- Home
- /
- Article



Integrate Cisco Meraki with Troubleshooting in Control Hub
 In this article
In this article Feedback?
Feedback?Integrate Cisco Meraki with Troubleshooting so you can see full path visibility of users across the Meraki platform to isolate issues with greater clarity.
Overview
You can only see Meraki data for meetings and calls that are hosted in your organization. If users join external meetings, then Meraki troubleshooting data for those external meetings won't be shown. Meraki data is kept up to a maximum of seven days in Troubleshooting.
Data is shown in five-minute intervals. The thresholds for good and poor data are:
- Good (green)—SNR >= 20db or RSSI >= -80dBm or Average wireless latency <= 200ms
- Poor (red)—SNR < 20db or RSSI < -80dBm or Average wireless latency > 200ms
Example of Meraki integration for Webex Meetings
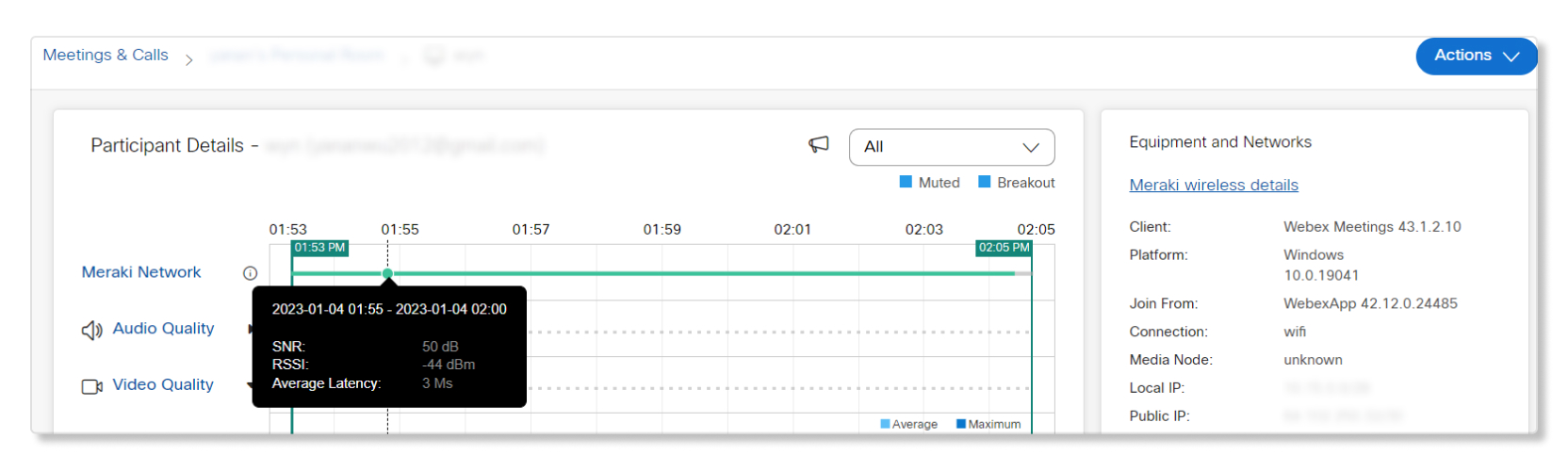
When you drill down to the Participant Details page of a user's meeting, you can hover over the Meraki Network line to get a quick glance at their SNR, RSSI, and latency data.
Example of Meraki integration for Webex Calling
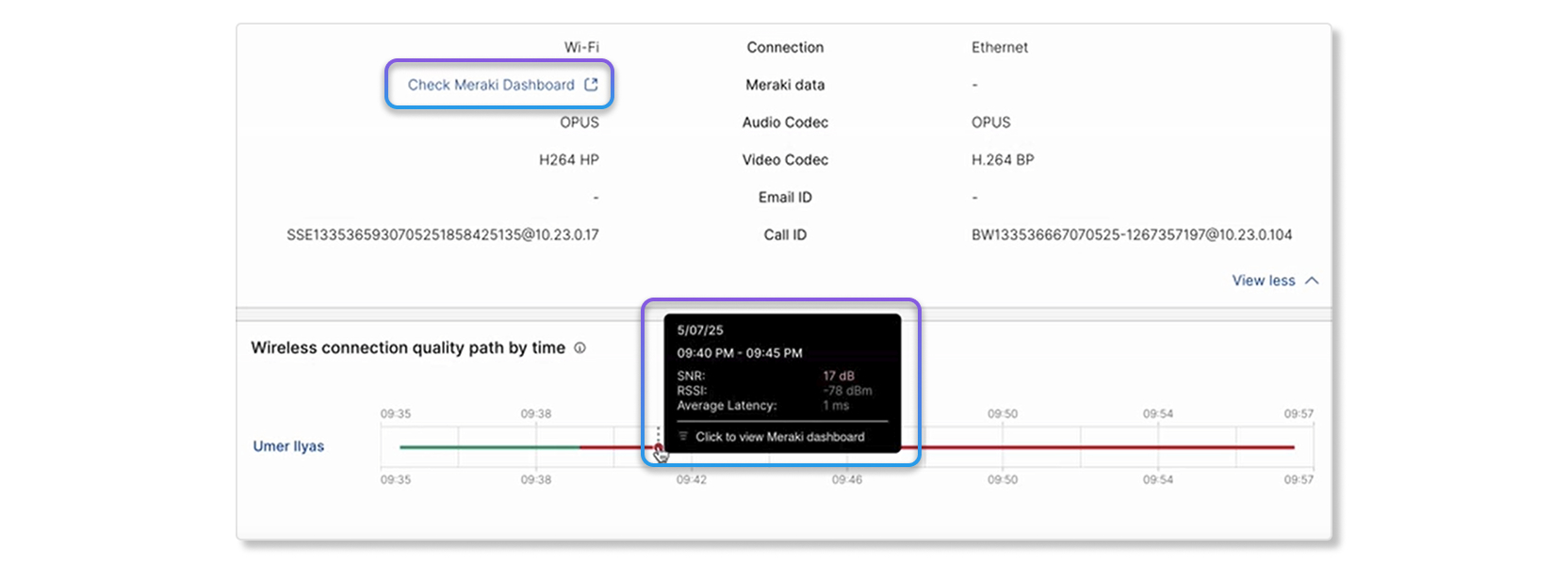
When you drill down to the Hop Detail page of a user's call, you can hover over the quality line in Wireless connection quality path by time to get a quick glance at their SNR, RSSI, and latency data. You can also cross launch into the Meraki dashboard of the device by clicking on Check Meraki Dashboard.
Limitations
Meraki troubleshooting data is only available:
- Up to a maximum of seven days. When viewing troubleshooting data for meetings beyond the previous seven days, the Meraki data line will be greyed out.
- For calls on Desk Phone devices with a client version of 3.4 or greater. RoomOS isn't supported yet.
- For the desktop version of Webex App and Cisco Room series devices. The mobile version of Webex App isn't supported.
- For devices that are online. The Meraki data line won't show for devices that are offline.
- When using the Meraki API, each organization has a call budget of 10 requests per second.
- For meetings and calls on Webex App if the Collect Client Metrics setting is enabled. If this setting isn't enabled, then users who join meetings and calls on Webex App won't have any data available. To enable this setting, Sign in to Control Hub as a full admin and go to , and then switch the Allow Cisco to collect Client IP Address and Mac address toggle to on.
- For wireless-connected devices. For wire-connected devices, the Meraki Network line
won't be available in the Participant Details page, but you can click on Meraki
wire details in the Equipment and networks tab to
cross launch to the Meraki portal for more details.
Devices on the Cisco Meraki MX platform will also show individual connections as wired instead of wireless.
Install and activate Meraki
You must have the full administrator role in order to set up Meraki integration for Troubleshooting.
| 1 |
Sign in to Control Hub, go to Organization Settings, and scroll to the Meraki section. |
| 2 |
Toggle the Allow Meraki API access switch to on. 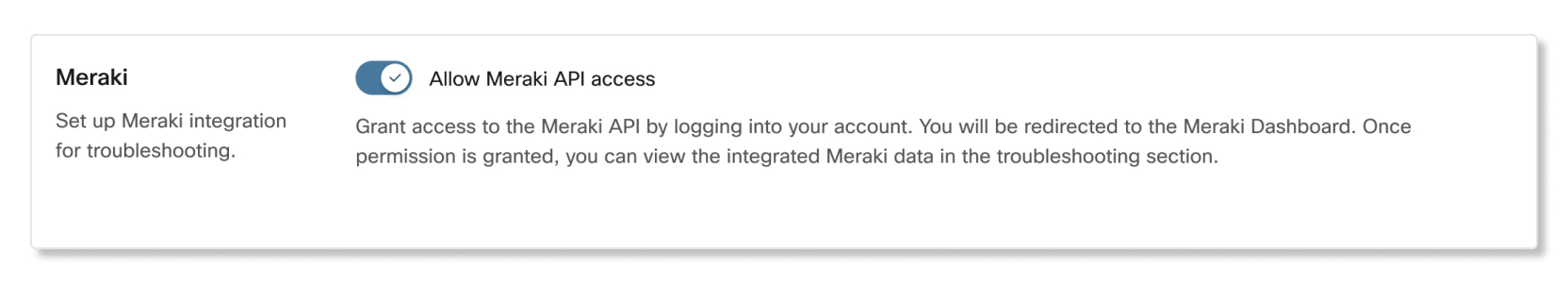
A pop-up window appears with a timer to show that Control Hub is requesting
access to your Meraki dashboard account. If you don't finish setting up Meraki before the
timer runs out, you must refresh the page to get the latest status update.
|
| 3 |
A tab page to the Meraki dashboard is shown. Sign in with your Meraki full administrator account to continue setting up the integration. 
|
| 4 |
Select a Meraki organization to integrate with Troubleshooting in Control Hub. 
|
| 5 |
Select Allow. The page returns to Control Hub with a success window if authorization has
succeeded.
|
| 6 |
Once you finish setting up the integration, you can view the Control Hub organization details in the Meraki dashboard by going to . |
Meraki data troubleshooting charts
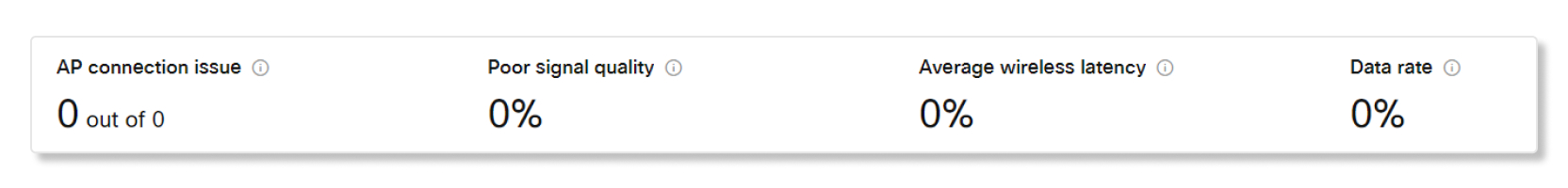
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
- AP connection issue—Number of failed connections to a Meraki access point (AP) during a meeting.
- Poor signal quality—Percentage of poor signal quality during a meeting. Signal quality is counted as poor if signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is < 20db or received signal strength indicator (RSSI) is < 80dBm.
- Average wireless latency—Average percentage of poor wireless latency during a meeting.
- Data rate—Percentage of poor data rate during a meeting.
Client connection
This chart shows details about the connection between the client, AP, and switch.

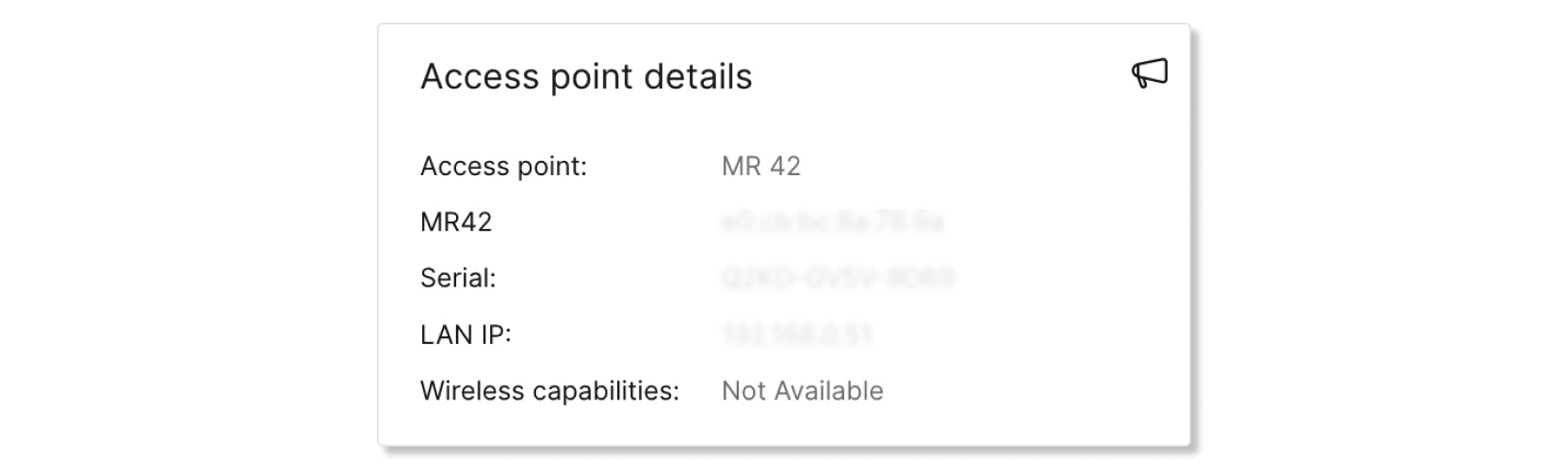
Access point details
This table provides information about the access point that a client connected to. Available details are:
- Access Point—Name of the AP.
- AP Model—Key and mac address of the AP.
- Serial—Serial number of the AP.
- LAN IP—LAN IP associated with the AP.
- Wireless capabilities—Type of wireless connections that the AP supports.
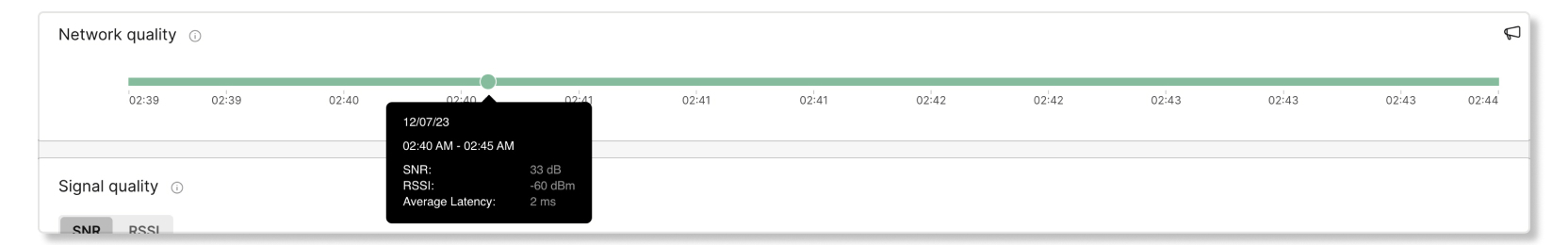
Network quality
This graph shows the signal quality and wireless latency of the client on the Meraki network in five-minute intervals. You can hover over a spot in the line to see more details about the quality.
Signal quality
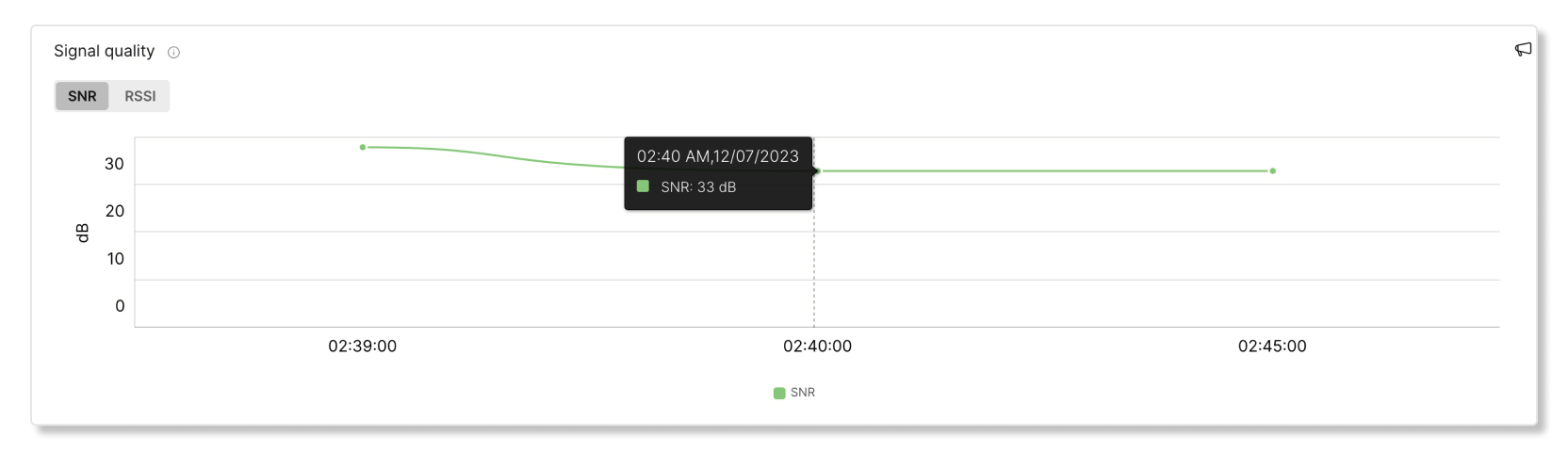
This graph shows the average SNR and RSSI for clients connected to the AP in five-minute intervals. If signal quality is poor, performance will likely be worse (i.e. more latency and slower data rates). The cause of poor signal strength can come from changes in the physical environment, RF configuration, or a far distance from the AP.
Wireless latency
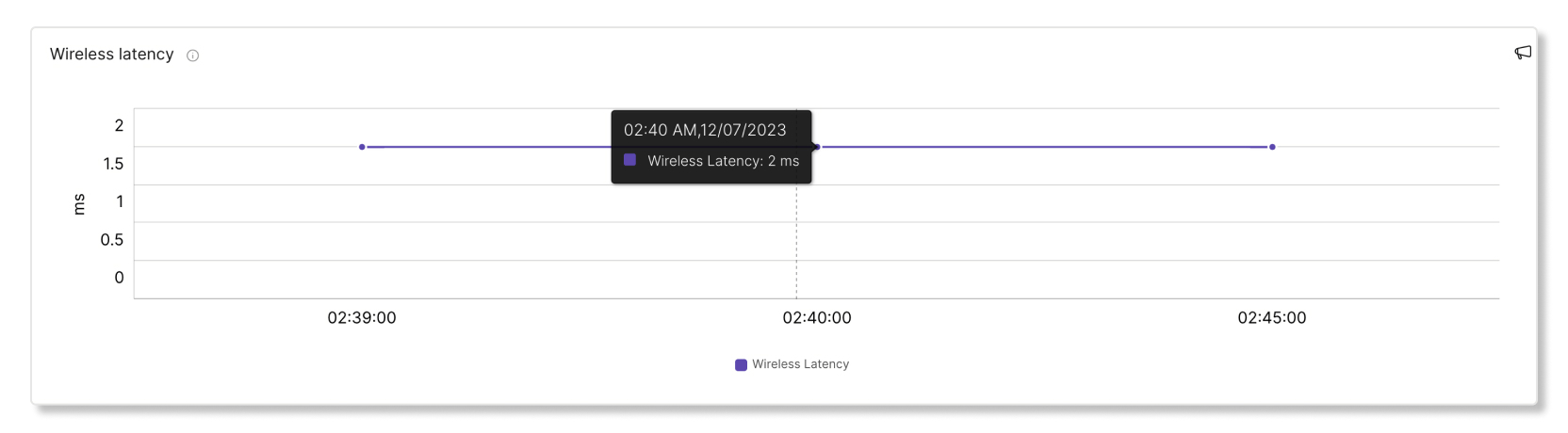
This graph shows the wireless latency of the client in five-minute intervals. A connection with high latency can cause slowness during meetings. The cause of high latency can come from poor signal quality, interference, or high load on the AP.
AP Channel utilization
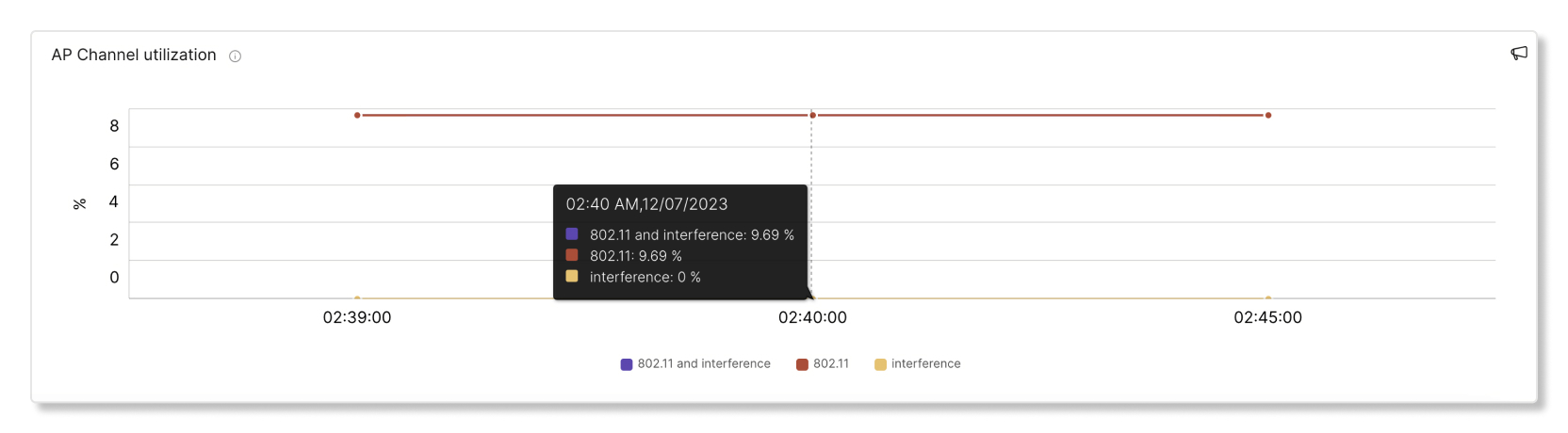
This graph shows the percentage of channels that were utilized by clients in ten-minute intervals. A high percentage of channel utilizations can cause higher than average latency. High channel utilization can also come from interference created by things like microwaves, bluetooth, and interference from neighboring APs.
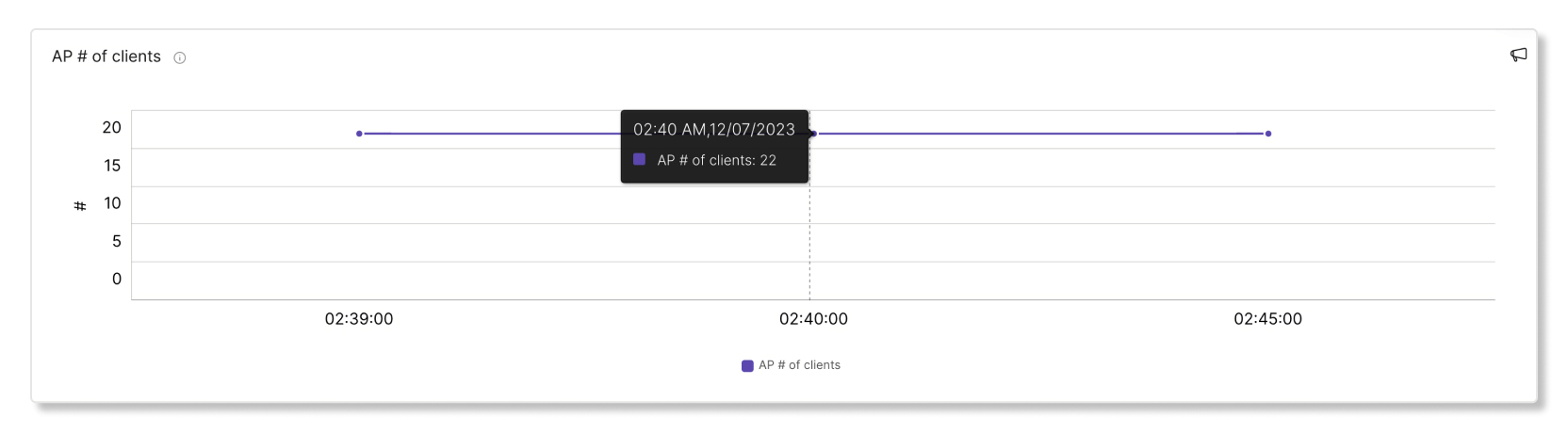
AP # of clients
This graph shows how many clients were connected to a specific access point (AP) in five-minute intervals. If an AP has a high number of clients connected to it, it can contribute to higher than average latency.
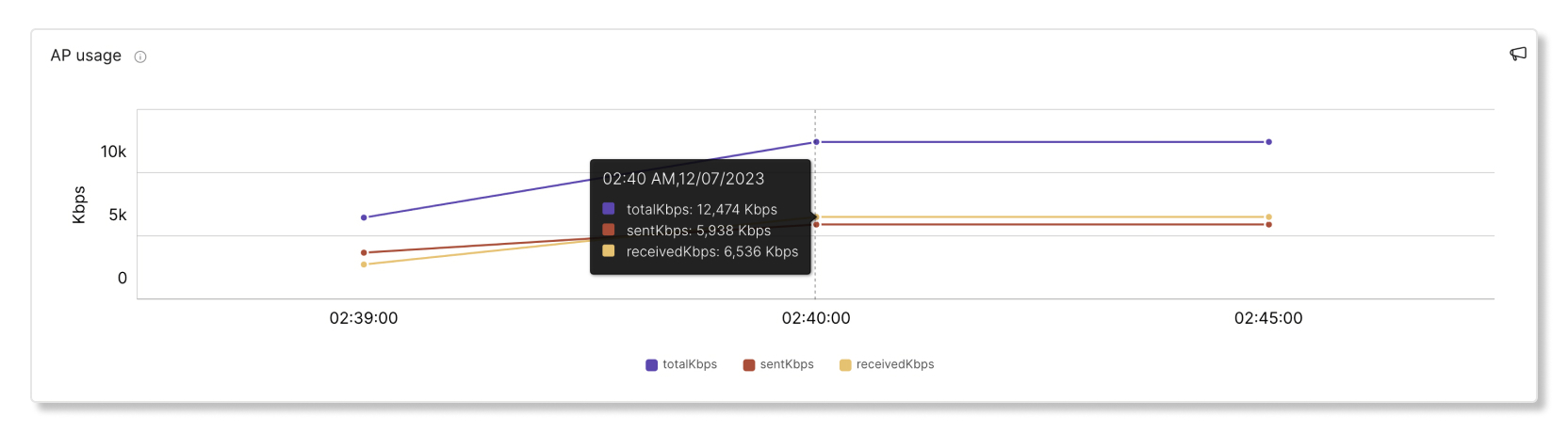
AP usage
This graph shows how many clients connected to a specific AP in five-minute intervals. If an AP has a high number of clients connected to it, it can contribute to higher than average latency.
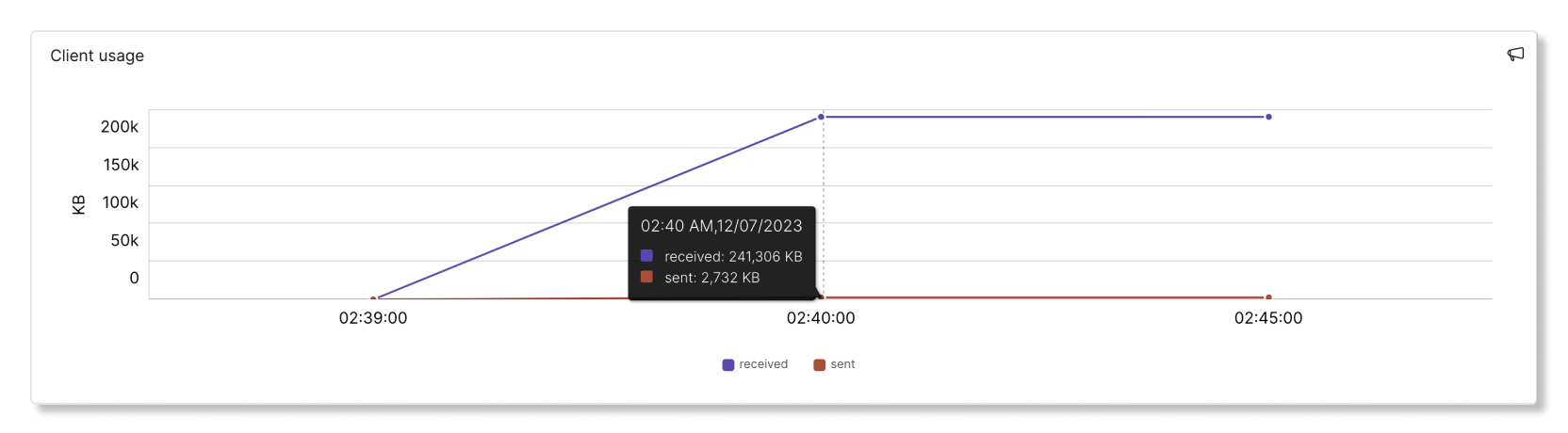
Client usage
This graph shows the received and sent data from a client in five-minute intervals.
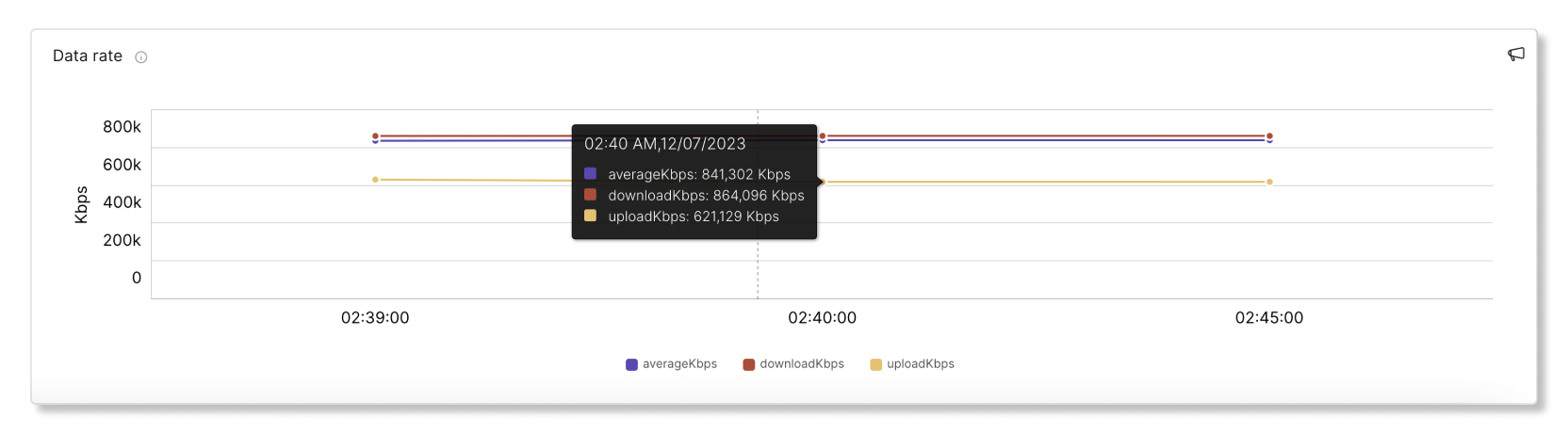
Data Rate
This graph shows data rates used as a percentage of the maximum data rate that this client supports. A connection with low data rates will feel consistently sluggish. Poor data rates can occur due to poor signal quality, or client device or AP capability limitations.