- Home
- /
- Article


Get started with Local Gateway
 In this article
In this article Feedback?
Feedback?This article enables the administrators with all the information and references to set up, maintain, and troubleshoot the Local Gateway.
The local gateway helps you migrate to Webex Calling at your own pace. The local gateway integrates your existing on-premises deployment with Webex Calling. You can also use your existing PSTN connection.
Ensure the following before configuring a Local Gateway for Webex Calling:
-
Knowledge of VoIP, such as SIP and media protocols, and the ability to perform basic troubleshooting.
-
Working understanding of the devices (session border controller) that are configured as a Local Gateway.
-
Required license to operate the session border controller.
-
Knowledge of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified CM) or equivalent PBX deployed on your premises and configured to work with Webex Calling. (In the case of an integration with an on-premises environment.)
The following articles can help you familiarize with the deployment options:
|
Term |
References |
|---|---|
|
Trunks and Route Groups |
For more information, see trunks and route groups in Webex Calling Preferred Architecture. |
|
ByoPSTN, Enterprise Dialing |
Stands for Bring Your Own PSTN. For more information, see PSTN access and on-premises interconnect in Webex Calling Preferred Architecture. |
|
Over the Top (OTT), Webex Edge Connect |
For more information, see Access Connectivity options in Webex Calling Preferred Architecture. |
Local Gateway trunking models
There are two types of Local Gateway trunking models:
-
Registration-based trunks
-
Certificate-based trunks
These models provide similar functionality, but they differ in scale and device support. Select the right trunking model that meets your requirement.
|
Functionality |
Registration-based |
Certificate-based |
|---|---|---|
|
Concurrent calls |
Concurrent calls of up to 250 per trunk. |
Concurrent calls of > 250 per trunk. |
|
Device type |
Supports only Cisco Unified Border Element (CUBE). For more information, see CUBE Platform Support. |
A choice of device types as mentioned in the table Device types supported for certificate based trunking. |
|
Authentication model |
Digest-based authentication model, which relies on a shared username and password used to authenticate registration and calls. For more information, see Registration-based trunk. |
Certificate-based authentication with LGW FQDN verification. For more information, see Certificate-based trunk. Every SIP transaction Local Gateway initiates towards Webex Calling cloud, should contain Contact header with FQDN of a Local Gateway. OPTIONS Transactions from Local Gateway is specially important for the Local Gateway status in the Control Hub to be online. |
|
Network, firewall, and NAT requirements For details on ingress and egress traffic, see Port Reference Information for Cisco Webex Calling. |
Any NAT or Public IP. Dynamic NAT is preferred since it’s easier for setup and requires less firewall configurations. Requires firewall to allow both ingress and egress traffic (Webex calling to Local Gateway and vice versa). For ingress traffic, inbound pinholes are opened by the firewall based on outbound registration messages. Pinhole opening is recommended for all Webex Calling IP address and ports. It isn’t specific to an IP address or port to which Local Gateway registers. |
Public internet-facing network including a public IP or Static NAT. Requires firewall to allow both ingress and egress traffic (Webex Calling to Local Gateway and vice versa). |
|
Public DNS service requirements |
No specific configuration is required on a public DNS service. |
|
|
CA and certificate requirements |
|
|
|
Onboarding and troubleshooting using a cloud connector |
Supports automated troubleshooting of configuration issues. |
Doesn't support automated troubleshooting of configuration issues. |
Supported session border controllers
Configure certificate-based trunking for Local Gateways in Webex for Government. Also, CUBE is the only session border controller (SBC) that currently supports Webex for Government.
|
SBC vendor and model |
Minimum version |
Open caveats |
Webex for Government |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cisco—CUBE models listed in Router platform support |
Cisco IOS XE Bengaluru 17.6.1a To configure Local Gateway in controller mode as part of a Cisco SD-WAN solution, use Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.7.1 or later releases. For the recommended versions, see the Cisco Software Research page. Search for the platform and select one of the "Suggested" releases. |
Cisco ISR 1100 platforms don’t support configuration validation. For a gateway deployed in controller mode with Cisco SD-WAN, the following aren’t supported:
|
Webex for Government doesn't support registration-based trunking. |
|
SBC vendor and model |
Minimum version |
Open caveats |
Webex for Government |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cisco—CUBE models listed in Router platform support |
Cisco IOS XE Cupertino 17.9.1a For the recommended versions, see the Cisco Software Research page. Search for the platform and select one of the "Suggested" releases. |
For a gateway deployed in controller mode with Cisco SD-WAN, the following aren’t supported:
|
Supported |
|
Oracle—AP series |
9.0.0 |
Limitation with ICE interoperability. See Section 9 in Cisco Webex - Oracle SBC integration with Cisco Webex Calling as 3rd party Local Gateway (LGW) solution documentation. |
Not supported |
|
Oracle—VME |
9.0.0 |
Limitation with ICE interoperability. See Section 9 in Cisco Webex - Oracle SBC integration with Cisco Webex Calling as 3rd party Local Gateway (LGW) solution documentation. |
Not supported |
|
Oracle—Oracle SBC on Public Cloud |
9.0.0 |
Limitation with ICE interoperability. See Section 9 in Cisco Webex - Oracle SBC integration with Cisco Webex Calling as 3rd party Local Gateway (LGW) solution documentation. |
Not supported |
|
AudioCodes—Mediant CE & VE |
7.40A.250.440 |
Limitation with ICE interoperability. See Section 2.4.2 of Connecting Webex Calling with AudioCodes SBC Configuration Note. |
Not supported |
|
AudioCodes—Mediant Appliances |
7.40A.250.440 |
Limitation with ICE interoperability. See Section 2.4.2 of Connecting Webex Calling with Audio Codes SBC Configuration Note. |
Not supported |
|
Ribbon—SBC 5000 Series, SBC 7000, and SBC SWe |
10.1 |
Limitation with ICE interoperability. See Caveats section. |
Not supported |
|
Ribbon—SBC SWe Edge |
11.0.2 |
Limitation with ICE interoperability. See workaround solution in Caveats section. |
Not supported |
|
Ribbon—SBC 1000, SBC 2000 |
11.0.1 |
Limitation with ICE interoperability. See workaround solution in Caveats section. |
Not supported |
|
Ribbon—8000 w/SBC SWe Edge |
25.0 |
See Ribbon Edge 8000 with Cisco Webex Calling:Interoperability Guide Caveats section. |
Not supported |
| anynode—SBC | 4.10 |
Not supported | |
| Italtel NetMatch-S SBC | NetMatch-S-CI 5.8.0-20240111 | For known limitations, download NetMatch-S CI SBC Configuration for WEBEX Calling and see Section 3.3 Caveats. |
Not supported |
Webex Calling supports the deployment of Local Gateways behind NAT. Call behavior may depend on the type of NAT firewall used in your network and the functionality provided by your SBC.
Calling capacity requirements
The Registration-based and Certificate-based trunking models have different concurrent call capacities, as shown in the following table:
|
Concurrent call requirement) |
Approximate user numbers |
Trunk type Preference |
Minimum link quality |
|---|---|---|---|
|
~ 2000–6500 |
65000 |
Certificate-based |
Interconnect |
|
~ 250–2000 |
20000 |
Certificate-based |
Over the top (OTT) |
|
Up to 250 |
2500 |
Registration-based |
OTT |
Connection qualifications
To ensure consistently high-quality calls, the network connection between the local gateway and Webex Calling should have the following maximum qualities:
-
100ms one-way latency
-
10ms packet jitter
-
0.5% packet loss
For more information on calling capacity, see Preferred Architecture for Webex Calling.
Connectivity model and requirements
-
During provisioning, each local gateway is assigned to two Webex Media PoP locations to ensure redundancy and high availability. This assignment is managed through a DNS SRV record.
-
Media PoP locations are determined based on the geographic location of the gateway, which is configured during the provisioning process in Control Hub. Typically, the gateway is assigned to two most appropriate, geographically separated Media PoPs within the same region. For example, if the gateway is provisioned in the EU, then the gateway uses two media PoPs within the EU.
For a full list of Webex Media PoP locations, see Data Center locations for Webex Calling.
The Webex Calling locations are also media PoPs.
-
Regional media capabilities also apply to gateway connections. Depending on the call scenarios, media is maintained locally within the region whenever possible.
-
Ensure that the certificates are signed for client and server usage.
Configure Local Gateway
| 1 |
Configure trunk from Control Hub. |
| 2 |
Configure your device to perform the role of a Local Gateway.
|
| 3 |
Confirm that the Local Gateway is active in the Control Hub status. For instructions on Partner Hosted gateway, see Configuring a Partner Hosted Gateway
|
Webex Calling currently doesn't support both CME and LGW running on a single instance of vCUBE.
Troubleshoot the Local Gateway
If the Local Gateway status isn’t active or there are other issues, refer to the following documents before you contact the support team:
-
Troubleshoot issues with Registration-based Local Gateway deployment from the Control Hub.
-
Troubleshoot issues with Certificate-based Local Gateway deployment from the Control Hub.
When the Local Gateway isn't active, check the trunk status in the Control Hub:
-
Sign in to Control Hub.
-
Go to .
-
Select the trunk that you want to check the status.
-
Click Trunk Info.
-
Online—Successful connection between all the Webex Calling edge proxies and Local Gateway
-
Offline—Unsuccessful connection between the Webex Calling and Local Gateway
-
Impaired—Unsuccessful connection between at least one Webex Calling edge proxy and Local Gateway
-
Unknown—While establishing a connection between Webex Calling and the recently added Local Gateway
-
For trunk status updates on certificate-based trunk or registration-based trunk, see Configure trunks, route groups, and dial plans for Webex Calling.
-
For more information on configuring trunk alerts, see Alerts center in Control Hub.
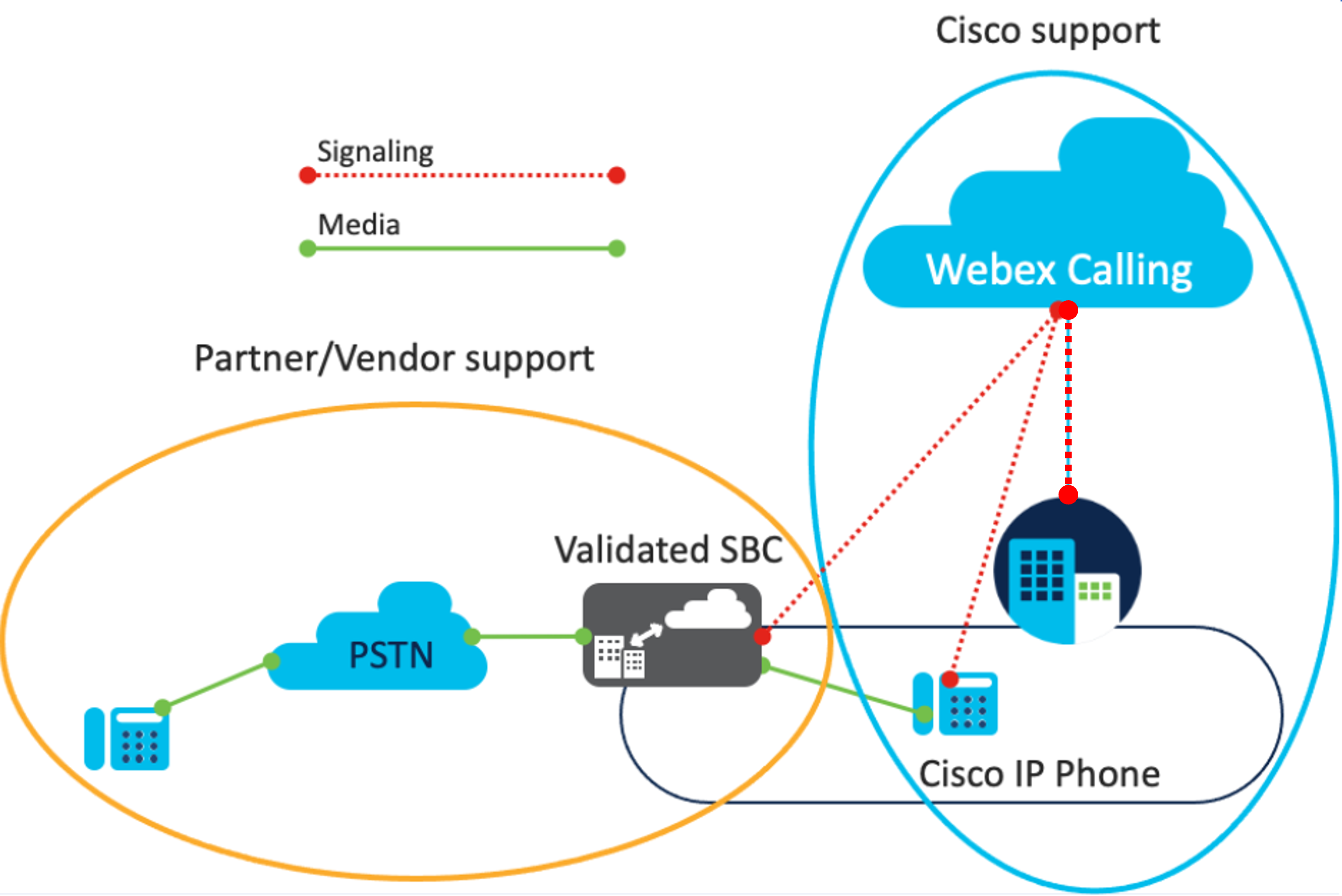
Support for Third-party Local Gateway
Support from both Cisco and the vendor partner are required for a Webex Calling deployment using a third-party SBC. The following outlines the support details:
-
Webex Calling support:
-
Cisco or partners who use Webex Calling are required to have a support agreement with Cisco in order to get Cisco assistance (TAC support).
-
Cisco provides customer assistance for the Webex Calling up to edge deployment and the Webex Calling registered Cisco IP Phones.
-
-
Vendor support:
-
During deployment, Cisco provides support for the customers or partners that have a validated third-party SBC device and is not responsible for providing assistance for the actual SBC.
-
Cisco isn’t responsible for non-Cisco support cases involving the customer and the SBC vendor. Issues or software defects that arise during deployment can be discussed with the SBC vendor and Cisco.
-