from a daily summary). |
Skills by Queue Skills by Agents |
|
Total |
The total number of calls. |
Skills by Queue |
|
Value |
The value of the skill requirement assigned to the call when the call was distributed to the agent. |
Skills by Agents |
Historical Threshold Alerts Report Parameters
If your enterprise uses the threshold alerts feature and your user profile authorizes you to view alerts, you can use the controls on the Threshold Alerts page of the Historical Reports module to display details about threshold alerts that were triggered between midnight of the current day and three months ago. The following table describes the available parameters.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Acknowledged |
Whether or not a supervisor acknowledged the alert. |
|
Acknowledged Time |
The time the alert was acknowledged. |
|
Actual Value |
The actual value that triggered the alert. |
|
Archived |
Whether or not a supervisor archived the alert. |
|
Comments |
Optional comments, if any, entered by the supervisor who acknowledged the alert. |
|
Metric |
The metric that the threshold is associated with. |
|
Operand |
> (greater than) >= (greater than or equal to) < (less than) <= (less than or equal to) = (equal to) |
|
Supervisor |
The name of the supervisor who acknowledged the alert. |
|
Time |
The date and time that the threshold alert was triggered. |
|
Trigger Interval |
The number of seconds specified in the threshold rule as the interval during which the system should generate only one alert for the threshold rule check. |
|
Trigger Value |
The value that the threshold rule defined as the trigger. |
Usage Metrics Report Parameters
The following table describes the parameters available in the Usage Metrics Report.
|
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Calls Duration (min) |
The total amount of time between when inbound calls arrived or outdial calls were placed and when they were terminated. |
|
Inbound |
Total Calls: The total number of inbound calls. Connected Calls: The number of inbound calls that were connected to an agent. IVR Duration (min): The number of minutes during which calls were in the IVR system. Queue Duration (sec): The number of seconds during which calls were in a queue. Talk Time (min): The number of minutes during which agents were talking with callers. Hold Time (min): The number of minutes during which inbound calls were on hold. |
|
Month |
The month during which the call activity occurred. |
|
Outdial |
Total Calls: The total number of outdial calls. Connected Calls: The number of outdial calls that were connected to an agent. Talk Time (min): The number of minutes during which an agent was talking with a party on an outdial call. Hold Time (min): The number of minutes during which outdial calls were on hold. |
|
Recorded Calls |
The number of calls that were recorded. |
|
Total Calls |
The total number of inbound and outdial calls. |


